A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-TEST PAPERS-PART - II PHYSICS
- A particle is moving on a circular path of radius R with constant spee...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving on a circular path of radius R with constant spee...
Text Solution
|
- Why does -NH2 group directs the incoming group at the ortho and para ...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mol of a real gas obeys P(V(m) - b) = RT , where 'b' and 'R' are con...
Text Solution
|
- One gram of a metallic chloride was found to contain 0.835 g of chlori...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of compressibility factor (Z) vs. P for one mole of a real g...
Text Solution
|
- N(2) undergoes photochemical dissociation into one normal N-atom and o...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas (C(v,m)=(5)/(2)R) at 300 K and 5 atm is expan...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour density of the mixture at equilibrium is 38.3 at 33^(@)C ...
Text Solution
|
- N(2)O(3) dissociates into NO and NO(2). At equilibrium pressure of 3 a...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of contriburing structures showing hurperconjugation ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving on a circular path of radius R with constant spee...
Text Solution
|
- Travelling wave travels in medium '1' and enters into another medium '...
Text Solution
|
- Name the functional groups present in the following compounds. (a) ...
Text Solution
|
- Name the functional groups present in the following compounds. (a) ...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- How many alkene/s from following are more stable than
Text Solution
|
- The system is released from rest with both the springs in unstretched ...
Text Solution
|
- On a disc of radius R a concentric circle of radius R//2 is drawn. The...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1 kg is thrown up with an initial speed of 4 m//s. A se...
Text Solution
|
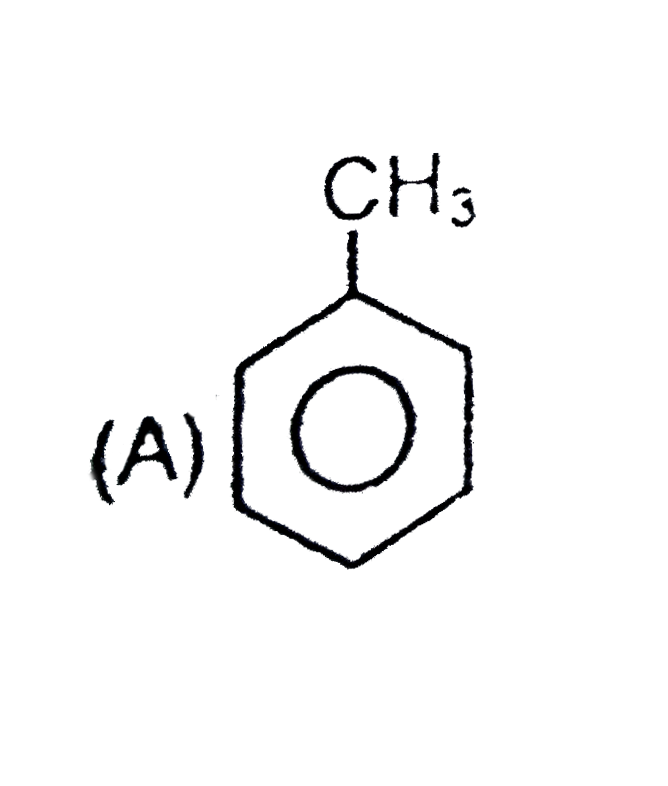
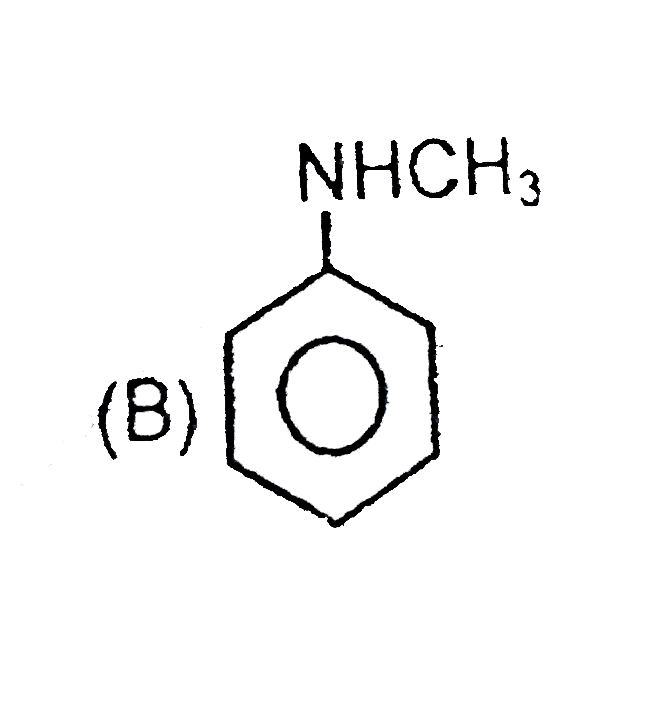
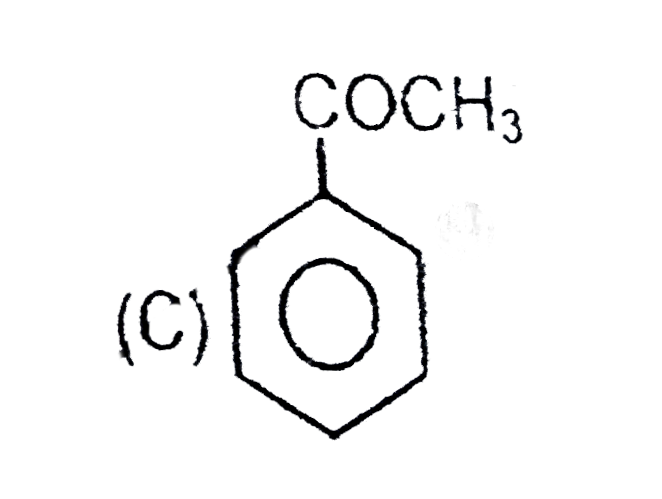
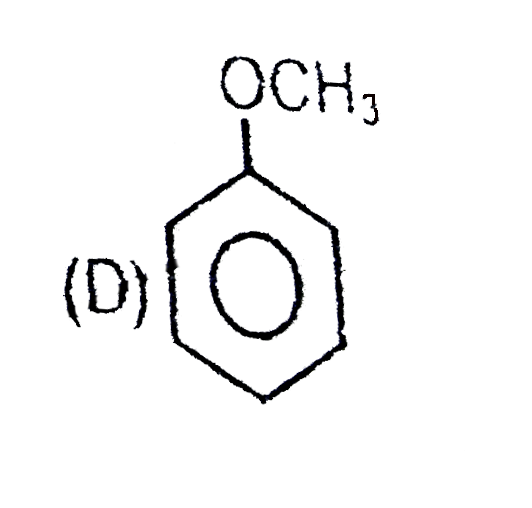
 have more `+m` effect
have more `+m` effect 