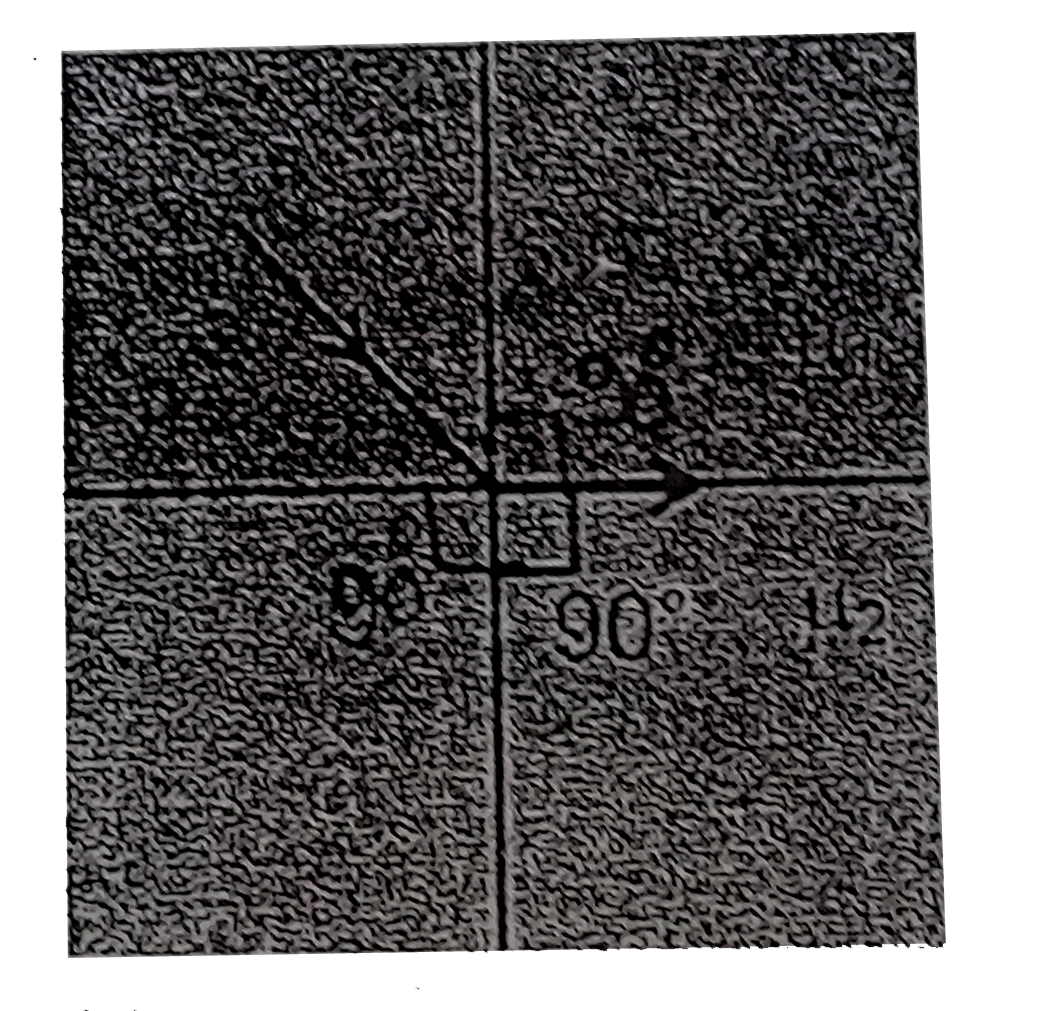
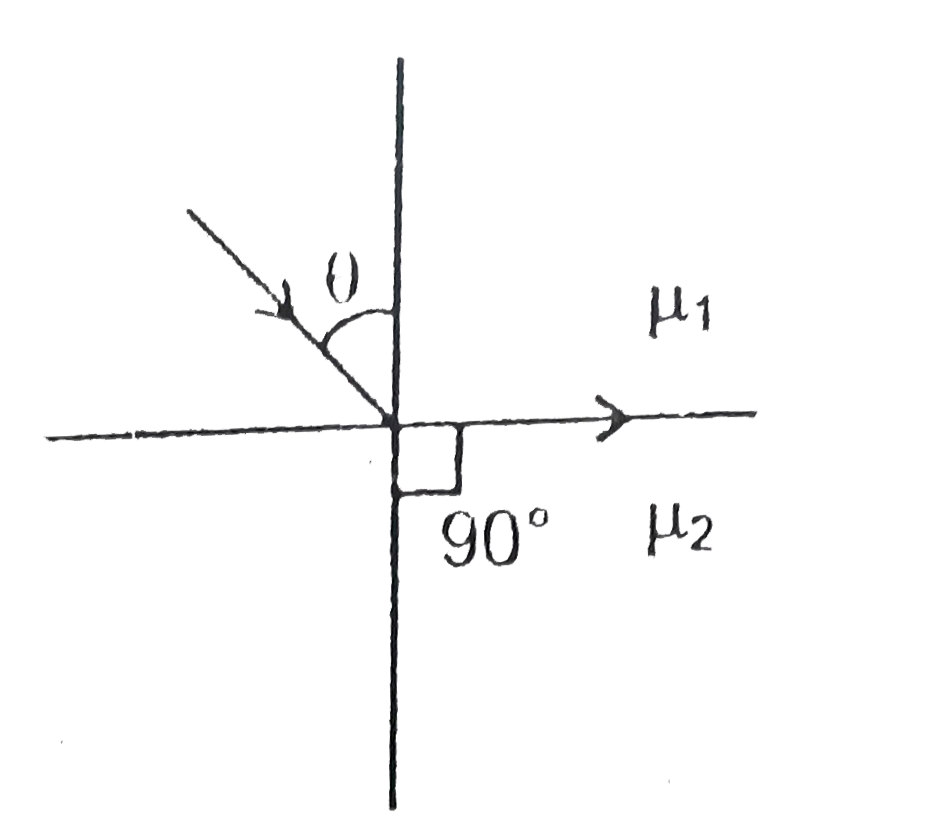
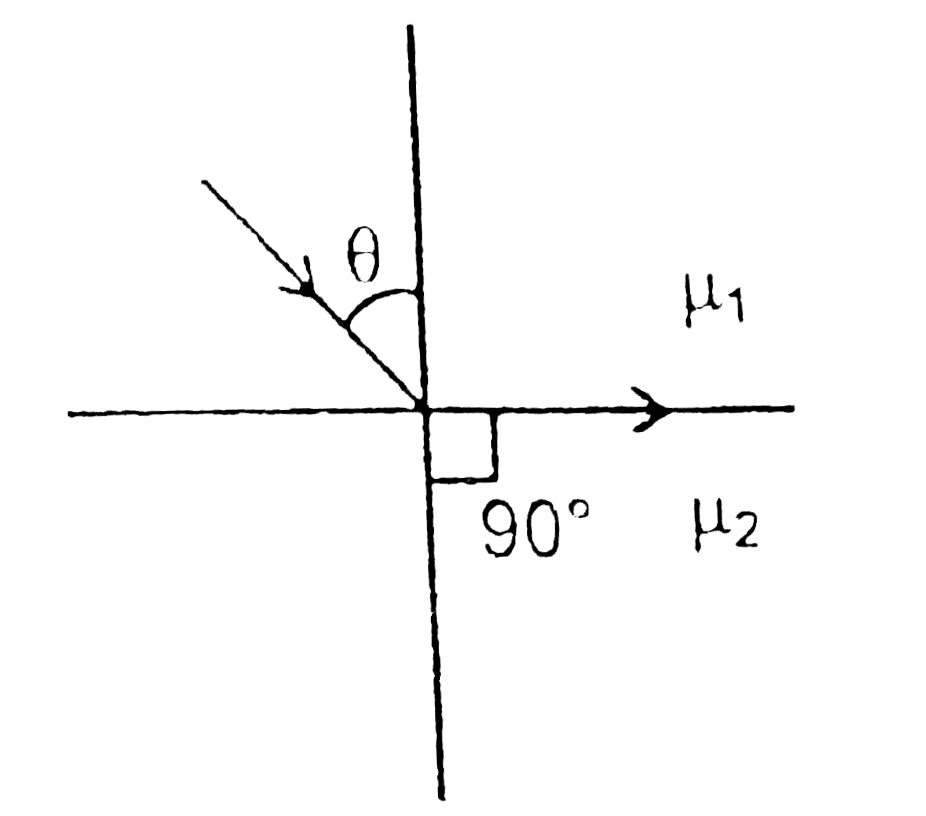
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ray is incident on interface of two media at critical angle as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the critical angle for a glass interface, if a ray of light,...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the critical angle for a glass air interface, if a ray of li...
Text Solution
|
- A ray is incident on interface of two media at critical angle as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- When a light ray is incident normal to the interface between any two m...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when a ray of light is incident normal to the interface b...
Text Solution
|
- When the light ray is incident normal to the interface between any two...
Text Solution
|
- When a ray of monochromatic light is incident obliquely on the interfa...
Text Solution
|