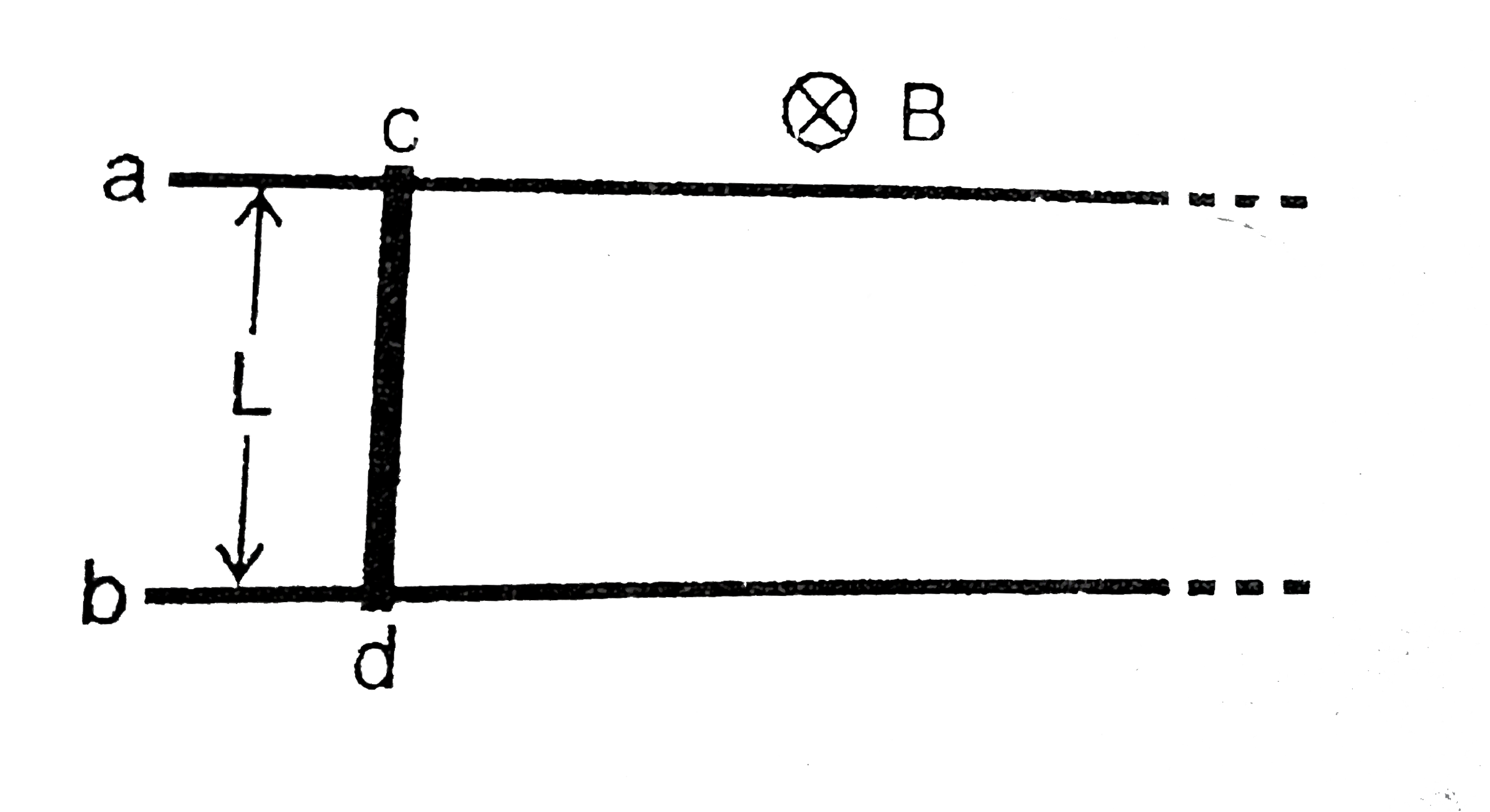
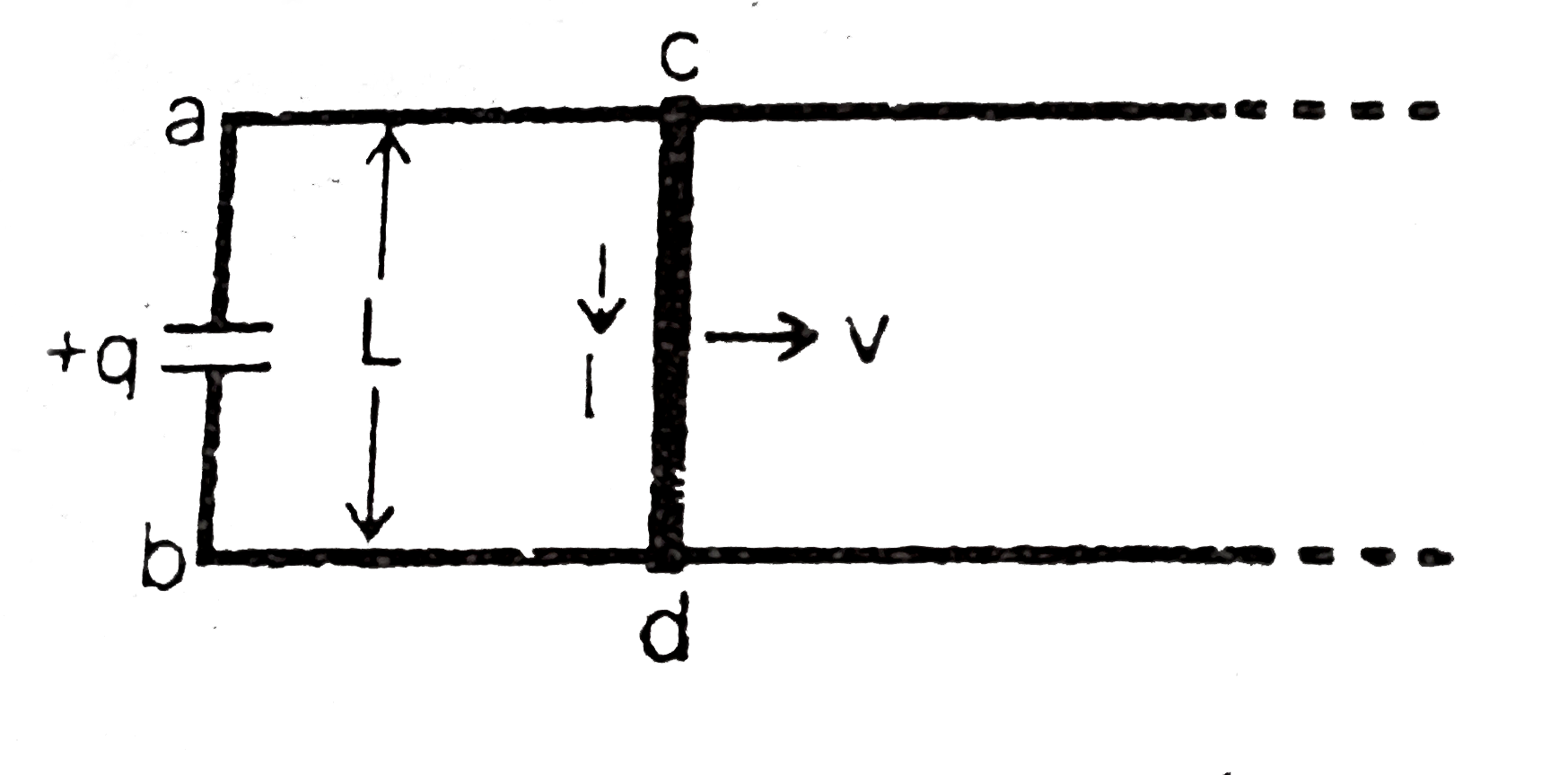
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.55|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.56|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.53|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|19 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.54
- In arrangement shown in figure, plane wavefront of monochromatic light...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic field along x-axis varies according to the relation vec(B) = ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of area A and separation d is charged to po...
Text Solution
|
- The spherical planets have the same mass but densities in the ratio 1:...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a LCR circuit connected with a battery emf epsilon and in...
Text Solution
|
- A current carrying ring, carrying a constant current (2)/(pi) Amp, rad...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rail...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rail...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rail...
Text Solution
|