A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CALORIMETRY AND THERMAL EXPANSION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2|1 VideosCALORIMETRY AND THERMAL EXPANSION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercie-3|1 VideosCALORIMETRY AND THERMAL EXPANSION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1|1 VideosCALORIMETRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|19 VideosCAPACITOR
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|45 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CALORIMETRY AND THERMAL EXPANSION-Exercise
- Earth receives 1400 W//m^2 of solar power. If all the solar energy fal...
Text Solution
|
- A 50gram lead bullet, specific heat 0.02 is initially at 30^(@) C. It...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of 100g of water is to be raised from 24^@C to 90^@C b...
Text Solution
|
- An electrically heated coil is immersed in a calorimeter containing 36...
Text Solution
|
- As a result of temp rise of 32^(@)C, a bar with a crack at its centre ...
Text Solution
|
- Level of a certain liquid at 0^(@)C and 100^(@)C are 0 and 10 mm on a ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple seconds pendulum is constructed out of a very thin string of ...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of length 25cm has a cross-sectional area of 0.8cm^(2) . T...
Text Solution
|
- A 1-L flask contains some mercury. It is found that at different tempe...
Text Solution
|
- When two non reactive samples at different temperatures are mixed in a...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical beakers with negligible thermal expansion are filled wit...
Text Solution
|
- When m gm of water at 10^(@)C is mixed with m gm of ice at 0^(@)C, whi...
Text Solution
|
- A bimetallic strip is formed out of two identical strips one of copper...
Text Solution
|
- There is a rectangular metal plate in which two cavities in the shape ...
Text Solution
|
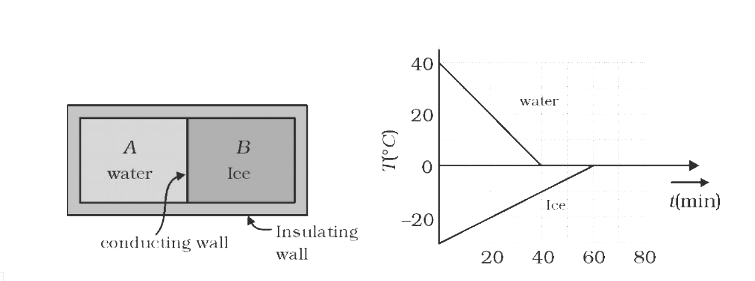
- A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compar...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compar...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compar...
Text Solution
|
- In a container of negligible heat capacity, 200 gm ice at 0^(@)C and 1...
Text Solution
|
- In a container of negligible heat capacity 200 gm ice at 0^(@)C and 10...
Text Solution
|
- In a container of negligible heat capacity, 200 gm ice at 0^(@)C and 1...
Text Solution
|