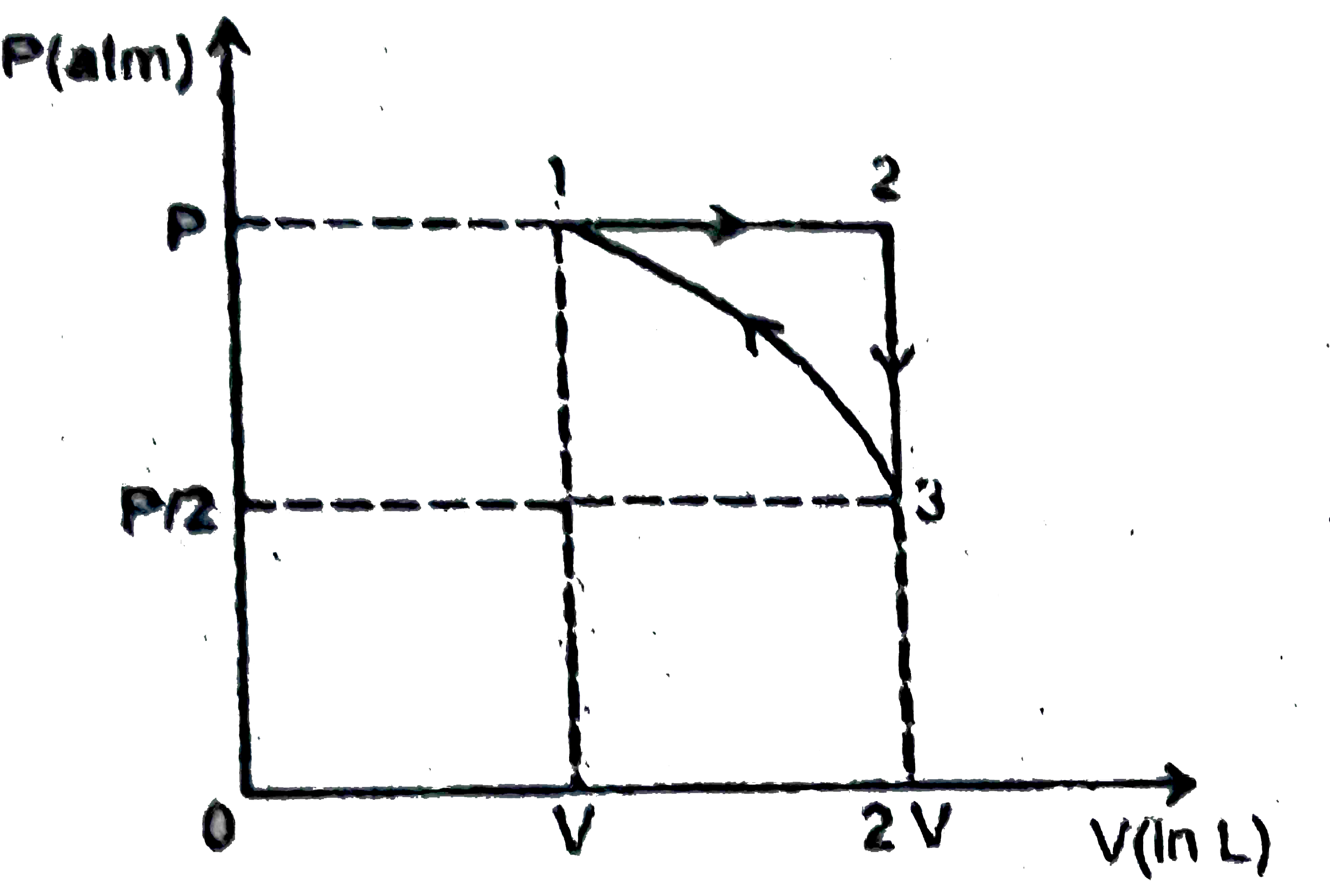
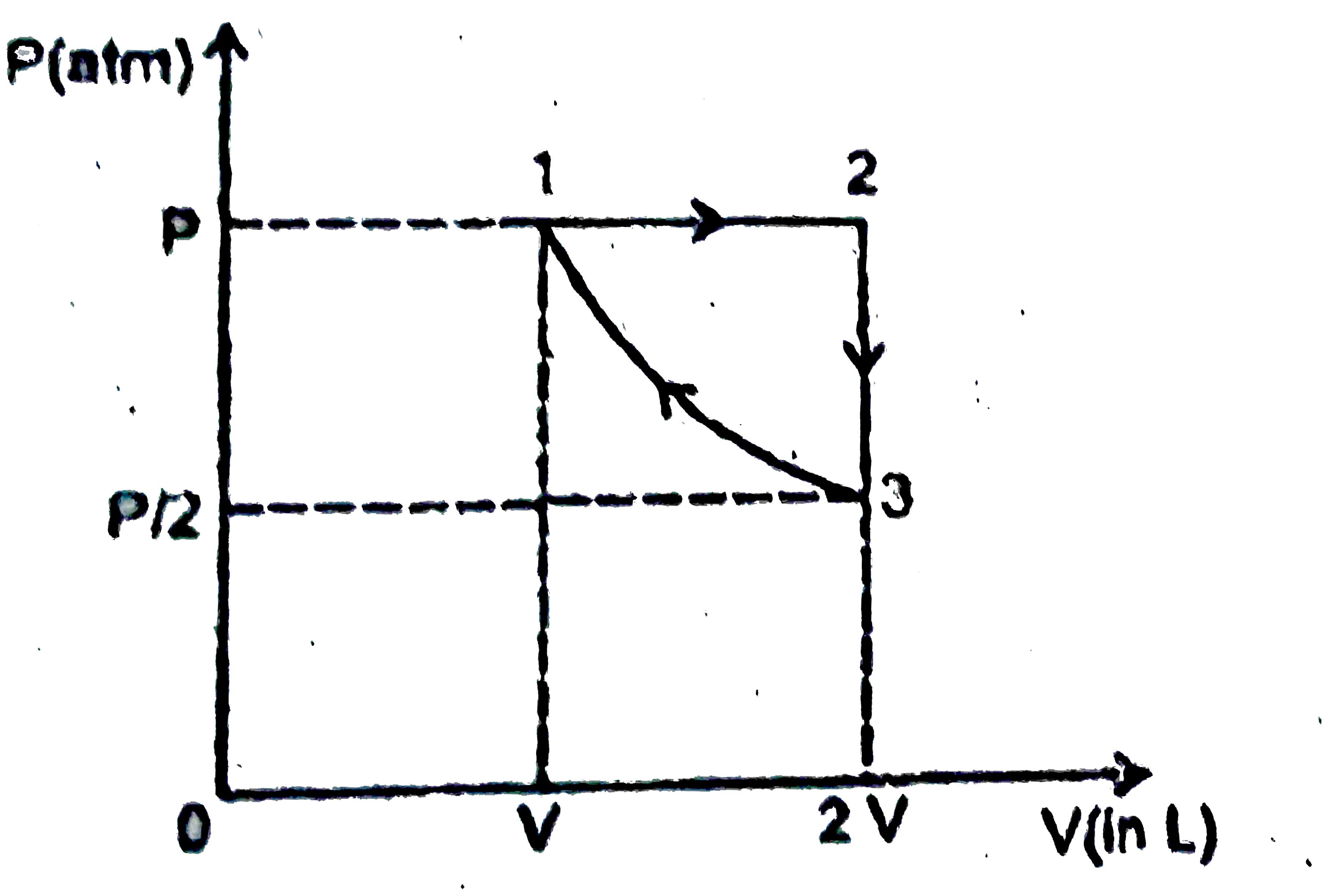
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMIC & THERMOCHEMISTRY-INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(P-Block Elements)
- In a system, a piston caused an external pressure of 1.25 bar giving a...
Text Solution
|
- If 1 mole of an ideal gas expands isothermally at 37^(@)C from 15 litr...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal gas undergo the following process : (a) a reve...
Text Solution
|
- What are the signs of the entropy change ( + or -) in the following: ...
Text Solution
|
- If HA+NaOH rarr NaA+H(2)O" "DeltaH=-12kcal and HB+NaOH rarr NaB+...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction has DeltaH=-33 kJ and DeltaS=-58 J//K. This reaction would ...
Text Solution
|
- In the isothermal reversible compression of 52.0m mol of a perfect gas...
Text Solution
|
- A child bought a balloon which became very small in size the next day....
Text Solution
|
- It the following processes, identify the irreversible process :
Text Solution
|
- If bond energy of H(2),F(2) and HF are in the ratio 2:1:3 and DeltaH(a...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state from (1.0 atm,...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the final pressure of a sample of carbon dioxide that expand...
Text Solution
|
- The heat evolved from the combustion of carbon is used to heat water. ...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for A(g)+B(2)(g) hArr AB(2)(g)" "k(p)=1...
Text Solution
|
- When 1L of NaOH(1M) is mixed with 1L of HCl(1M) the temperature of rea...
Text Solution
|
- 2Fe + 3/2 O2 rarr Fe(2)O(3) " "xkJ//"mole" 2Fe + O(2) rarr 2F...
Text Solution
|
- The species which by definition has zero standard molar enthalpy of fo...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following changes at constant pressure, is work done b...
Text Solution
|
- One gram of an organic liquid X (molecular mass 78) liberates 160 J of...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies are equal to dissociation energies in case of :
Text Solution
|