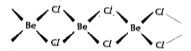
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE S-BLOCK ELEMENTS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS |20 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS GROUP-14
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|4 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Important Questions|41 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-THE S-BLOCK ELEMENTS -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Justify the inclusion of alkali metals in the same group of the period...
Text Solution
|
- Write an essay on the differences between lithium and other alkali met...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the preparation and properties of sodium carbonate.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the similarities between alkaline earth metals and gradation i...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss on : (i) Carbonates.
Text Solution
|
- What are the common physical and chemical features of alkali metals?
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the general characteristics and gradation in properties of alk...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the various reactions that occur in the Solvay process.
Text Solution
|
- Starting with sodium chloride how would you proceed to prepare (1) S...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) magnesium is burnt in air (ii) quick lime is hea...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the significance of sodium , potassium, magnesium and calcium ...
Text Solution
|
- Write a few lines about cement.
Text Solution
|