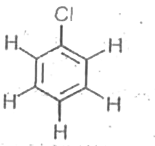
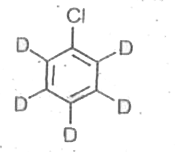
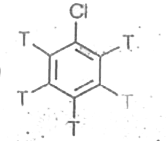
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section - C (Previous Years questions)|25 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section - C (Questions asked Prior to medical Ent. Exams. 2005)|13 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section - A (Objective type questions)|45 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS-Assignment Section - B (Objective type questions)
- Product(A) and (B)can be distinguished by
Text Solution
|
- The end product (D) of the reaction is
Text Solution
|
- What is Z in the following sequence of reactions? Phenolunderset("du...
Text Solution
|
- overset(OH)overset(|)(CH(2))-overset(OH)overset(|)(CH)-overset(OH)over...
Text Solution
|
- What Y ?
Text Solution
|
- What is A ?
Text Solution
|
- What is Y ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will not give positive test with neutral FeCl(3...
Text Solution
|
- In Dow's process haloarene is converted to phenol with fused NAOH . Th...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following four compounds (a) Phenol (b) methyl phenol ...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of tertiary butyl bromide with sodium methoxide gi...
Text Solution
|
- B is
Text Solution
|
- Product (C) is
Text Solution
|
- Ethyl chloride is converted into diethyl ether by
Text Solution
|
- Ethylene oxide when treated with Grignard reagent yields
Text Solution
|
- Product (C) is
Text Solution
|
- Product © is
Text Solution
|
- The product is
Text Solution
|
- What is B ?
Text Solution
|
- Product (C) is
Text Solution
|