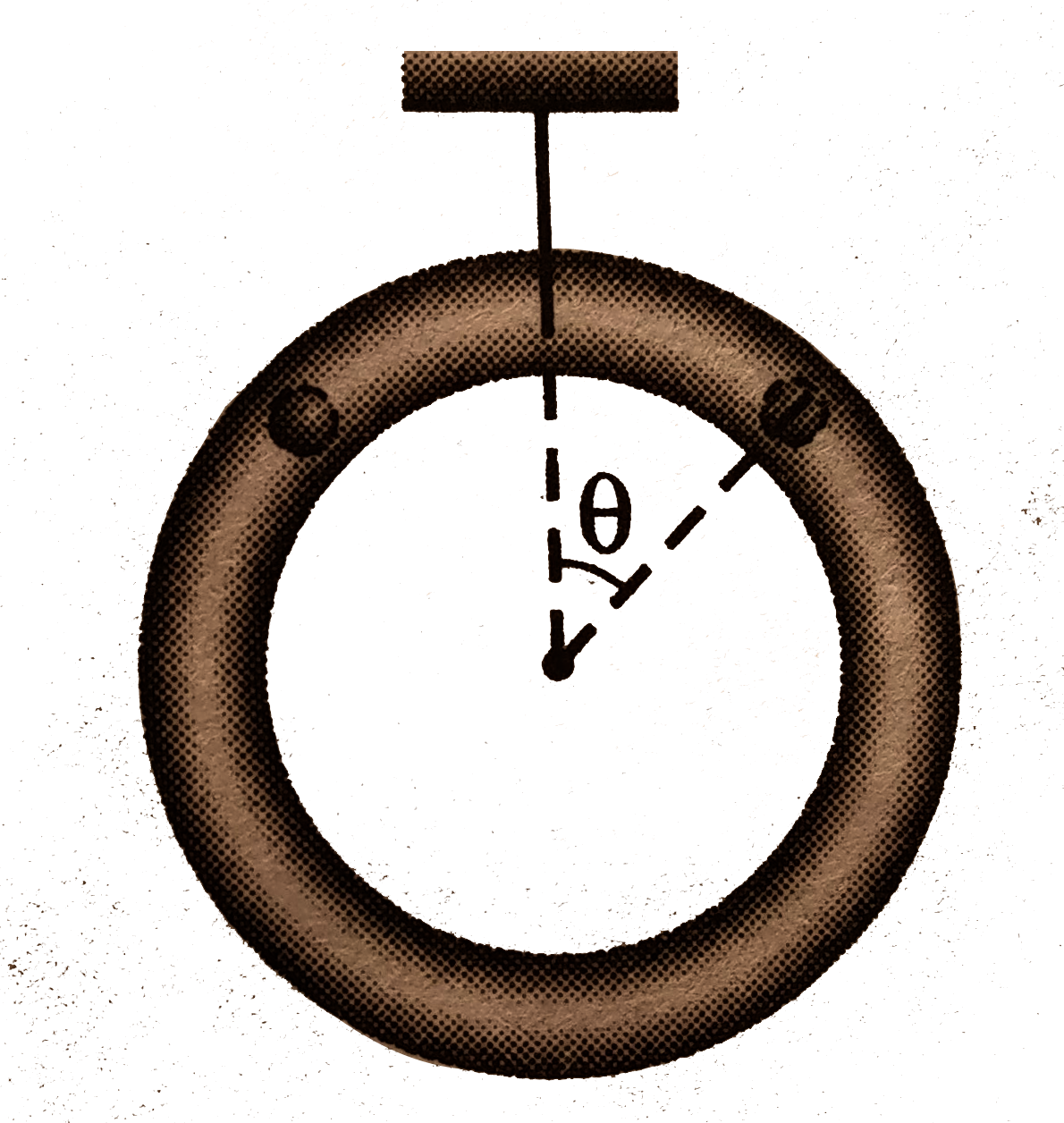Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 59|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 60|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 57|7 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 58
- In the figure m(A) = m(B) = m(C) = 60 kg. The coefficient of friction ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is given initial horizontal velocity of magnitude...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a thin sheet of mass M of the given shape abo...
