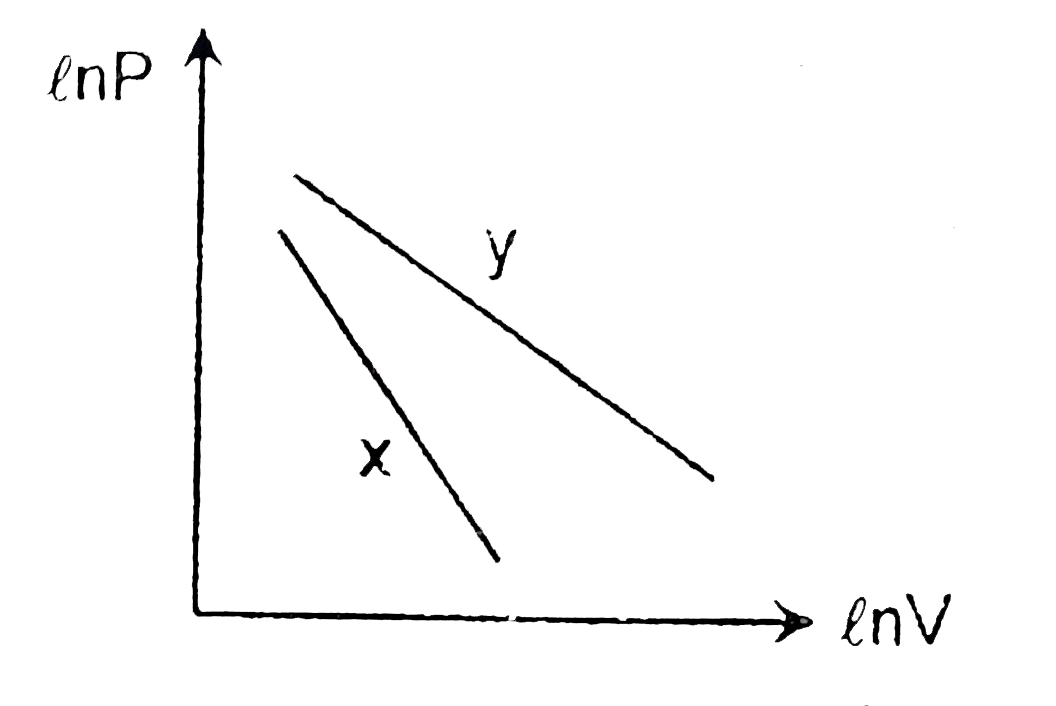
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For two different gases x and y have degree of freedon f(1) and f(2) a...
Text Solution
|
- Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at consta...
Text Solution
|
- The capacities of two conductors are C(1) and C(2) and their respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Three uncharged capacitors of capacities C(1),C(2) and C(3) are connec...
Text Solution
|
- The capacities of two parallel plate capacitors are C(1) and C(2) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors C(1) and C(2) in a circuite are joined as shown. If V(A...
Text Solution
|
- A gaseos mixture consists of equal number of moles of two ideal gases ...
Text Solution
|
- For two different gases x and y have degree of freedon f(1) and f(2) a...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors C(1) and C(2) are connected in a circuit as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|