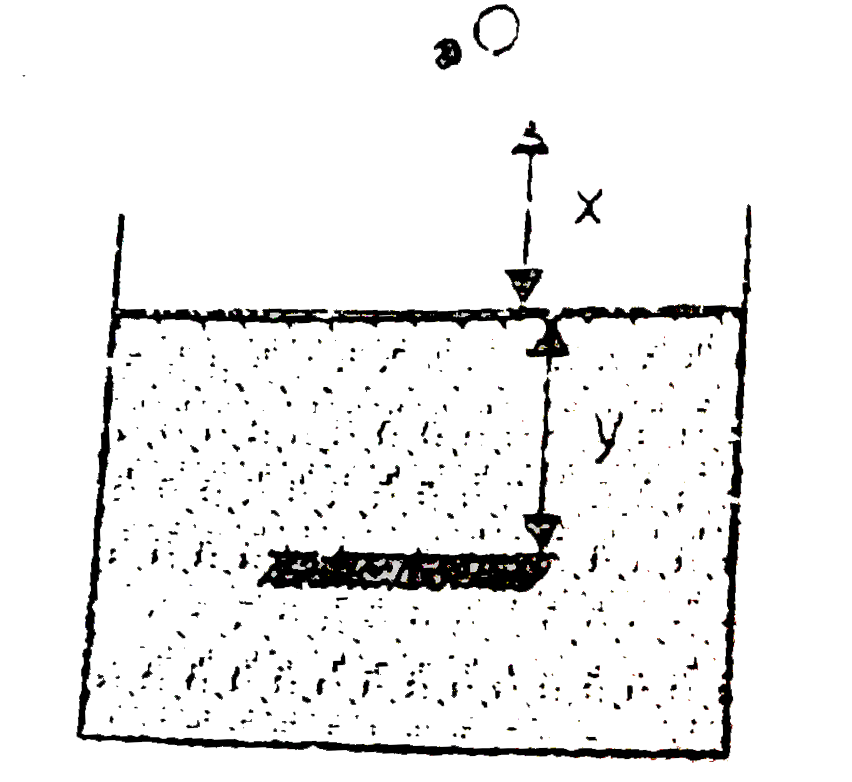
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.24|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.25|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.22|9 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|19 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.23
- A block B is pushed momentarily along a horizontal surface with an ini...
Text Solution
|
- A 60kg is pushed horizontaly with just enough force to start it moving...
Text Solution
|
- If the eye is kept very close to a coverging lens (focal length = 10 c...
Text Solution
|
- If the eye is kept very close to a coverging lens (focal length = 10 c...
Text Solution
|
- With what angular velocity the earth should spin in order that a body ...
Text Solution
|
- Position vector of a particle moving in space is given by : vec(r)=3...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P is projected with speed 20 m//s at angle 37^(@) from hori...
Text Solution
|
- Mirror in the arrangement shown in figure is moving up with speed 8 cm...
Text Solution
|
- A force vec(F) is applied to block (m = 6 kg) at rest on an inclined p...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 20 kg is acted upon by a force F=30N at an angle 53^@ ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected vertically upwards with a speed of 16ms^-1. Af...
Text Solution
|
- Three forces are acting on a particle of mass m intially in equilibriu...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of length 2m is kept on a table such that a length of...
Text Solution
|
- Two carts of masses 200 kg and 300 kg on horizontal rails are pushed a...
Text Solution
|
- X-ray beam can be deflected by
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies P and Q of equal masses are suspended from two separate mas...
Text Solution
|
- the photon radiated from hydrogen corresponding to the second line of ...
Text Solution
|
- Which electronic transition in Li^(2+) ion would emit radiation of sam...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m, moves in such a way that the potential ene...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m(1) lies on the top of fixed wedge as shown in fig. a...
Text Solution
|
 .
.