Text Solution
|
- A man stands at one end of a boat which is stationary in water. Neglec...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a uiform semicircular disc of mass M and radi...
Text Solution
|
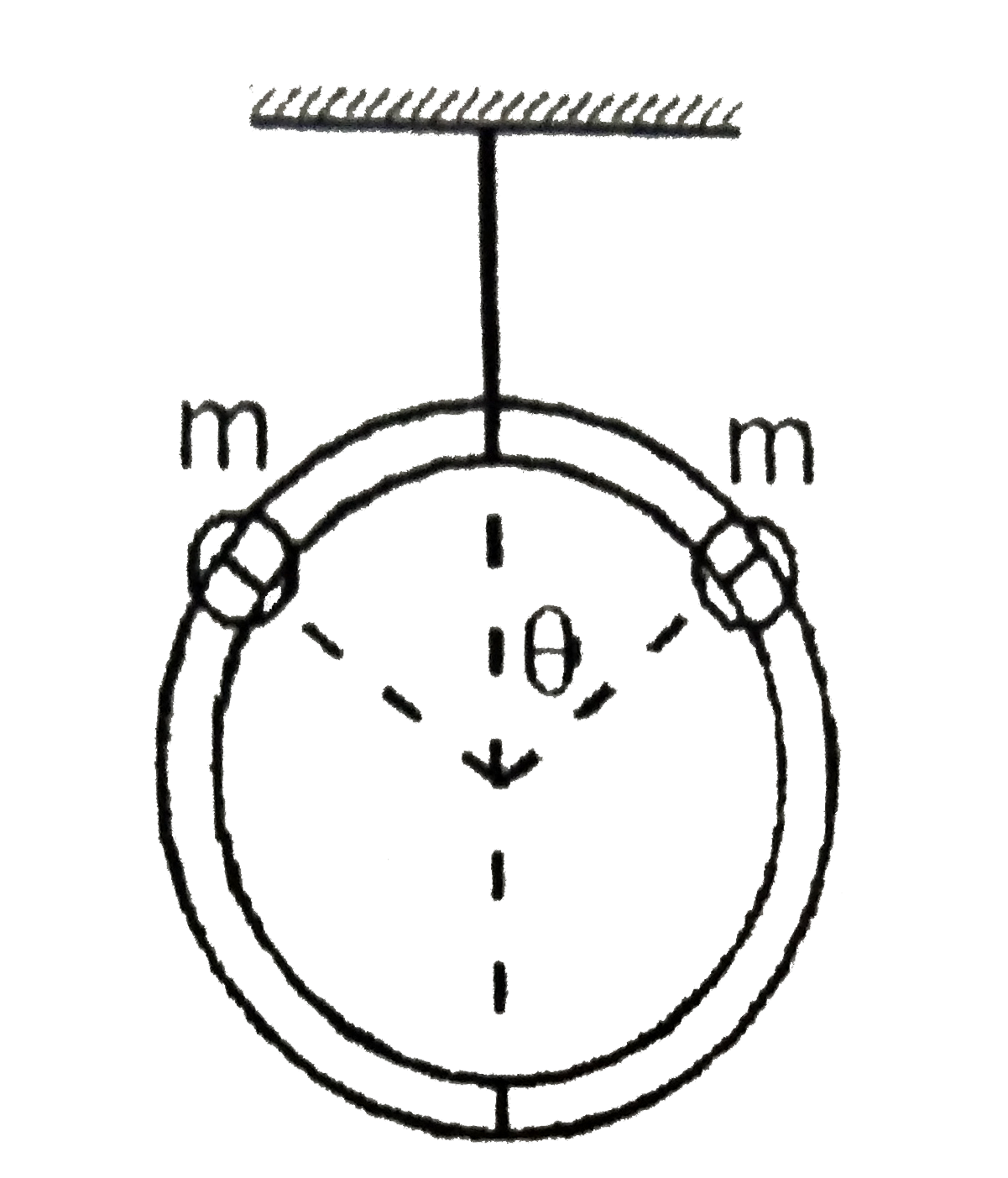
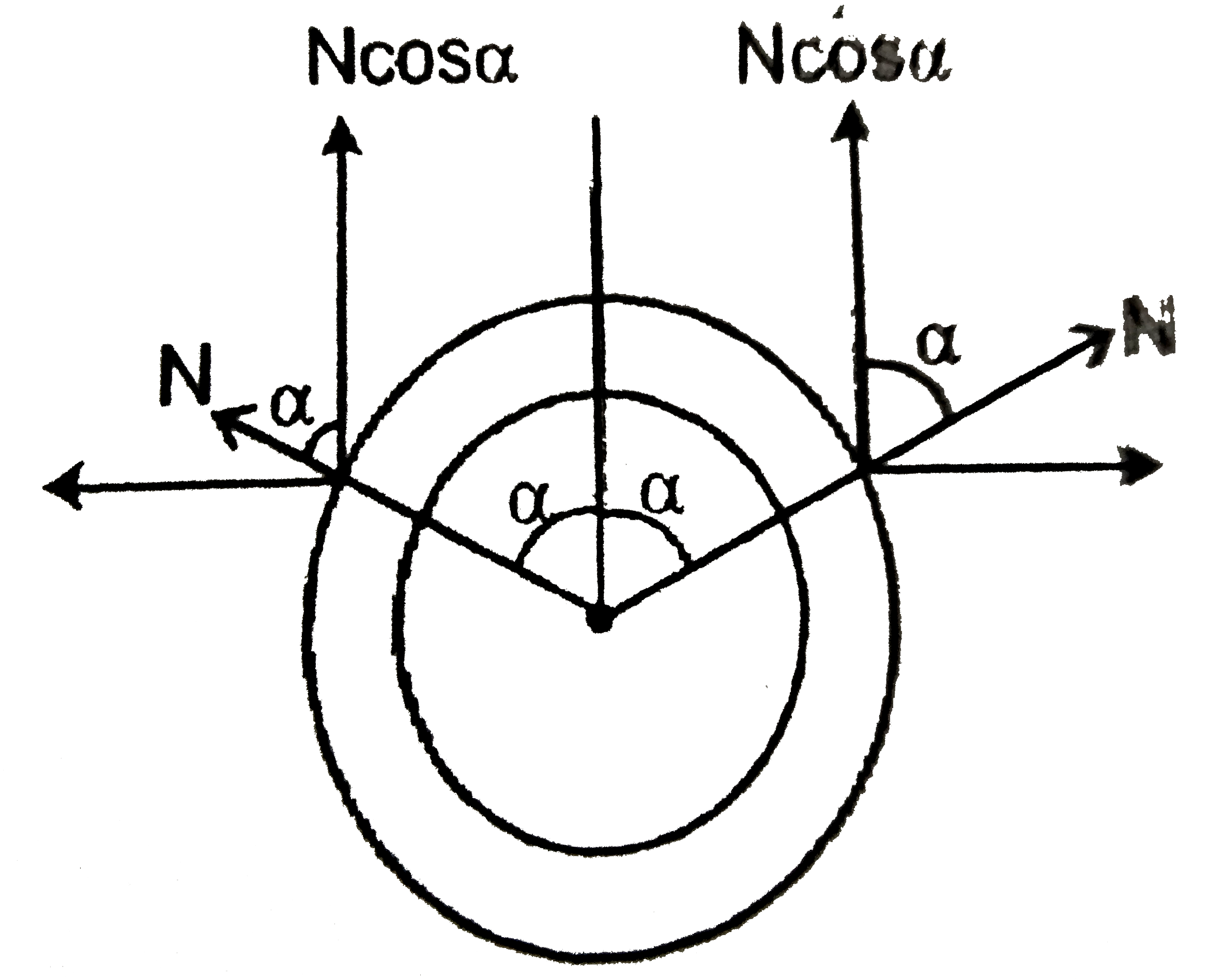
- A ring of mass M hangs from a thread and two beads of mass m slides on...
Text Solution
|
- Find out the moment of inertia of the following structure ( written as...
Text Solution
|
- The uniform solid sphere shown in the figure has a spherical hole in i...
Text Solution
|
- Statement 1: Two spheres undergo a perfectly elastic collision. The ki...
Text Solution
|