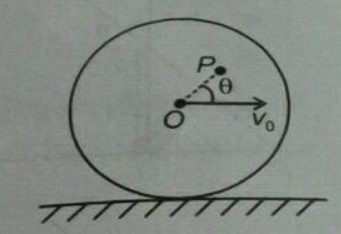
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform disc of radius R is in pure rolling on a fixed horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc is rolling on a horizontal surface. At a certain instan...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R rolls without slipping ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius r rolls without slipping on a rough horizontal floor....
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass M and radius R is rolling with angular speed w on horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of radius R rolls without slipping along the horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is thrown on horizontal law in s...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius r rolls without slipping on a rough horizontal floor....
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R rolls without slipping ...
Text Solution
|