A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 3 PART - I|7 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 3 PART - IV|9 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 2 PART - II|6 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 92 illustration|2 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|43 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY-Exercise- 2 PART - III
- The wires A and B shown in Fig. are made of the same material and have...
Text Solution
|
- When a tensile or compressive load 'P' is applied to rod or cable, its...
Text Solution
|
- When a tensile or compressive load 'P' is applied to rod or cable, its...
Text Solution
|
- When a tensile or compressive load 'P' is applied to rod or cable, its...
Text Solution
|
- Viscosity is the property of fluid by virtue of which fluid offers res...
Text Solution
|
- Viscosity is the property of fluid by virtue of which fluid offers res...
Text Solution
|
- Viscosity is the property of fluid by virtue of which fluid offers res...
Text Solution
|
- Viscosity is the property of fluid by virtue of which fluid offers res...
Text Solution
|
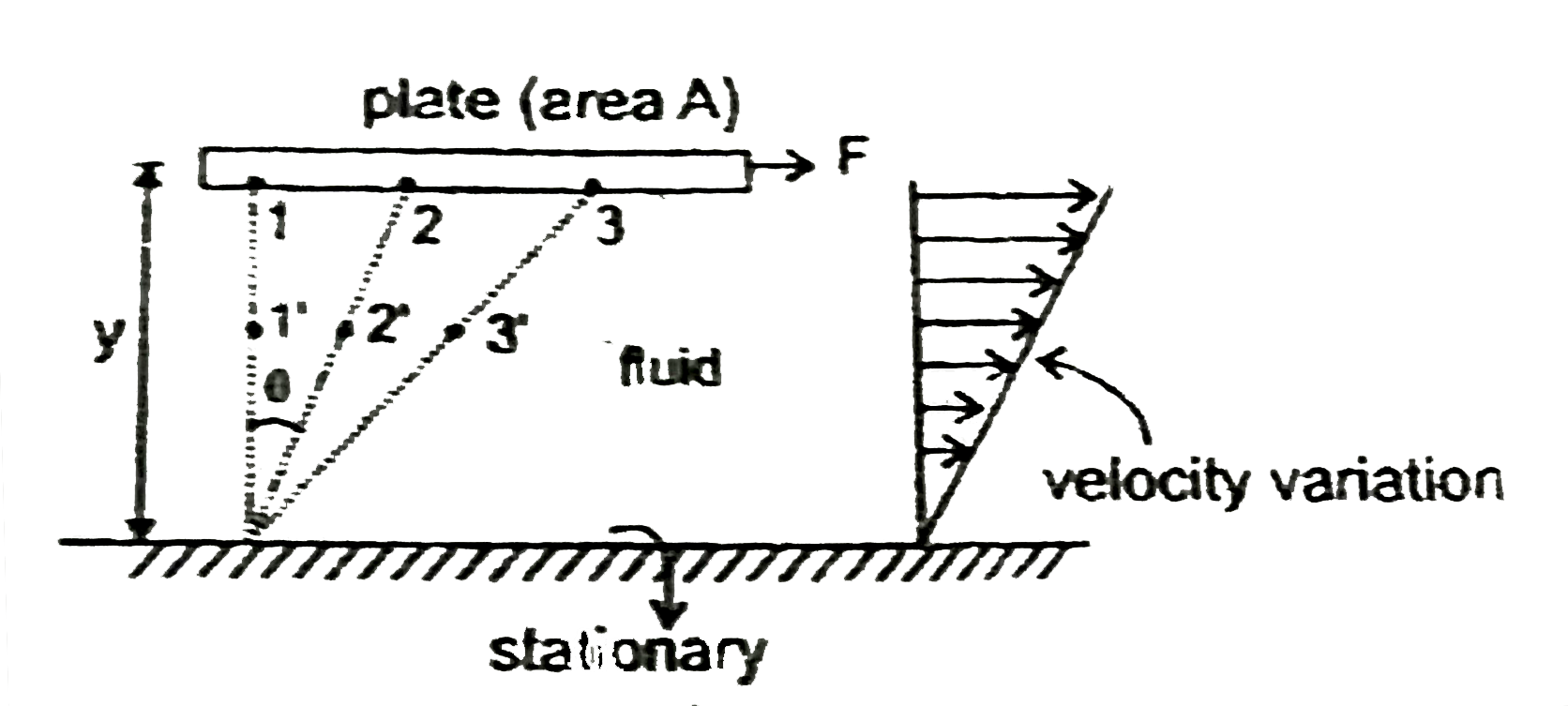
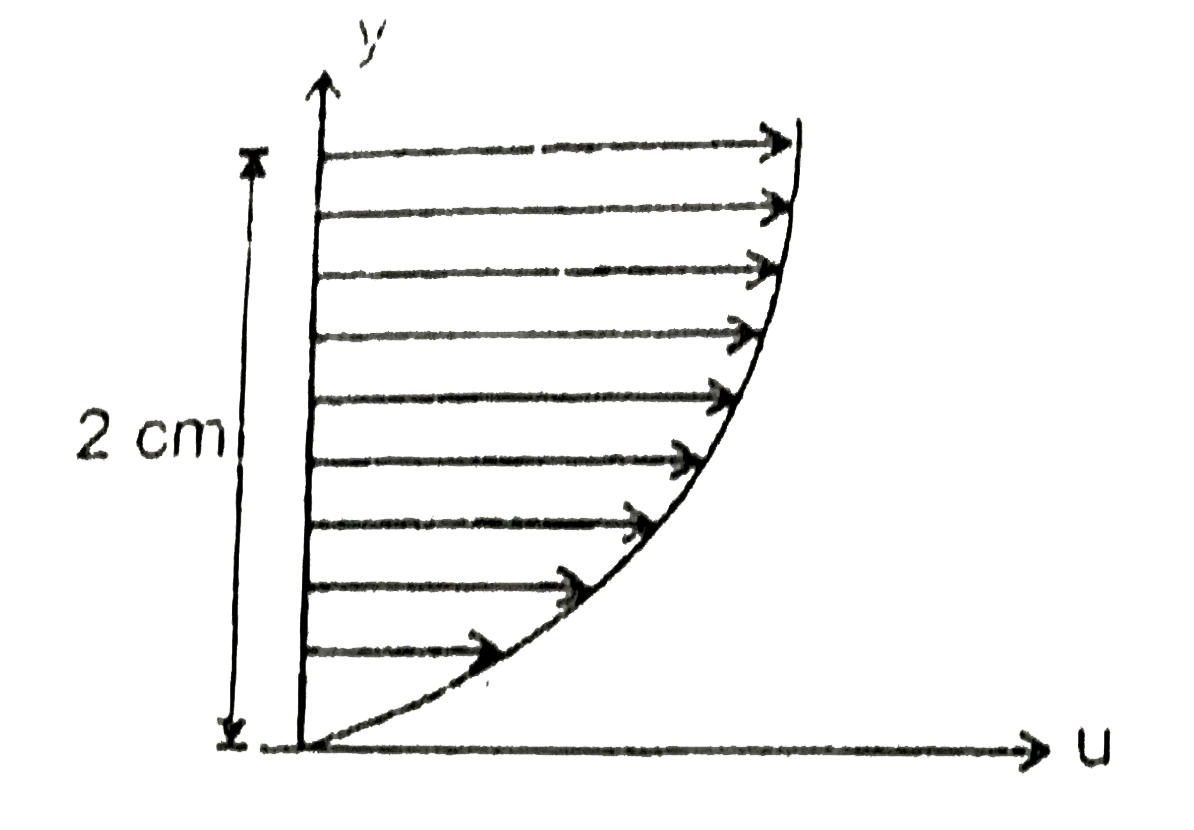 For the same force of `2N` and the speed of the plate `2 m//sec`, and area of plate is 1 and viscousity is .001, the constant `C_(1), C_(2)` & `C_(3)` are
For the same force of `2N` and the speed of the plate `2 m//sec`, and area of plate is 1 and viscousity is .001, the constant `C_(1), C_(2)` & `C_(3)` are