To determine which of the given reactions produce the same product, we will analyze each option step by step.
### Step 1: Analyze Option A
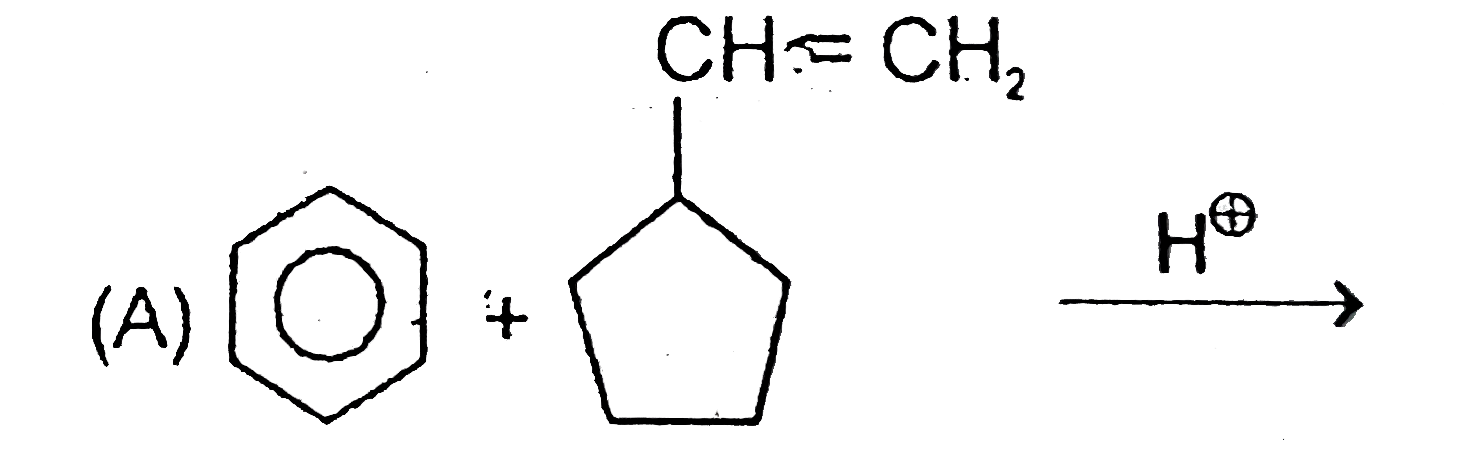
1. **Reactants**: Benzene ring and a 5-membered ring with a CH=CH2 group.
2. **Protonation**: The alkene (CH=CH2) gets protonated, forming a carbocation on the adjacent carbon.
3. **Carbocation Stability**: The initial carbocation formed is a 1-degree carbocation, which is less stable than a 2-degree carbocation. Therefore, rearrangement occurs to form a more stable 2-degree carbocation.
4. **Ring Expansion**: The 5-membered ring expands to a 6-membered ring due to the rearrangement.
5. **Final Product**: The benzene ring attacks the carbocation, leading to the formation of a substituted benzene product.
### Step 2: Analyze Option B
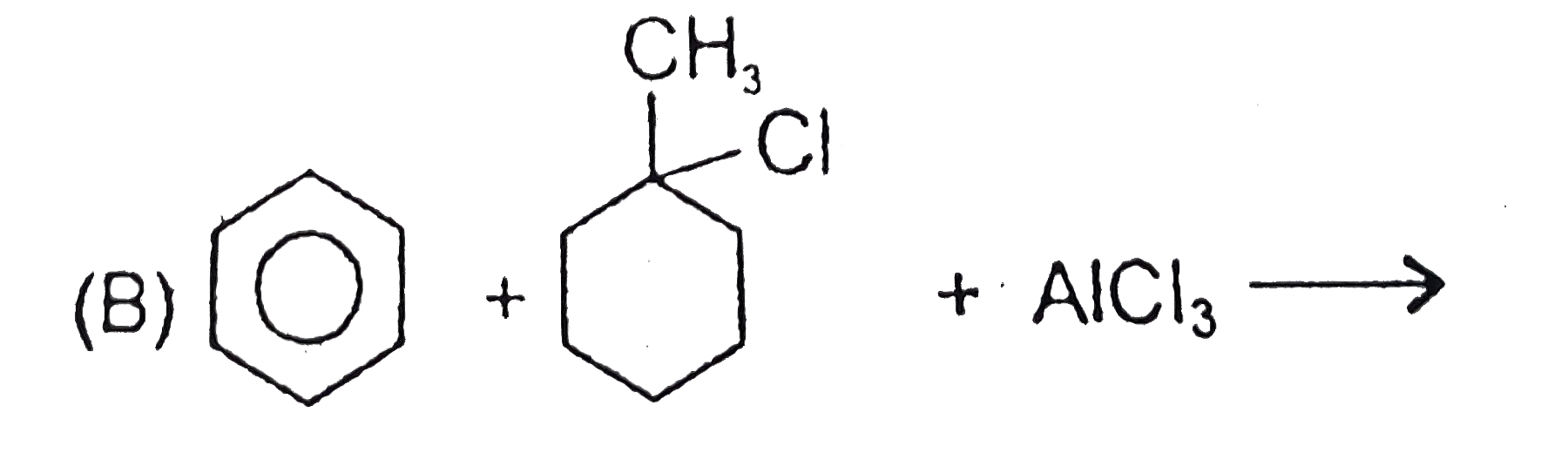
1. **Reactants**: Benzene ring with a CH3 group and Cl, reacting with AlCl3.
