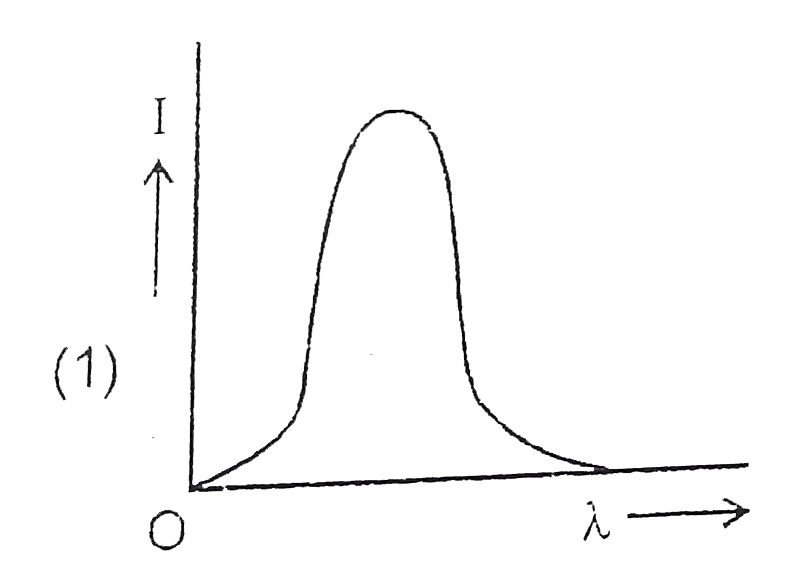
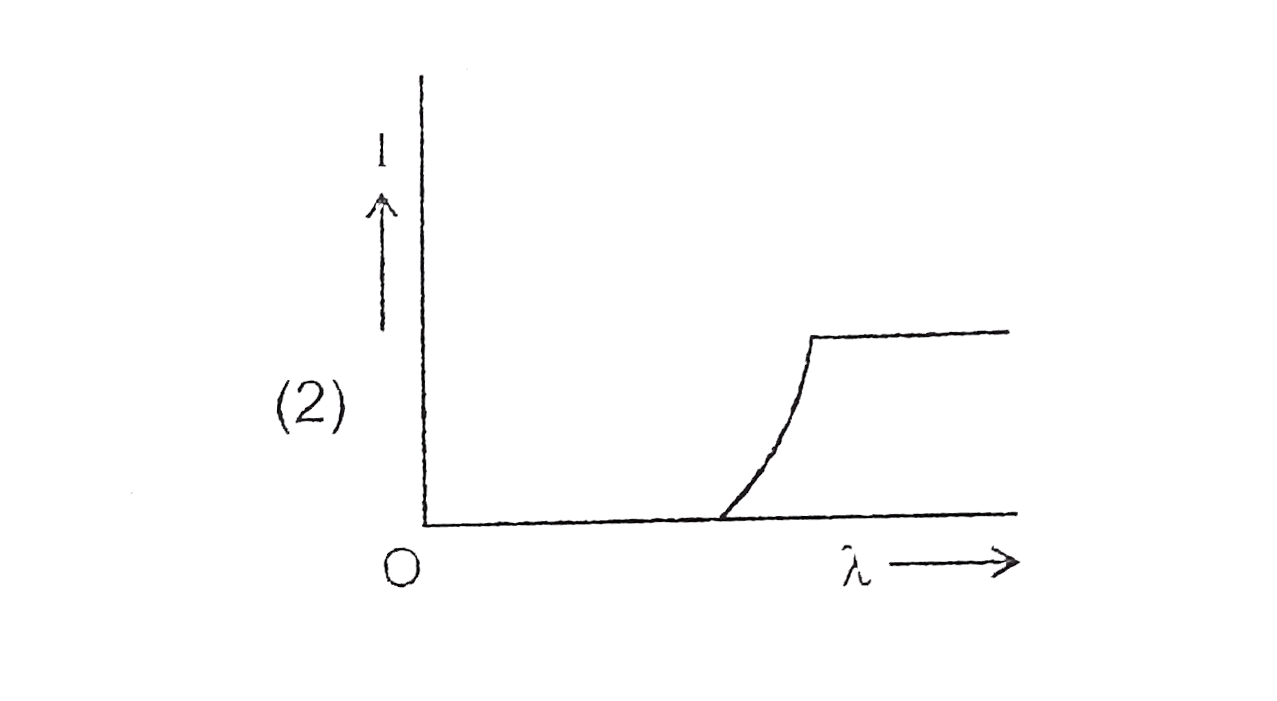
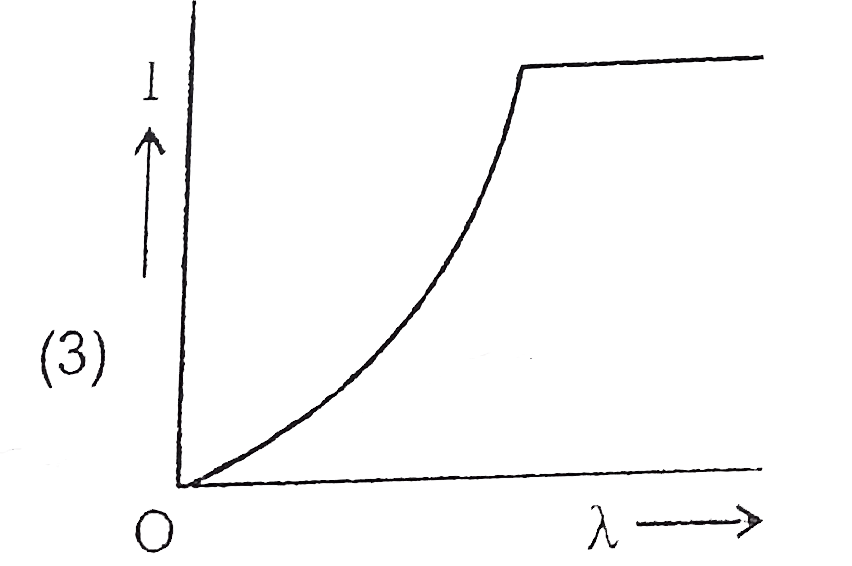
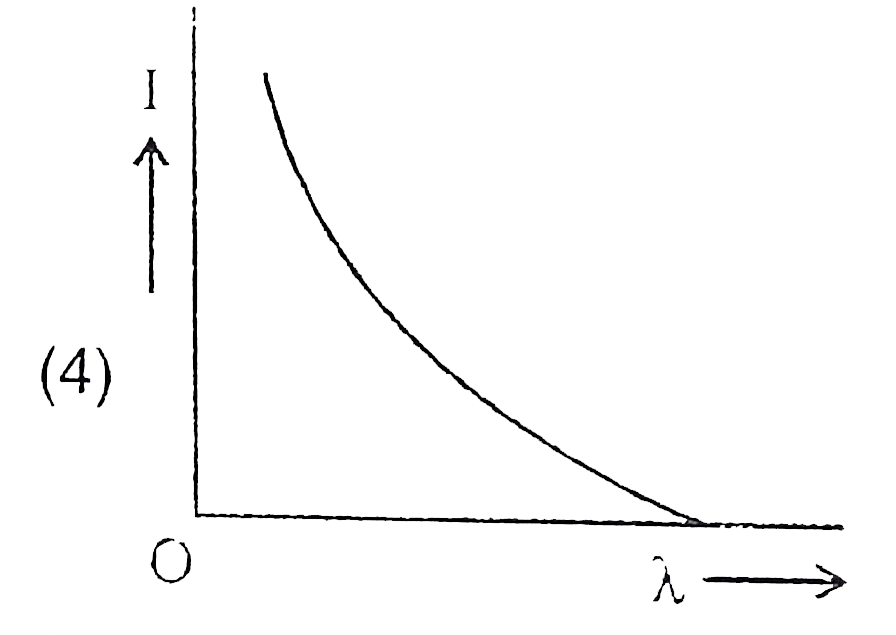
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanved level problems|17 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 Part-III : Comprehension|12 VideosALTERNATING CURRENT
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS|11 VideosCAPACITANCE
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise High Level Problems|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ATOMIC PHYSICS-Exercise -3 part -I JEE (Advanced)
- Hydrogen atom is excited from ground state to another state with prin...
Text Solution
|
- A diatomic molecule is made of two masses m(1) and m(2) which are sepa...
Text Solution
|
- The anode voltage of a photocell is kept fixed. The wavelength lamda o...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen like atom electron makes transition from an energy level...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen (.(1)H^(1)), Deuterium (.(1)H^(2)), singly ionised Helium (...
Text Solution
|
- As an electron makes a transition from an excited state to the ground ...
Text Solution
|
- Ultraviolet light is incident on two photosensitive materials having w...
Text Solution
|
- Mention the significance of Davisson-Germer experiment. An alpha-parti...
Text Solution
|
- De Broglie wavelength associated with an electron acclerated through a...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrogen atom initially in the ground level absorbs a photon, which ...
Text Solution
|
- Plot a graph showing the variation of stopping potential with the freq...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a schematic diagram of the experiment used by. Davisson and Germe...
Text Solution
|
- The two lines A and B in fig. shows the plot of de- Broglie wavelength...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows the variation of stopping potential V0 with the frequency v...
Text Solution
|
- The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. (i) What is...
Text Solution
|
- The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5...
Text Solution
|
- Define ionisation energy . What is its value for a hydrogen atom ?
Text Solution
|
- Write Einstein's photoelectric equation . State clearly the three sali...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the magnetic moment (vec mu) of an electron r...
Text Solution
|
- Define the term 'stopping potential' in relation to photoelectric effe...
Text Solution
|