A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 89 illustration|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 90 Illustration|2 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 88|7 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-Now answer the following :
- A wire elongates by 1.0 mm when a load W is hanged from it. If this wi...
Text Solution
|
- The length of a metal is l(1) when the tension in it is T(1) and is l(...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical c...
Text Solution
|
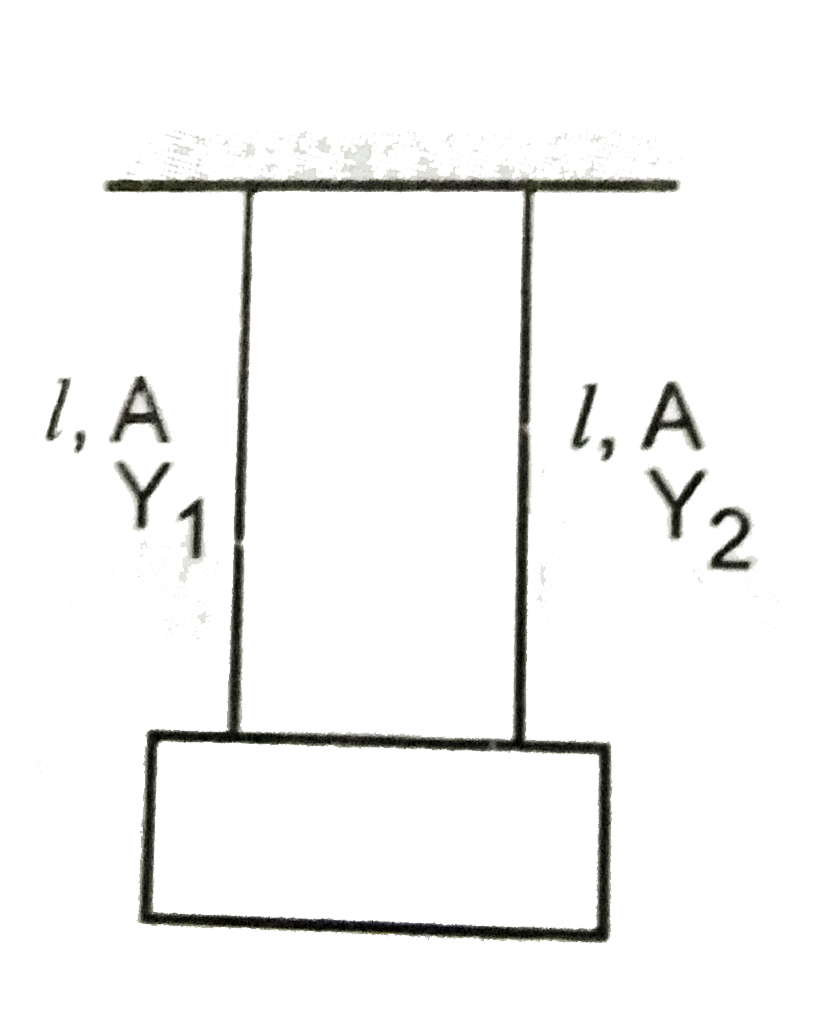
- Two wires of equal length and cross sectional area suspended as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire and a copper wire of equal length and equal cross- sectio...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of cross sectional area 4cm^2 and length 2m shrinks by 0.1...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The force F is equal to the (m...
Text Solution
|
- If in a wire of Young's modulus Y, longitudinal strain X is produced t...
Text Solution
|
- A metal wire of length L is suspended vertically from a rigid support....
Text Solution
|
- A metal wire of length L, area of cross-section A and young's modulus ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of the same material and length but diameter in the ratic 1:...
Text Solution
|
- The workdone in increasing the length of a one metre long wire of cro...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a long metallic wire of length L is tied to the ceiling. Th...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown the straing versus stress graph for two values of...
Text Solution
|
- A metal square plate of 10cm side rests on 2mm thick caster oil layer....
Text Solution
|
- A man starts rowing his stationary cuboidal boat of base area A=10m^(2...
Text Solution
|
- As per the shown figure the central solid cylinder starts with initial...
Text Solution
|
- A ball bearing of radius of 3mm made of iron of density 7.85g cm^(-3) ...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble of 1cm radius is rising at a steady rate of 0.5cms^(-1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic sphere of radius 1.0 xx 10^(-3) m and density 1.0 xx 10^(4)...
Text Solution
|