2. **Carbocation Formation**: The Lewis acid (AlCl3) abstracts Cl-, forming a carbocation on the carbon attached to the CH3.
3. **Benzene Attack**: The benzene ring acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming a similar substituted benzene product as in Option A.
### Step 3: Analyze Option C
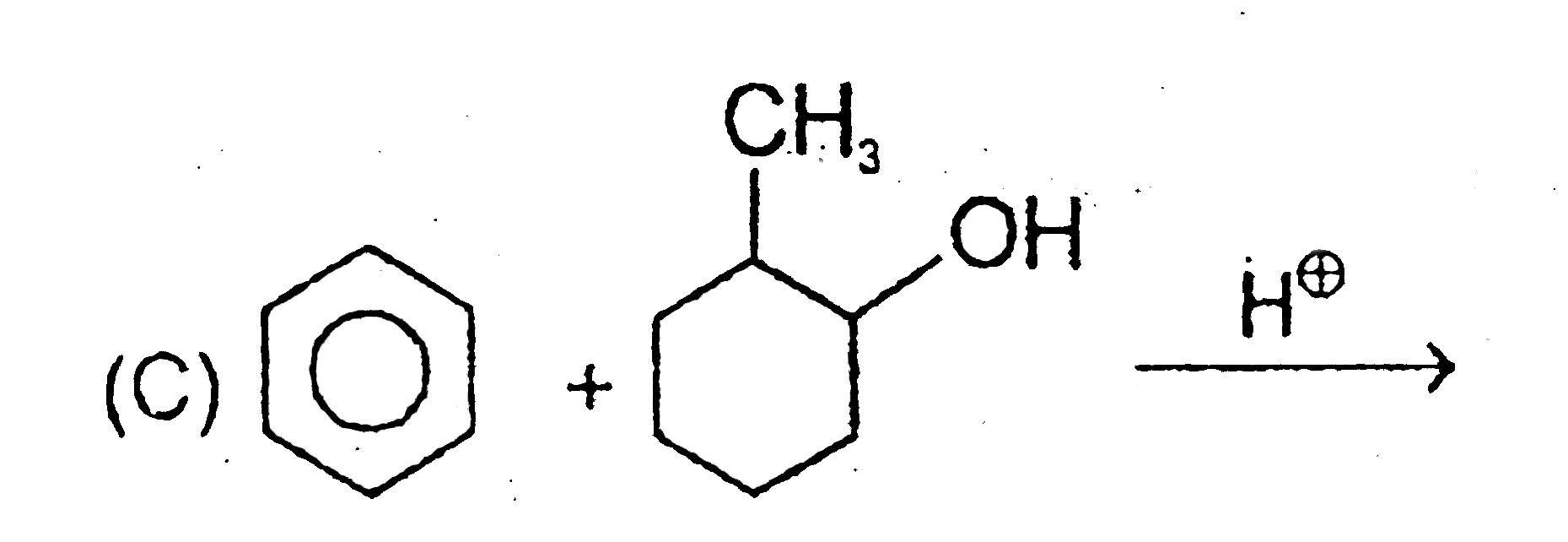
1. **Reactants**: Cyclohexanol (with a methyl group) and H+.
2. **Protonation**: The OH group is protonated to form OH2+, which leaves, forming a carbocation.
