Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HISTOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise TEXTUAL EXERCISES|3 VideosHISTOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise IMPORTANT QUESTIONS |7 VideosHISTOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS |10 VideosECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise IMPORTANT QUESTIONS |45 VideosLOCOMOTION AND REPRODUCTION IN PROTOZOA
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Important Questions|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-HISTOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS -LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Explain the process of secondary growth in stems of woody angiosperm w...
Text Solution
|
- Draw illustrations to bring out the anatomical difference betweeen ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw illustrations to bring out the anatomical difference betweeen ...
Text Solution
|
- Simple tissues is/are
Text Solution
|
- Complex tissues are
Text Solution
|
- Describe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help o...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help o...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Exarch and endarch condition or pr...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Stele and vascular bundle .
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Protoxylem and metaxylem .
Text Solution
|
- Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium are
Text Solution
|
- What do you mean by closed vascular bundles
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Stem hair and root hair .
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Heart wood and sap wood .
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following Spring wood and Autumn wood .
Text Solution
|
- What is stomatal apparatus? Explain the structure of stomata with a la...
Text Solution
|
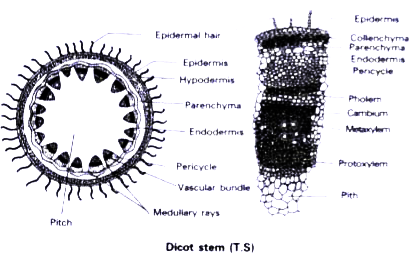
- Describe the T.S of a dicot stem .
Text Solution
|
- Describe the T.S of a Monocot stem .
Text Solution
|
- Describe the internal structure of a Dicot Root .
Text Solution
|
- Describe the internal structures of a Monocot Root .
Text Solution
|
 .
.