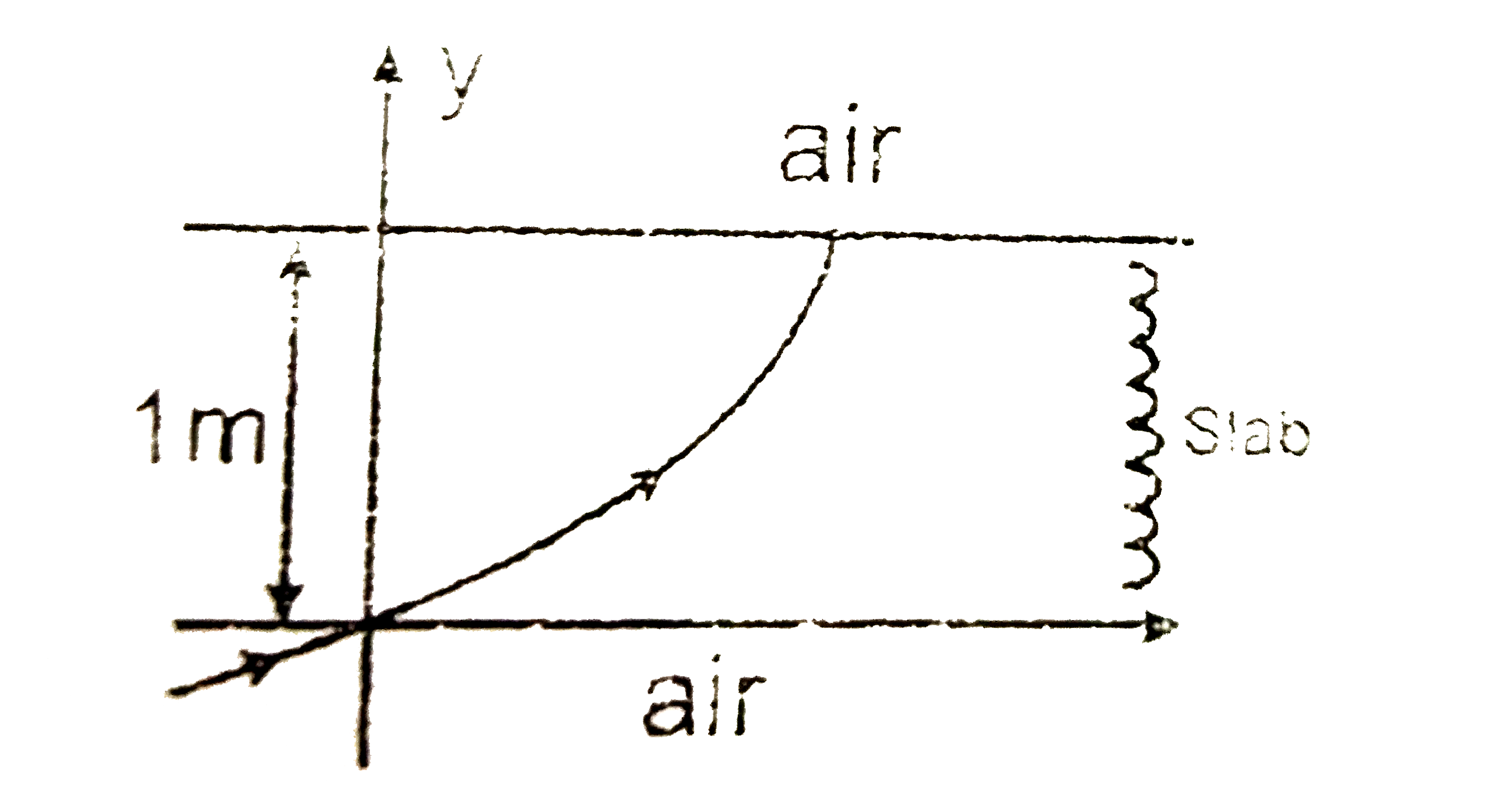
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Exercise
- The angle of incidence at which reflected light is totally polarised f...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomucal telescope has an eyepiece of focal-length 5 cm If the ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing incidence on a...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light is converging towards a point I on a screen. A plane g...
Text Solution
|
- A prism having an apex angle 4^(@) and refraction index 1.5 is located...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-concave lens is placed on a paper on which a flower is drawn. ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If ...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray I is incident on a plane mirror M. The mirror is rotated i...
Text Solution
|
- The image formed by a concave mirror is twice the size of the object. ...
Text Solution
|
- For the system as shown in the figure, the image formed by the concave...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, light is incident at an angle theta which is slightly great...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral prism deviates a ray through 45^(@) for the two angles ...
Text Solution
|
- A man is sitting in a room at 2m from a wall W1, wants to see the full...
Text Solution
|
- A flint glass prism and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is moving with velocity 4 (hat i) + 4 (hat j) + 8 (hat ...
Text Solution
|
- A light waves travels from glass to water. The refractive index for gl...
Text Solution
|
- When a beam of light goes from denser medium (m(d)) to rarer medium (m...
Text Solution
|
- The image for the converging beam after refraction through the curved ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin linear object of size 1mm is kept along the principal axis of a...
Text Solution
|
- A medium has nv = 1.56, nr=1.44. Then its dispersive power is:
Text Solution
|