A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CIRCULAR MOTION-Exercise
- In the figure shown a lift goes downwards with a constant retardation....
Text Solution
|
- In the motorcycle stunt called " the well of death" the track is verti...
Text Solution
|
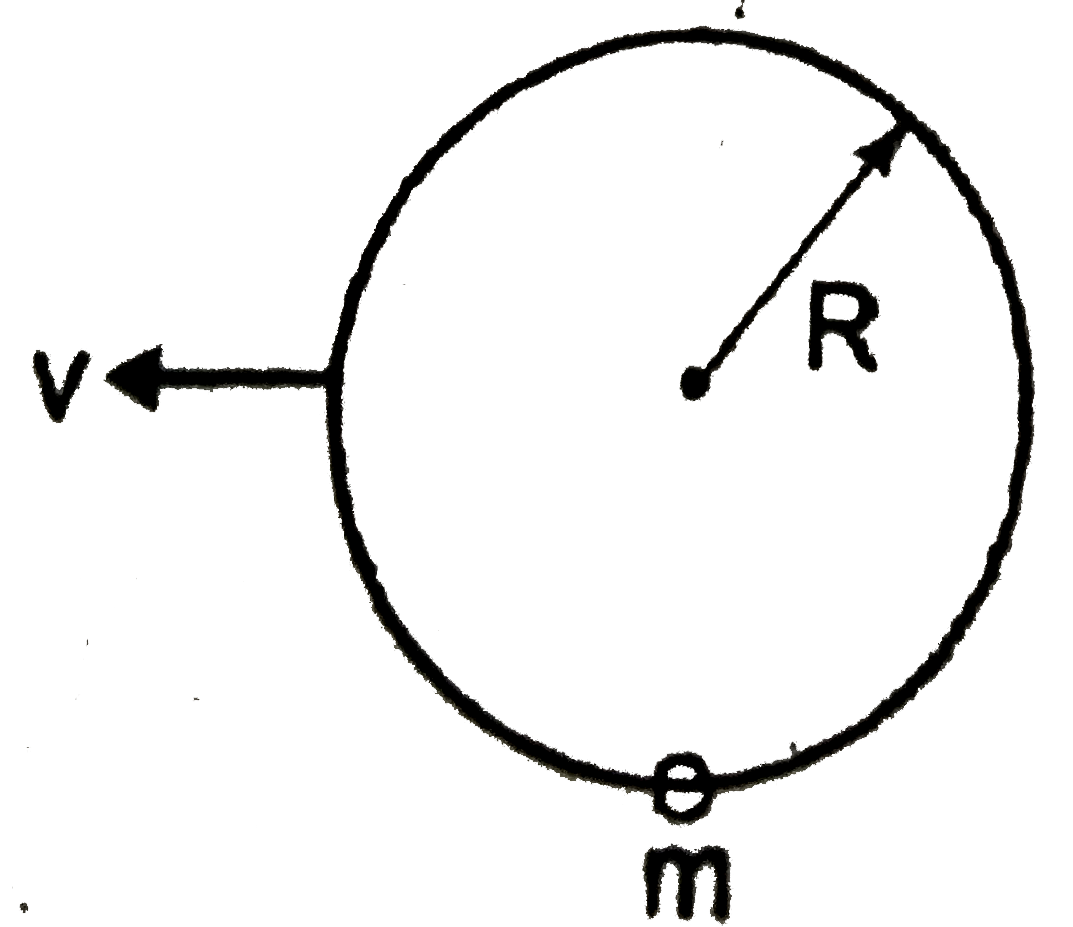
- A ring of radius R lies in vertical plane. A bead of mass 'm' can move...
Text Solution
|
- A circular curve of a highway is designed for traffic moving at 72kmh^...
Text Solution
|
- A section of fixed smooth circular track of radius R in vertical plane...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m starts to slide down from the top of the fixed sm...
Text Solution
|
- Spotlight S rotates in a horizontal plane with constant angular veloci...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected with speed u and angle of projection is theta. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moving along a circular path due to a centripetal force hav...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected horizontally from the top of a tower with a ve...
Text Solution
|
- A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in tak...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of mass m tied to a string of length l is rotated in a circle ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum is oscillating without damping. When the displacemen...
Text Solution
|
- A stone tied to a string of length L is whirled in a vertical circle w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- A bird is flying in the air. To take a turn in the horizontal plane of...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along a circle of radius (20/pi) m with constant tan...
Text Solution
|
- For a body in circular motion with a constant angular velocity, the ma...
Text Solution
|
- A ball suspended by a thread swings in a vertical plane so that its ac...
Text Solution
|
- The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origi...
Text Solution
|