3. **Carbocation Rearrangement**: A hydrogen migration occurs, leading to a more stable carbocation.
4. **Final Product**: The benzene ring attacks the carbocation, resulting in a product similar to that of Options A and B.
### Step 4: Analyze Option D
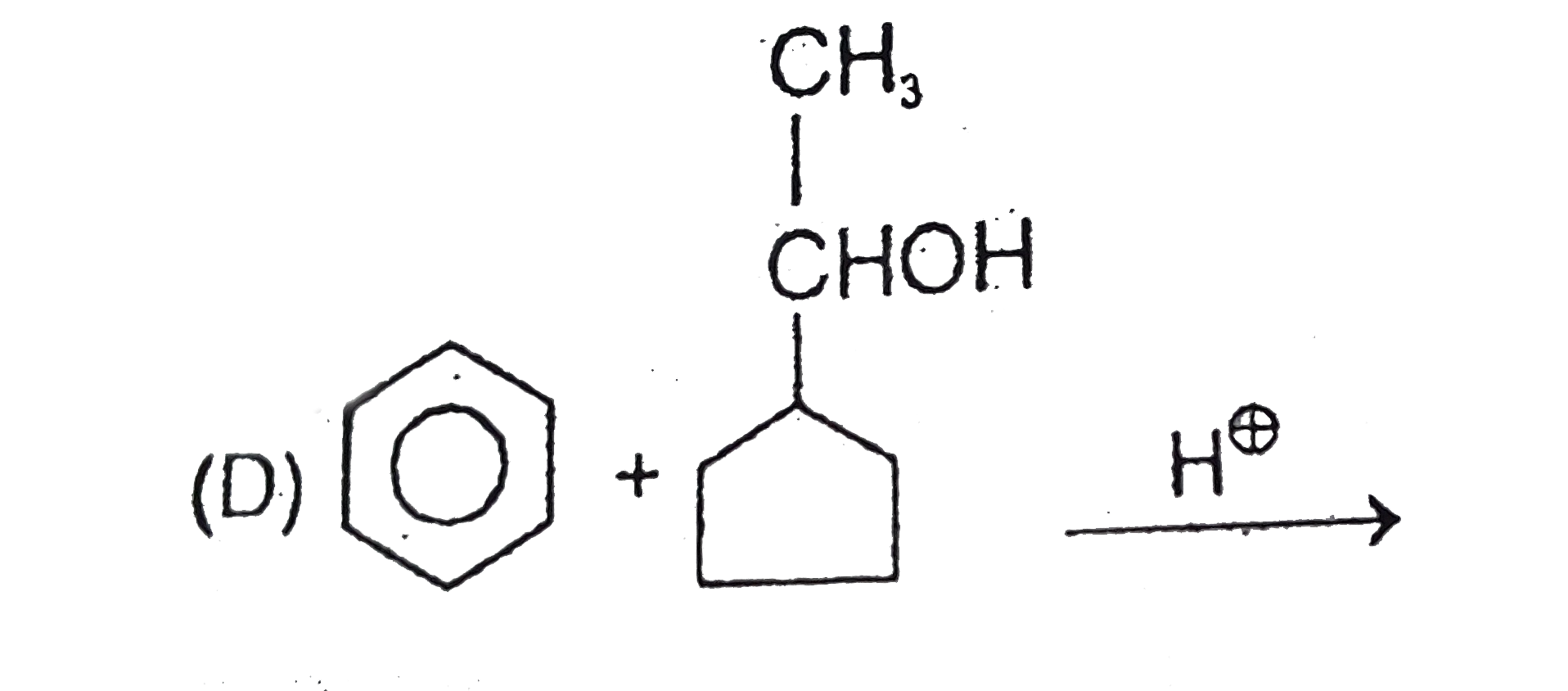
1. **Reactants**: A 5-membered ring with CH, OH, and CH3, reacting with H+.
2. **Protonation**: The OH group is protonated to form OH2+, which leaves, creating a carbocation.
3. **Ring Expansion**: The 5-membered ring expands, leading to a carbocation.
4. **Final Product**: The benzene ring attacks the carbocation, yielding a product that matches those from Options A, B, and C.
### Conclusion
After analyzing all four options, we find that all of them lead to the formation of the same final product: a substituted benzene compound. Therefore, the answer is that all options (A, B, C, and D) give the same product.
### Final Answer
**All options (A, B, C, and D) give the same product.**
---