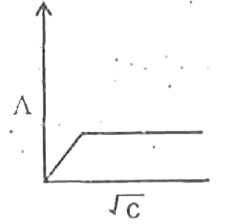
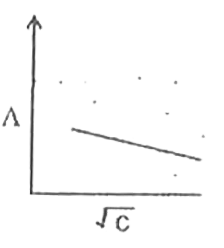
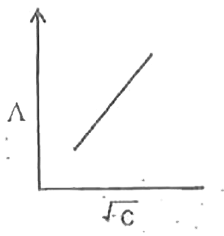
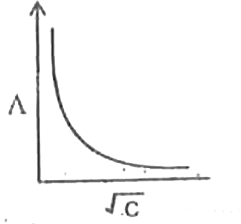
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The variation equivalent conductance of stronge electrolyte with sqrt(...
Text Solution
|
- For a dilute solution of a strong electrolyte, the variation of molar ...
Text Solution
|
- The variation equivalent conductance of stronge electrolyte with sqrt(...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of equivalent conductance versus concentration of a stro...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the variation of molar conductivity with concentration for str...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following plots represents correctly variation of equival...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of equivalent conductance of strong electrolyte with (co...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent conductance of strong electrolyte:
Text Solution
|
- The various of equivalent conductance of strong electrolyte with sqrt(...
Text Solution
|