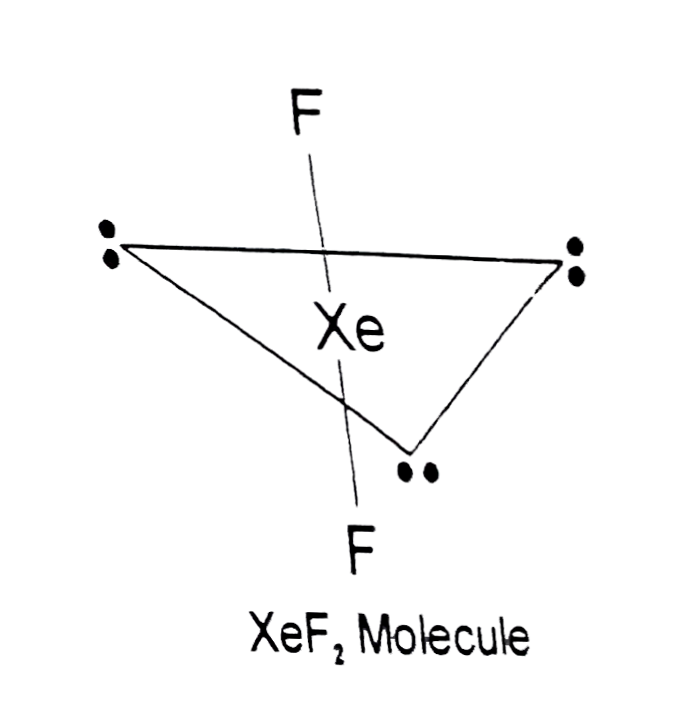Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
P BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ALP PART 1 SUBJECTIVE|3 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ALP PART II AIEEE OBJECTIVE|1 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ALP EX #3 OBJECTIVE|1 VideosNUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise STAGE-II|1 VideosP-BLOCK ELEMENT (BORON AND CARBON FAMILY)
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART - III : OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS) STAGE - V (INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD (IChO)) Problem 3|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-P BLOCK ELEMENTS-ALP PART 1 OBJECTIVE
- Bi(V) and Sb(V) which may be a stronger oxidizing agent and why ?
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical reaction equations : (i) P(4(s)) + N...
Text Solution
|
- Account for the following : (i) NH(3) is a stronger base than PH(3) ...
Text Solution
|
- Though nitrogen exhibits +5 oxidation state , it does not form pentaha...
Text Solution
|
- Why does NO(2) dimerise ?
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of white phosphorus and red phosphorus. Which one...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical reaction equations : (i) l(2)+HNO(3...
Text Solution
|
- Give reason for : (i) SF6 is kinetically an inert substance. (ii...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Explain the following : (i) NF3 is an exothermic compound where...
Text Solution
|
- State true or Fasle: H(2)S is acidic thanH(2)O.
Text Solution
|
- Why is BiH(3) the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following facts giving appropriate reason in each case : ...
Text Solution
|
- (A) Complete the following chemical equations : (i) Cu+HNO(3) (dilut...
Text Solution
|
- Covalency and oxidation number of nitrogen in N(2) O(5) is respectivel...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) PCl5 is heated ? (ii) H3PO3 is heated ? Wr...
Text Solution
|
- Oxidation states in nitrogen can range from
Text Solution
|
- Dinitrogen gas is evolved when sodium nitrite is heated below 500 degr...
Text Solution
|
- Dinitrogen cannot be librated by :
Text Solution
|
- Dinitrogen can be purified from the impurities of NO and NH(3) by pass...
Text Solution
|
- Ammonia and red hot CuO react to produce :
Text Solution
|