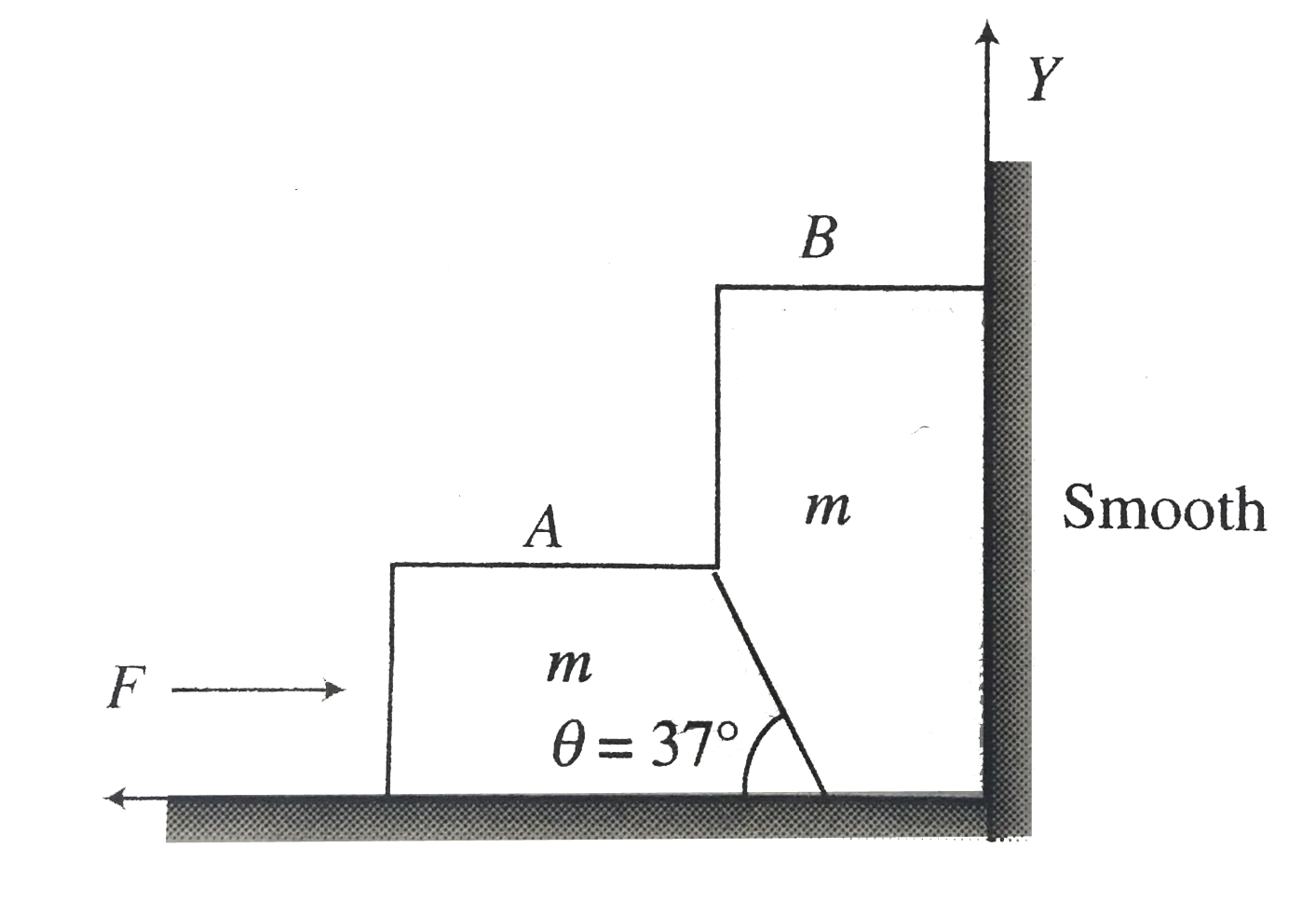
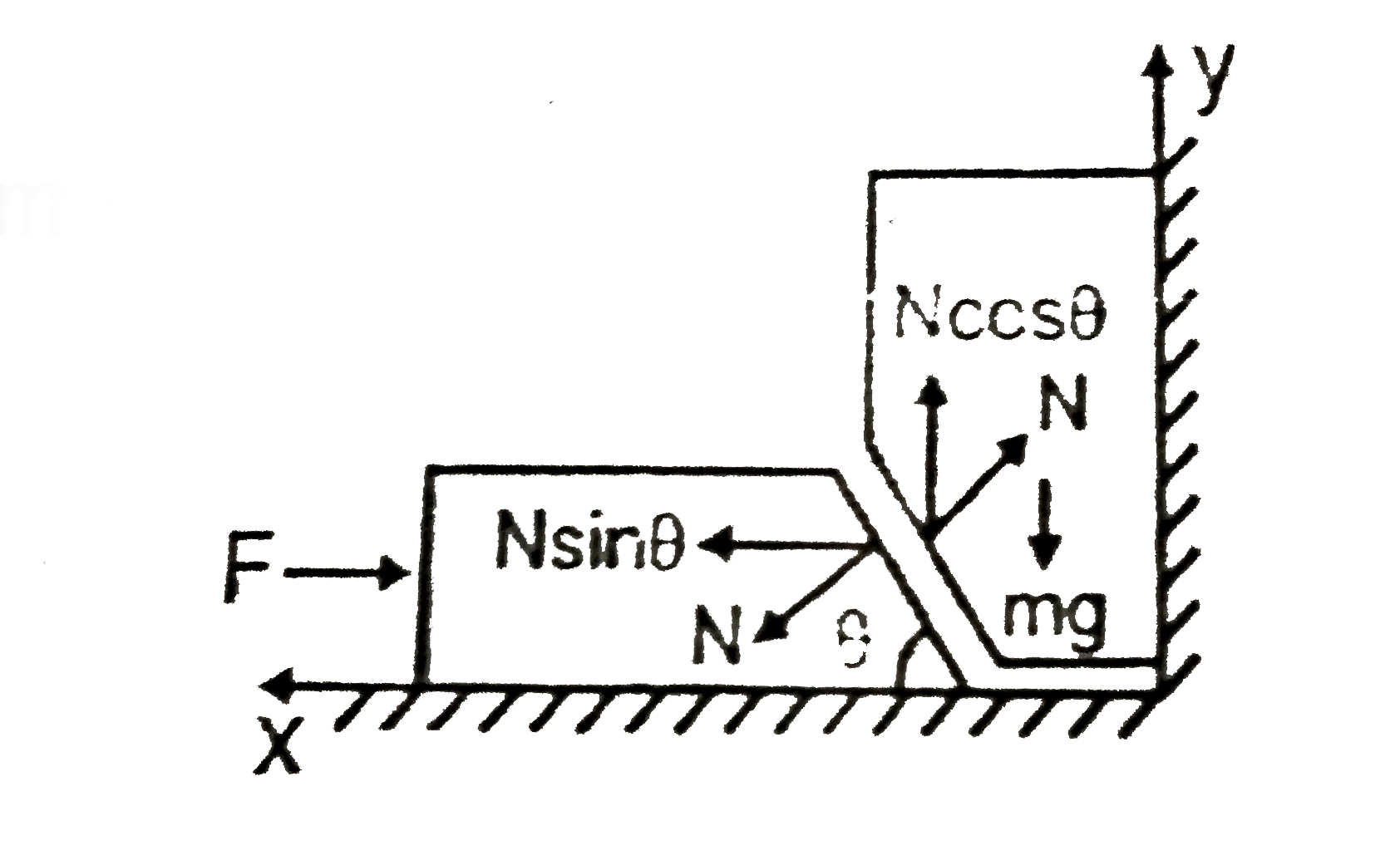A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 70|7 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 71|8 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 69|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-comprehension
- A particle which is initially at rest at the origin, is subjection to ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle which is initially at rest at the origin, is subjection to ...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- A meter stick AB of length 1 meter rests on a frictionless floor in ho...
Text Solution
|
- A meter stick AB of length 1 meter rests on a frictionless floor in ho...
Text Solution
|
- A meter stick AB of length 1 meter rests on a frictionless floor in ho...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an arrangement of pulleys and two blocks. All surfaces ar...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an arrangement of pulleys and two blocks. All surfaces ar...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an arrangement of pulleys and two blocks. All surfaces ar...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses 6 kg, 4 kg and 2 kg are pulled on a rough surfa...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses 6 kg, 4 kg and 2 kg are pulled on a rough surfa...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses 6 kg, 4 kg and 2 kg are pulled on a rough surfa...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a rough inclined plane. The corfficient...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a rough inclined plane. The corfficient...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a rough inclined plane. The corfficient...
Text Solution
|
- Rain is falling with a velocity (-4hat(i)+8hat(j)-10hat(k)). A person ...
Text Solution
|
- Rain is falling with a velocity (-4hat(i)+8hat(j)-10hat(k)). A person ...
Text Solution
|
- Rain is falling with a velocity (-4hat(i)+8hat(j)-10hat(k)). A person ...
Text Solution
|