True sexual reproduction is absent in Bacteria. However, the exchange of genetic material takes place in three ways. They (1) Conjugation (2) Transformation (3) Transduction
(1) Conjugation :- Transfer of Genetic material between two live Bacteria is called conjugation. It was first observed in 1946 by Lederberg and Tatum in Escherichia coli .
In E.coli, a small circular DNA strand occurs in the cytoplasm in addition to nucleoid called or F plasmid. The cell with F plasmid is called `F^(+)` cell without F plasmid is called `F^(-) ` cell. The `F^(+)` cell or Donor cell produces the sex pilus that makes contact contact with the recipient cell or `F^(-)` cell. During conjugation , `F^(+) and F^(-)` cells bind with each other with the help of sex pilus forms a bridge between them. The F plasmid replicates and the replicated DNA passes through bridge to the `F^(-)` cell. The `F^(-)` cell becomes `F^(+)` cell as it receives the F plasmid . After conjugation, the two cells separater from each other
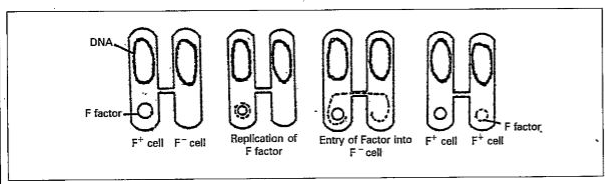
(2) Transformation :- It is uptake of naked DNA fragments from the surrounding environment and their incorporation into the recipient chromosome in a heritable form is known as transformation. It was discovered by Frederick Griffith (1928) in Streptococcus pneumoniae .
(3) Transduction :- The transfer of genetic material from one Bacterium to another through Bacteriophage is known as transduction. It was discovered by Lederberg and Zinder in Salmonella typhimurium
