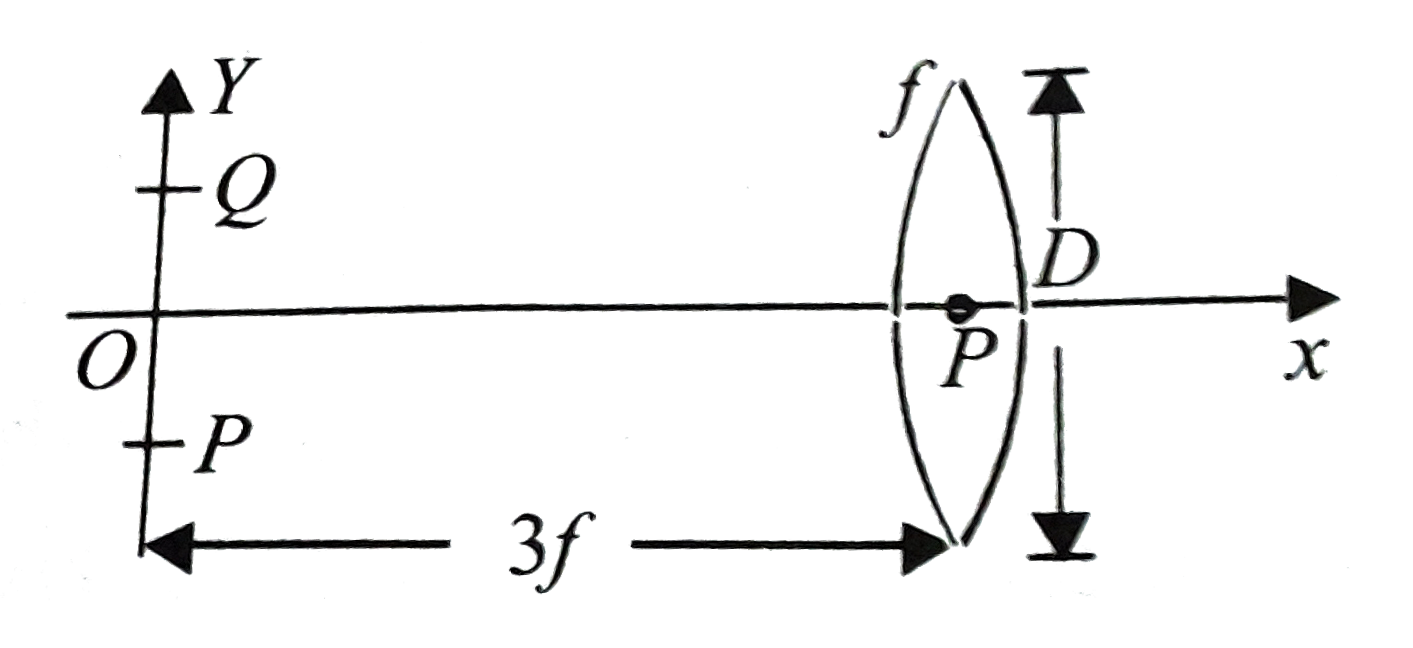
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- A particle executes a simple harmonic motion of amplitude 1.0 cm along...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- A thin linear object of size 1mm is kept along the principal axis of a...
Text Solution
|
- Two point objects A and B are kept on the principal axis of a convex l...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light rays parallel to the principal axis (the x axis) a...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length f and a plane mirror are y distance apar...
Text Solution
|