Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-PYTHAGORAS THEORAM-QUESTIONS
- A ladder reaches a window which is 15 metres above the ground on one ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given diagram, AB=3CD =18 cm" and "3BP =4CP=36 cm. Show that t...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, AD is perpendicular to BC produced. Prove that: c...
Text Solution
|
- M and N are point on sides QR and PQ respectively of /\ PQR, right-an...
Text Solution
|
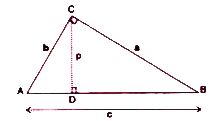
- In triangle ABC, /ABC= 90^(@), AB= c unit, BC= a unit, AC=b unit, CD i...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an equilateral triangle, P is a point in BC such that BP : PC =...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure shows a triangle ABC, in which AB gt AC. E is the mid...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB=AC =20 cm and BC=24 cm. PQRS ...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of a parallelogr...
Text Solution
|