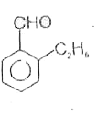
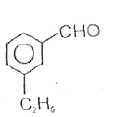
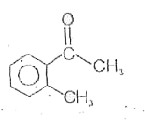
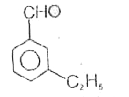
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An aromatic compound X with molecular formula C(9)H(10)O gives followi...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound with the molecular folmula C(9)H(10)O form 2,4-DNP...
Text Solution
|
- An aromatic compound, A [C(5)H(10)O] undergoes Cannizzaro reaction, fo...
Text Solution
|
- An organic commpound with the jmolecular formula C(9)H(10)O forms a 2,...
Text Solution
|
- An aromatic compound X with molecular formula C(9)H(10)O gives followi...
Text Solution
|
- An aromatic compound X with molecular formula C(9)H(10)O gives followi...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound with the molecular formula C(9)H(10)O forms 2,4-DN...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound with the molecular formula C(8)H(8)O forms 2,4-DNP...
Text Solution
|
- An aromatic compound 'X' with molecular formula C(9)H(10)O gives the f...
Text Solution
|