A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-MOCK TEST 21-Example
- Which of the following methods could be employed for the preparation ...
Text Solution
|
- Surface tension of lyophobic sols is usually
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true with respect to chemical adsorption (ch...
Text Solution
|
- 10 % sites of catalyst bed have adsorbed by H(2) on Heating H(2) gas i...
Text Solution
|
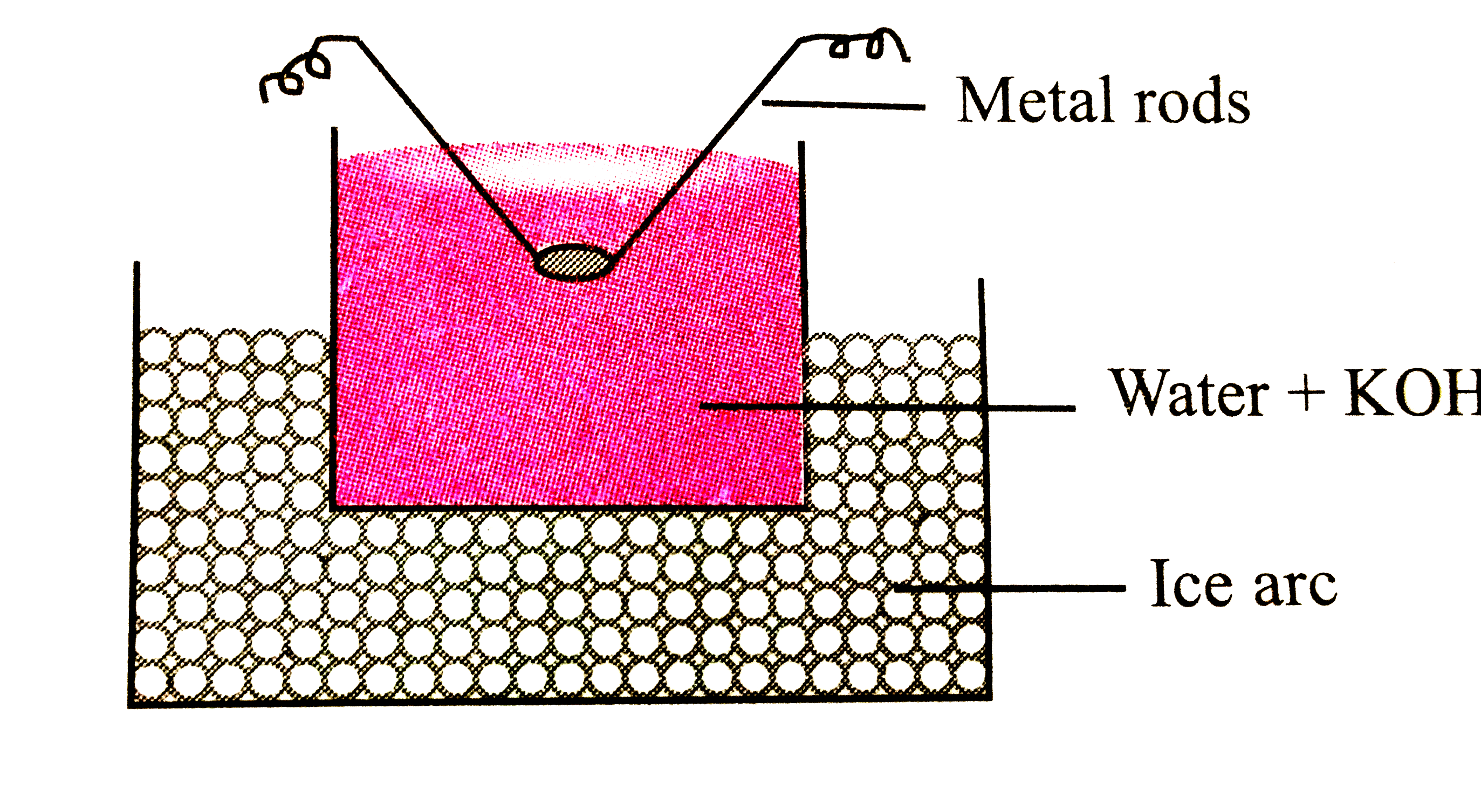
- In Bredig's arc method an electric arc is struck between the metal ele...
Text Solution
|
- The electrical charge on the the colloidal particles is indicated by
Text Solution
|
- The gold number of protective colloids A,B,C and D are 0.02, 0.002, 10...
Text Solution
|
- For the coagulation of 40ml of ferric hydroxide sol, 10ml of 0.4 M KCI...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following given statements is/are correct? (a) cold crea...
Text Solution
|
- Range the following electrolytes in the increasing order of coagulatin...
Text Solution
|
- The factors responsible for the stability of lyophilic sols are
Text Solution
|
- To stop bleeding from an injury ferric chloride can be applied. Which ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the items given in column-I with that in column-II column-I (I) ...
Text Solution
|
- A certain metal M ocas in four compounds namely A,B,C and D. A has 20%...
Text Solution
|
- The incorrect statement regarding forth floatation process is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following given properties of colloidal particles is its ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the methods of concentration of ore given in column-I with the d...
Text Solution
|
- Oxidation states of the metal in the minerals haematite and magnetite,...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is/are incorrect? (a) Cassiterite is...
Text Solution
|
- On addition of 1 ml of solution of 10% NaCl to 100ml corporate gold so...
Text Solution
|