A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 70|7 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 71|8 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 69|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-comprehension
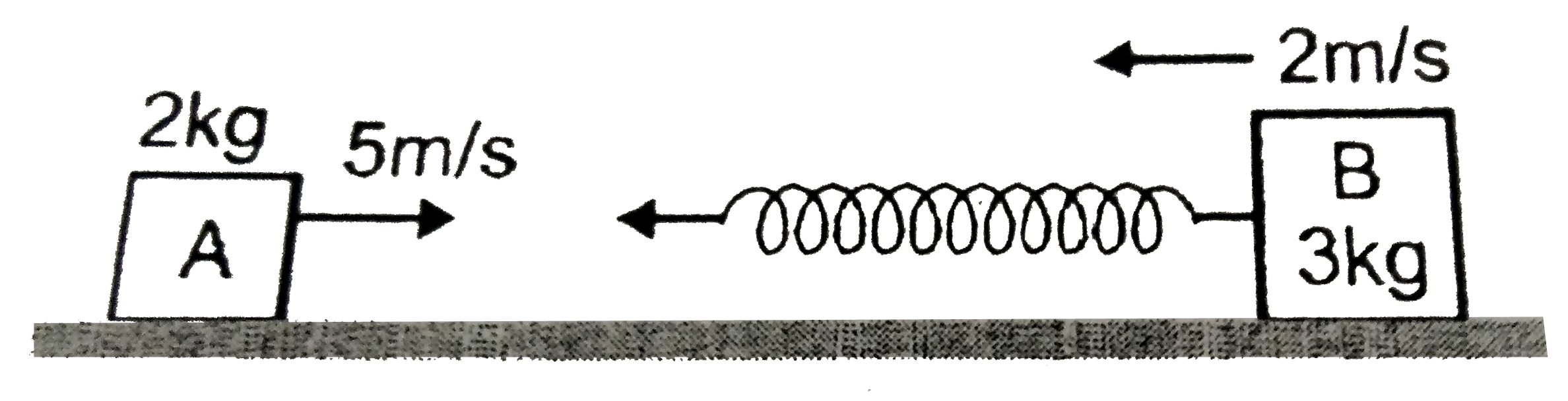
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth horizontal fixed pipe is bent in the form of a vertical circl...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth horizontal fixed pipe is bent in the form of a vertical circl...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth horizontal fixed pipe is bent in the form of a vertical circl...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down a wedge of mass M as shown . The whole s...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down a wedge of mass M as shown . The whole s...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down a wedge of mass M as shown . The whole s...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light string of length L is connected to a ball and the o...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light string of length L is connected to a ball and the o...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light string of length L is connected to a ball and the o...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical rods of mass M = 6 kg each are welded at their ends to ...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical rods of mass M = 6 kg each are welded at their ends to ...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical rods of mass M = 6 kg each are welded at their ends to ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a block of mass 2kg moving along x- axis at any time t...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a block of mass 2kg moving along x- axis at any time t...
Text Solution
|