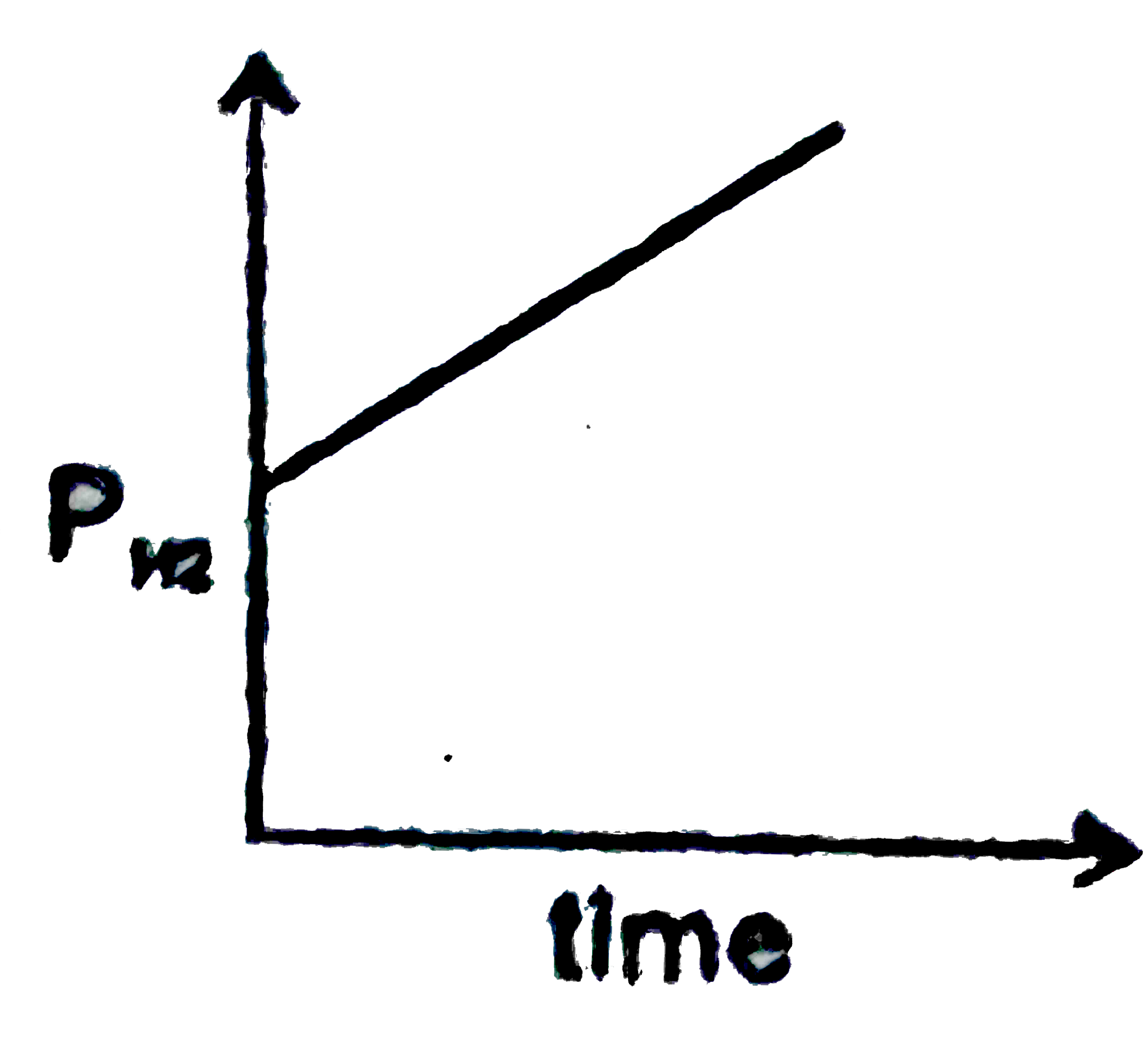
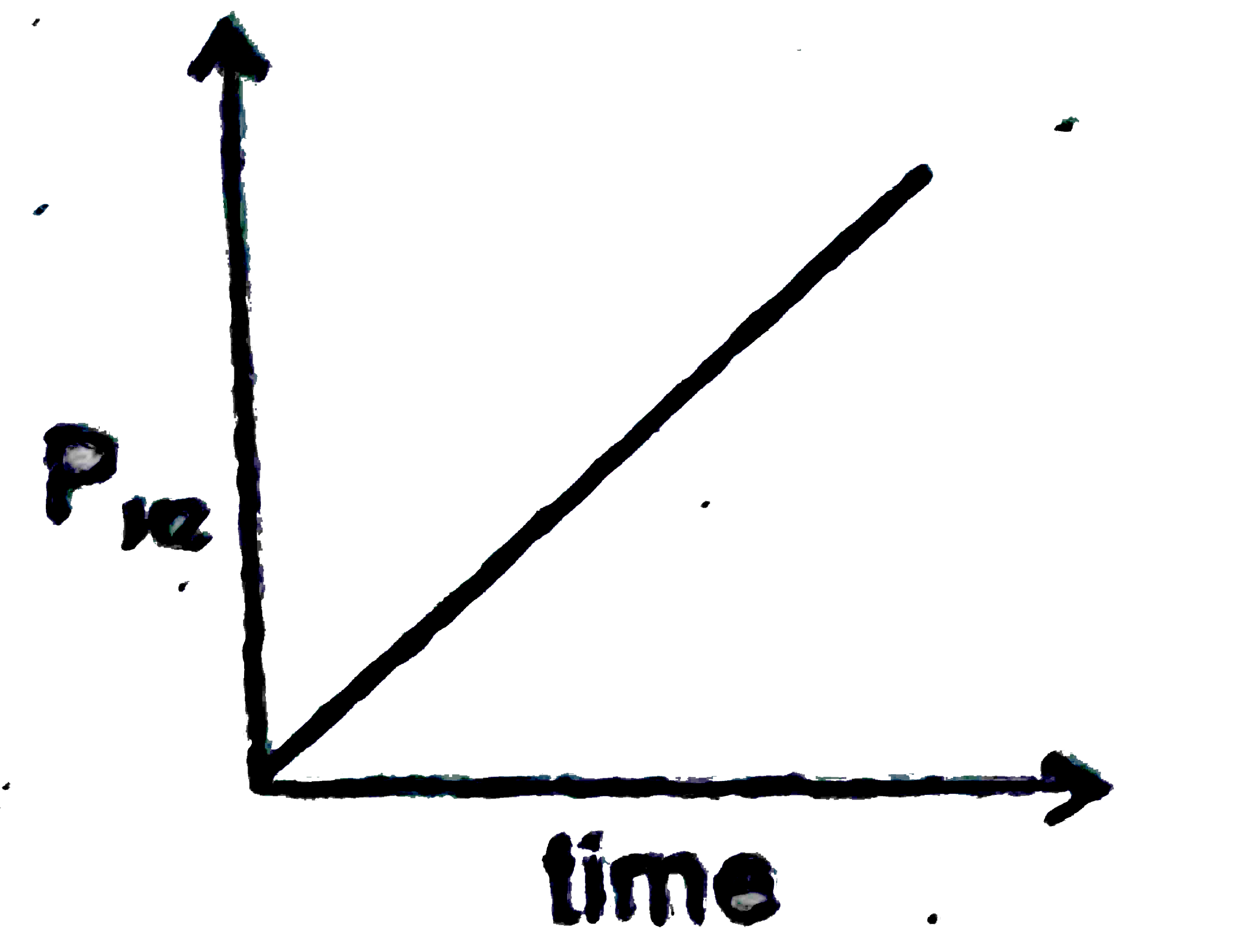
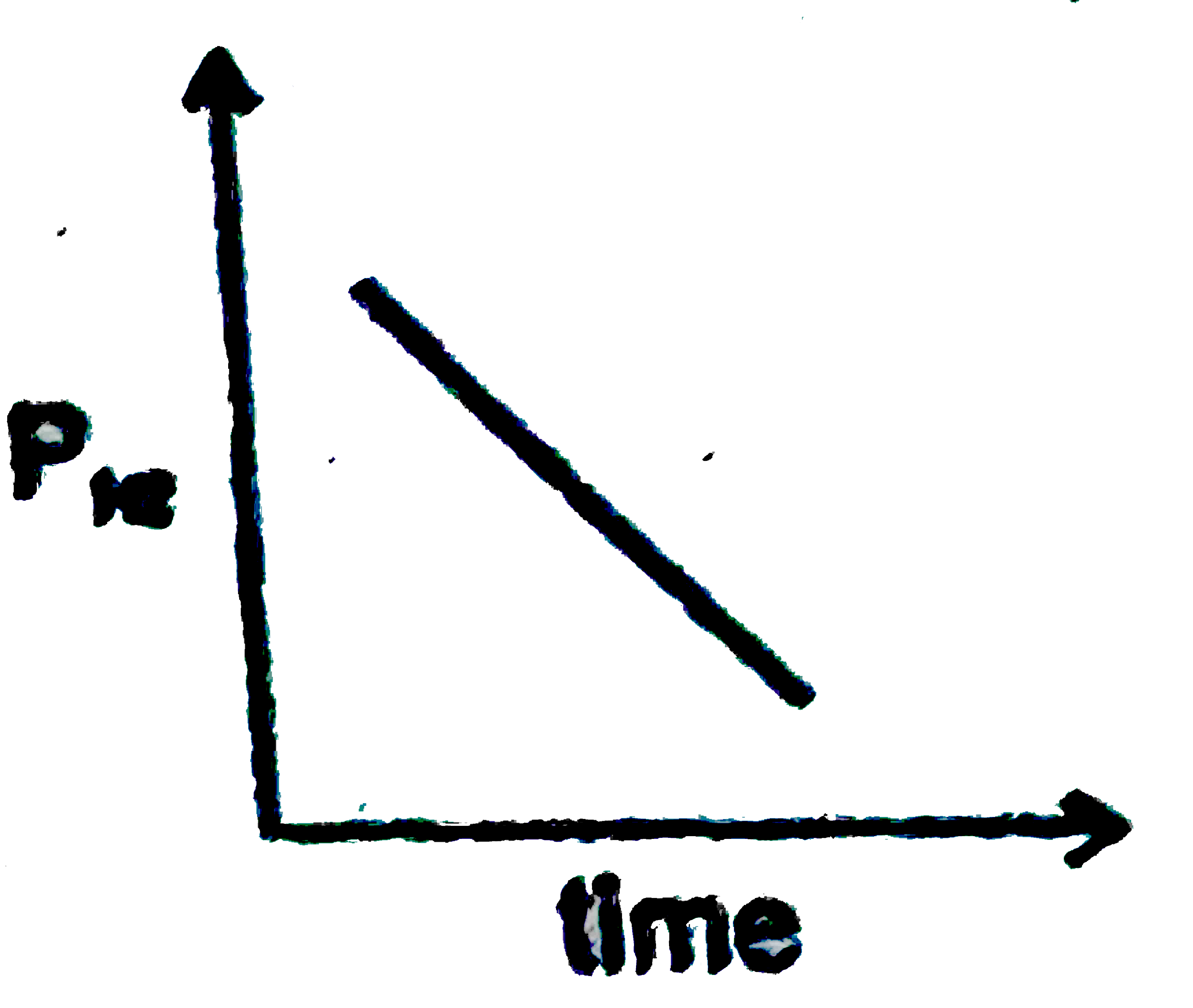A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CHEMICAL KINETICS-PHYSICAL CHEMITRY (CHEMICAL KNIETICS & RADIOACTIVITY)
- For the reaction A rarr products , the graph of the fraction of A rema...
Text Solution
|
- For the zero order reaction A rarr B+C, initial concentration of A is ...
Text Solution
|
- Decomposition of Hl (g) on Gold surface is zero order reaction. Initia...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
Text Solution
|
- The rate expression for reaction A(g) +B(g) rarr C(g) is rate =k[A]^(1...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 2 times that of B, what will be the densi...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 10 times that of B, what will be the dens...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction A(g) + 2B(g) rarr C(g) + D(g) is an elementary process. I...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 11 times that of B, what will be the dens...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 12 times that of B, what will be the dens...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 13 times that of B, what will be the dens...
Text Solution
|
- The graph between concentration (X) of the Product and time of the rea...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of the reaction A rarr 2B is 1.0 xx 10^(-3) mol "lit...
Text Solution
|
- At 227^(@)C , the presence of catalyst causes the activation energy of...
Text Solution
|
- Half life of reaction : H(2)O(2)(aq) rarr H(2)O(l)+(1)/(2)O(2)(g)is in...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 20% complete in 10 min. Calculate (a) the sp...
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 15 times that of B, what will be the dens...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the reaction mechanism: A(2) overset(k(eq))hArr 2A ("fast")...
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction A rarr produce, when from 8.0xx10^(-2) M of A, half life...
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst lowers the enrgy of activation by 25%, temperature at which...
Text Solution
|