Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KTG & THERMODYNAMICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART - II|27 VideosKTG & THERMODYNAMICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advancel Level Problems|1 VideosKTG & THERMODYNAMICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3|1 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|64 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND FORCES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|64 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-KTG & THERMODYNAMICS-PART - I
- Calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise temperature...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: The total translational kinetic energy of fall the molecu...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is expanding such that PT^2=constant. The coefficient of ...
Text Solution
|
- Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at consta...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the P-V plot of an ideal gas taken through a cycle AB...
Text Solution
|
- A real gas behaves like an ideal gas if its
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas in initial state A undergoes a cyclic process...
Text Solution
|
- A diatomic ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to 1/32 of its initia...
Text Solution
|
- 5.6 liter of helium gas at STP is adiabatically compressed to 0.7 lite...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of 2 moles of helium gas ( (atomic mass)=4a.m.u ) and 1 mole...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of ideal helium gas are in a rubber balloon at 30^@C. The ba...
Text Solution
|
- Two non-reactive monoatomic ideal gases have their atomic masses in th...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows the variation of specific heat capacity (C) of ...
Text Solution
|
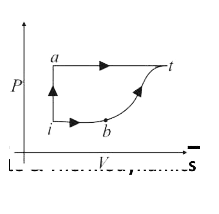
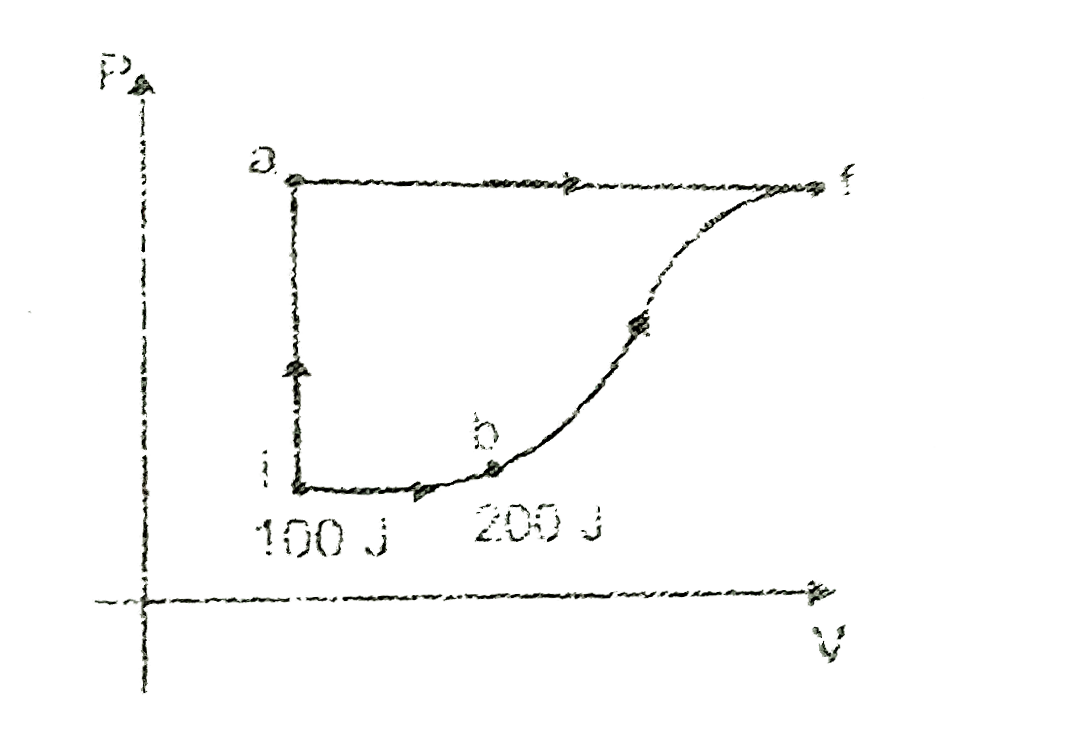
- A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state i with internal ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction...
Text Solution
|
- A container of fixed volume has a mixture of a one mole of hydrogen an...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spri...
Text Solution
|