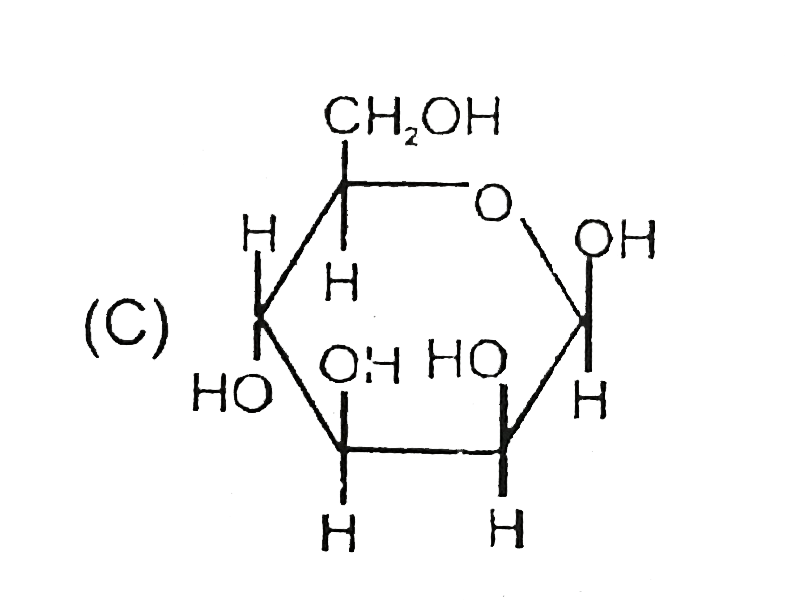
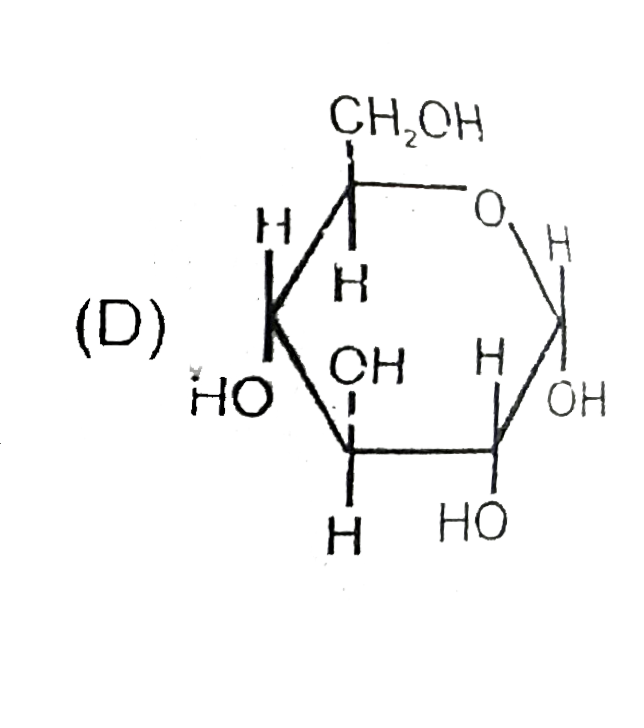
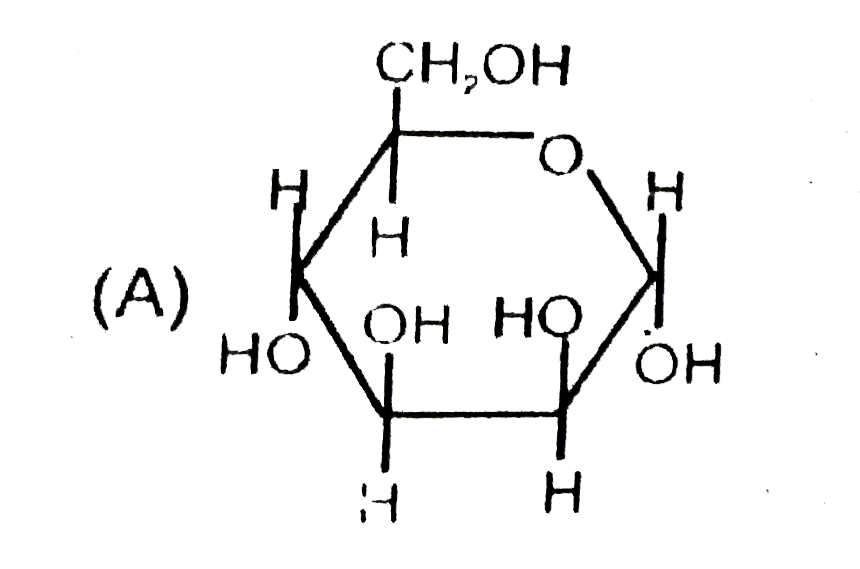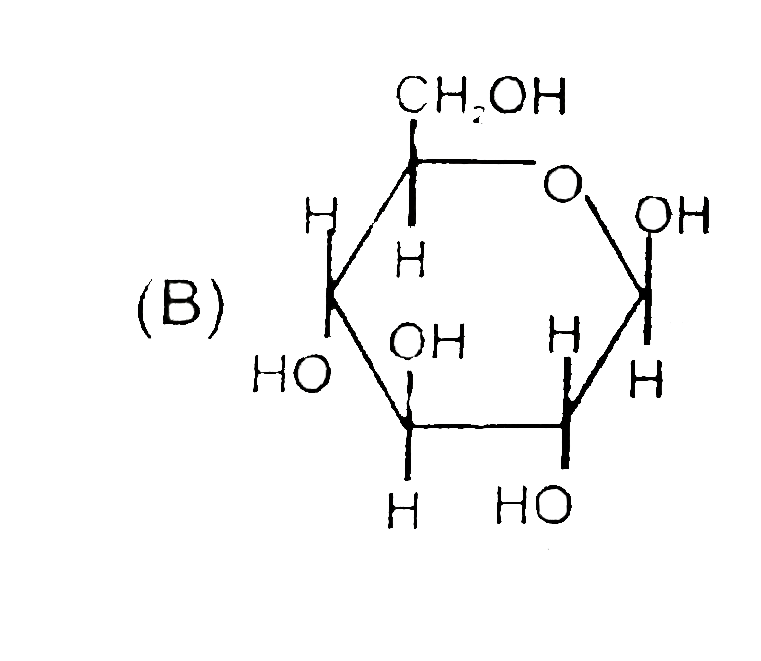A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Ex-2(Comprehension)Part-IV|5 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Ex-3(IIT-JEE)Part-I|18 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Ex-2(Single correct)Part-II|17 VideosBASIC CONCEPTS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)|27 VideosBIOMOLECULES & POLYMER
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Biomolecules & Polymer)|34 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-BIOMOLECULES-Ex-2(More correct)Part-II
- The rms speed of helium gas at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure is 1100 ms^(...
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement about the sugars given above are
Text Solution
|
- Glucose The correct statements about above structure of glucose are ...
Text Solution
|
- D-Mannose differs from D-glucose in its stereochemistry at C-2. The py...
Text Solution
|
- The correct statements about anomers are
Text Solution
|
- The correct statements about peptides are
Text Solution
|
- The rms speed of helium gas at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure is 500 ms^(-...
Text Solution
|
- The rms speed of helium gas at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure is 700 ms^(-...
Text Solution
|
- The rms speed of helium gas at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure is 400 ms^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pair is (are) correctly matched
Text Solution
|
- Which of these are polysaccharides of glucose ?
Text Solution
|
- The correct structure of glycine at given pH are :
Text Solution
|
- Preparation of nylon from hexamethylene diamene and adipic acid is an ...
Text Solution
|
- The rms speed of helium gas at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure is 1000 ms^(...
Text Solution
|