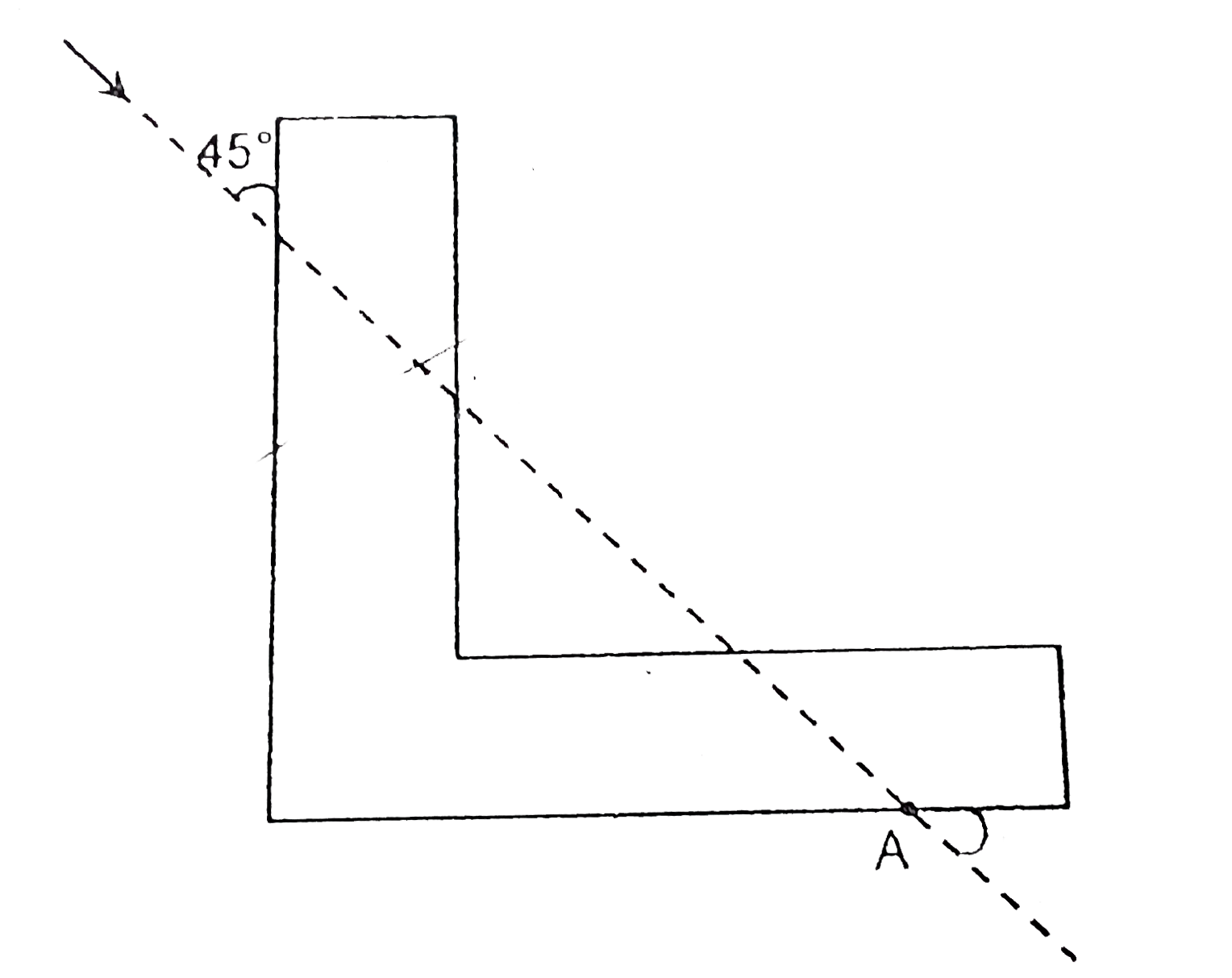
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two identical glass slabs of same thickness are joined to form an L sh...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical glass slabs of same thickness are joined to form an L sh...
Text Solution
|
- A student performs an experiment with glass slab to trace the path of ...
Text Solution
|
- A rays of light is incident on a thick slab of glass of thickness t a...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident at 45^(@) on a glass slab. The slab is 3cm thi...
Text Solution
|
- When rays of light are incident on a glass slab, then the incident ray...
Text Solution
|
- When rays of light are incident on a glass slab, then the incident ray...
Text Solution
|
- When light passes through glass slab, the incident ray and emergent ra...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes throught a plane glass slab of thickness t and r...
Text Solution
|