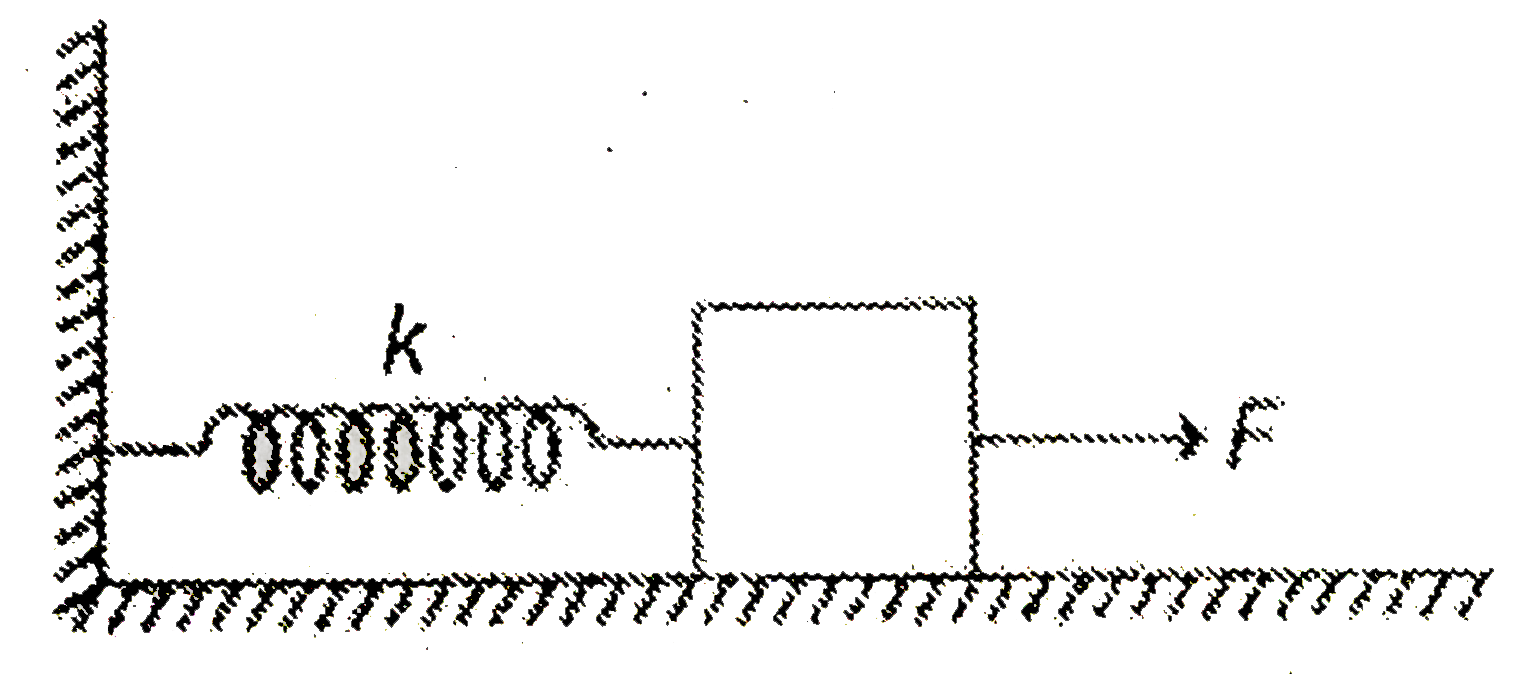A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-WORK POWER AND ENERGY-Exercise
- In figure, the ball A is released from rest, when the spring is at its...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown initial spring is in unstretched state and blocks ...
Text Solution
|
- A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, i...
Text Solution
|
- A body is projected with kinetic energy k at angle phi with the vertic...
Text Solution
|
- A man places a chain (of mass m and length l) on a table slowly. Initi...
Text Solution
|
- Power supplied to a mass 2 kg varies with time as P = (3t^(2))/(2) wat...
Text Solution
|
- A constant power P is applied to a particle of mass m. The distance tr...
Text Solution
|
- The force acting on a body is inversely proportional to the distance (...
Text Solution
|
- The graph between the resistance force F acting on a body and the dist...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a straight line with retardation proportional to i...
Text Solution
|
- A body is falling under gravity . When it loses a gravitational potent...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring con...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m dropped from a certain height strikes a light vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves with a velocity 5hati-3hatj+6hatk ms^(-1) under the i...
Text Solution
|
- An electric motor creates a tension of 4500 newton in a hoisting cable...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a partical veries with distance x as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a force filed vec(F) is given by U(x,y)=sin(x+...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of force constant 800 Nm^(-1) has an extension of 5 cm. The w...
Text Solution
|
- A body is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering constant...
Text Solution
|
- The total work done on a particle is equal to the change in its mechan...
Text Solution
|