Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-TEST SERIES-PHYSICS
- Consider a long solenoid of radius R which has n turns per unit length...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with mass m and charge q moving with a velocity v, enters a...
Text Solution
|
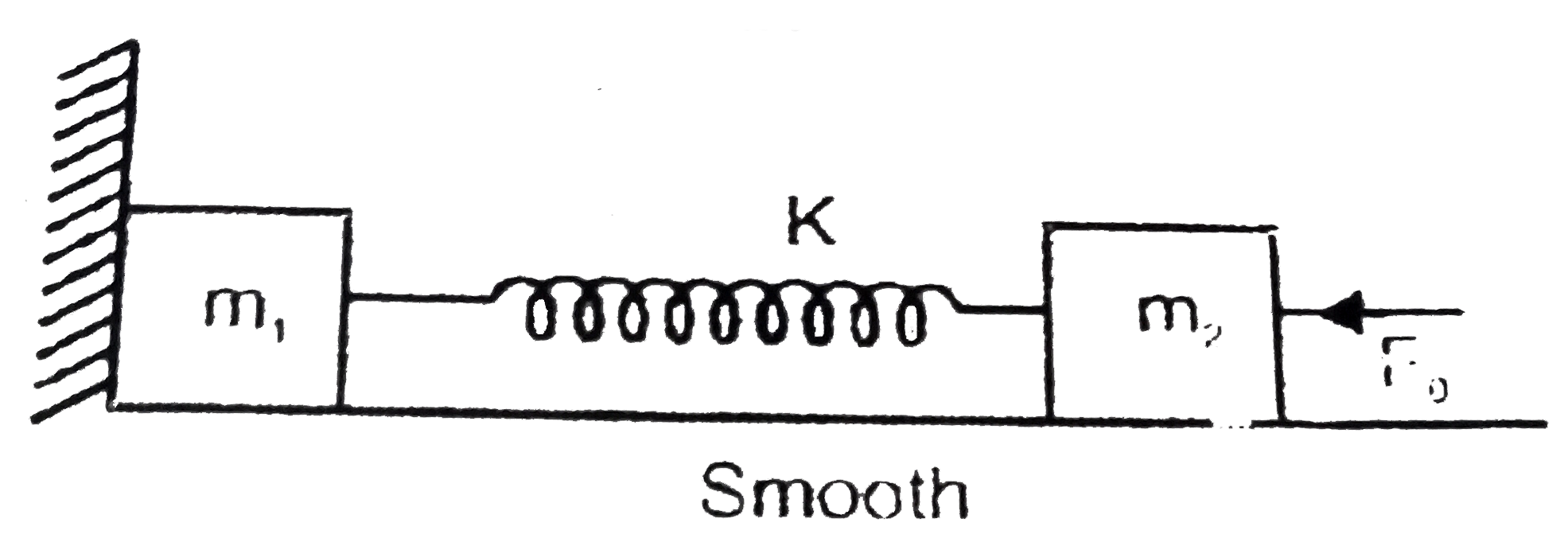
- Given system is in equilibrium. All surfaces are smooth. Spring is ide...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of side 10sqrt(10) cm is connected to a smooth and uni...
Text Solution
|
- A masonary column of density rho has height h top cross sectional area...
Text Solution
|
- In a carburator of an engine, aire is drawn from atmosphere through se...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l and total charge 'q' which is uniformly distributed ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field vecB=0.25hatkT exists in a circular region of...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m=2kg is at rest point P of the stationary wedge...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of different masses projected from a tower with same spe...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles with radius 2r and 3r come in contact. Their common ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane. The co...
Text Solution
|
- P is the centre of mass of four points masses A, B, C and D which are ...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment the ratio of intensitities of bright...
Text Solution
|
- A Young's double slit experiment is performed with white light.
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle is tied to the end A of a string of the length1.6 m. ...
Text Solution
|
- An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain c...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, white light is used. The separation...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder rests in a supporting carriage as shown. The side AB of car...
Text Solution
|