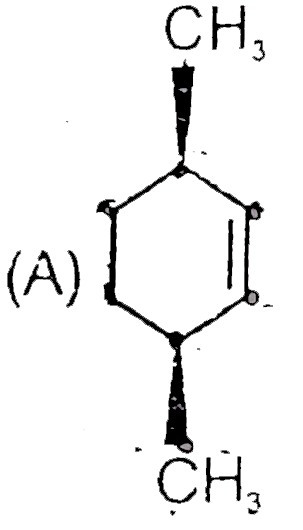
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-TEST PAPERS-Chemistry
- Find A,B and C
Text Solution
|
- is this orientation have non-zero dipole moment : Anti conformation of...
Text Solution
|
- An optically active compound A with molecular formula C(8)H(14) underg...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following rection given secondary alcohol?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds shows geometrical isomerism ?
Text Solution
|
- Which is/are correct for given structres?
Text Solution
|
- Which set of the following compound(s) give benzene on reaction with P...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the radii of two nuclei with mass number 27 and 125 respective...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the radii of two nuclei with mass number 64 and 1 respectively...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reaction is/are incorrect?
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is/are correct:
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following statement/s is/are correct? (1). For isoth...
Text Solution
|
- The freezing point of 0.08 molal aq NaHSO(4) solution is -0.372. Calcu...
Text Solution
|
- Given P(C Cl(4)^(0))=100 torr, P(H(2)O)^(0)=300 torr What will be to...
Text Solution
|
- henry's law constant for CO(2) in water is 2.5xx10^(8) Pa at 298K calc...
Text Solution
|
- 0.1 litre so.ution is made by mixing 4 gram NaOH, 20 millimoles of H(2...
Text Solution
|
- 2 moles of an ideal monoatomic gas undergo a reversible process for wh...
Text Solution
|
- Conductivity of a saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt AB at...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement given below 20 mole of N(2) and 5 mole of He are pr...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas initially in state 1 with pressure P(1)=20 atm...
Text Solution
|