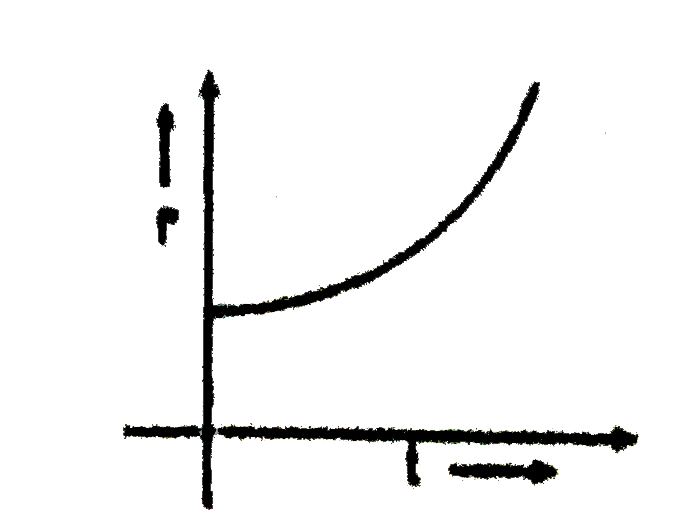
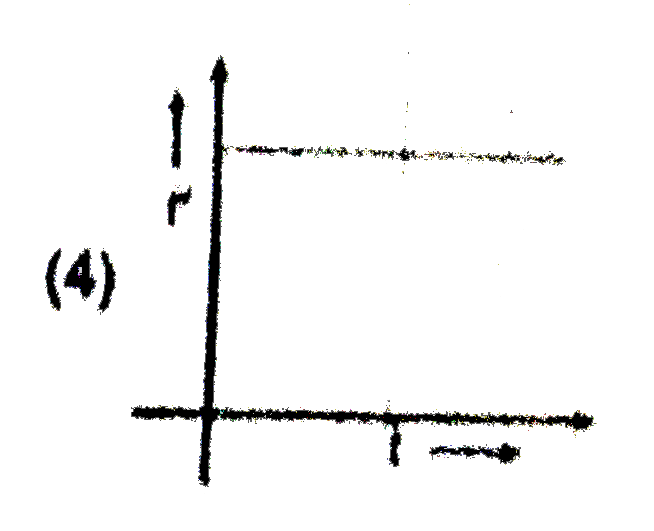A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-SOUND WAVES-Exercise- 3 PART - I
- A source of frequency 'f' is stationary and an obsercer starts moving ...
Text Solution
|
- An observer standing on a railway crossing receives frequencies 2.2 kH...
Text Solution
|
- An open pipe is in resonance in 2nd harmonic with frequency f(1). Now ...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane harmonic sound waves are expressed by the equations. y(1)(...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane harmonic sound waves are expressed by the equations. y(1)(...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane harmonic sound waves are expressed by the equations. y(1)(...
Text Solution
|
- Two trains A and B moving with speeds 20m//s and 30m//s respectively i...
Text Solution
|
- Two trains A and B are moving with speeds 20 m/s and 30 m/s, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Two trains A and B are moving with speeds 20 m//s respectively in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A vibrating string of certain length l under a tension T resonates wit...
Text Solution
|
- A student performed the experiment to measure the speed of sound in ai...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary source is emitting sound at a fixed frequency f(o), which...
Text Solution
|
- hollow pipe of length 0.8 m is closed at one end. At its open end a 0....
Text Solution
|
- A police car with a siren of frequency 8 kHz is moving with uniform ve...
Text Solution
|
- A person blows into the open-end of a long pipe. As a result, a high-p...
Text Solution
|
- A student is performing the experiment of resonance column. The diamet...
Text Solution
|
- Two vehicles, each moving with speed u on the same horizontal straight...
Text Solution
|
- A student is performing an experiment using a resonance column and a t...
Text Solution
|
- Four harmonic waves of equal frequency and equal intensity I(0) have p...
Text Solution
|
- An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity...
Text Solution
|
- A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is ap...
Text Solution
|