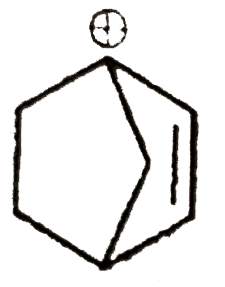
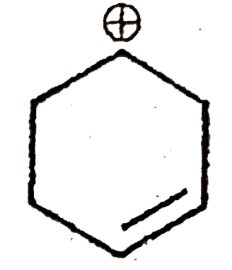
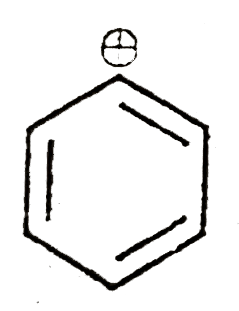
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In which of the following carbocations, delocalisation of positive cha...
Text Solution
|
- In which delocalisation of positive charge is possible?
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following carbocations, delocalisation of positive cha...
Text Solution
|
- In which delocalisation of positive charge is possible
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following , delocalisation of pi-electrons is/are poss...
Text Solution
|
- In the given structure at how many atoms the positive charge will be d...
Text Solution
|
- In which delocalisation of positive charge is possible ?
Text Solution
|
- Identify the number of compounds in which positive charge will be delo...
Text Solution
|
- In how many of the following cases, the negative charge is delocalised...
Text Solution
|