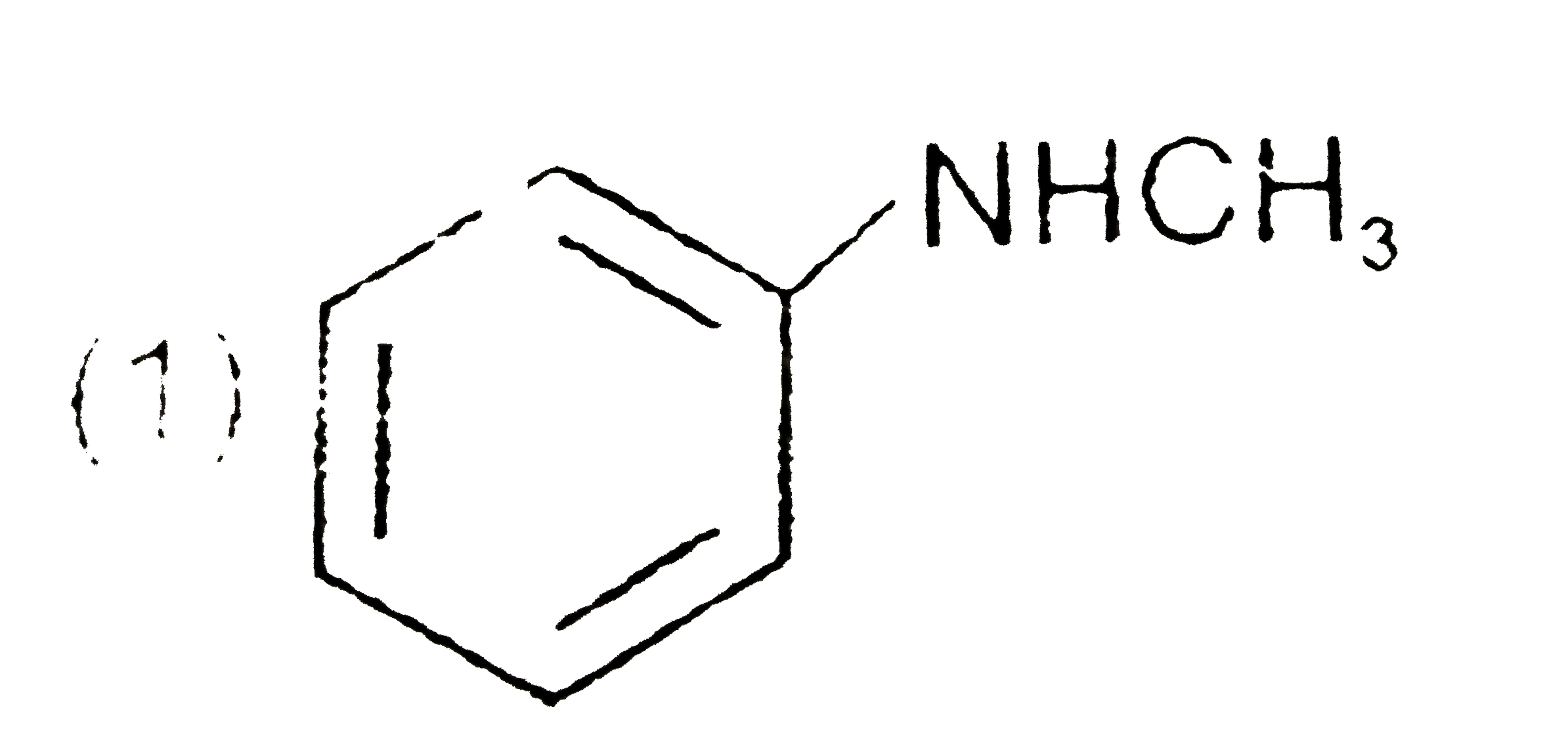
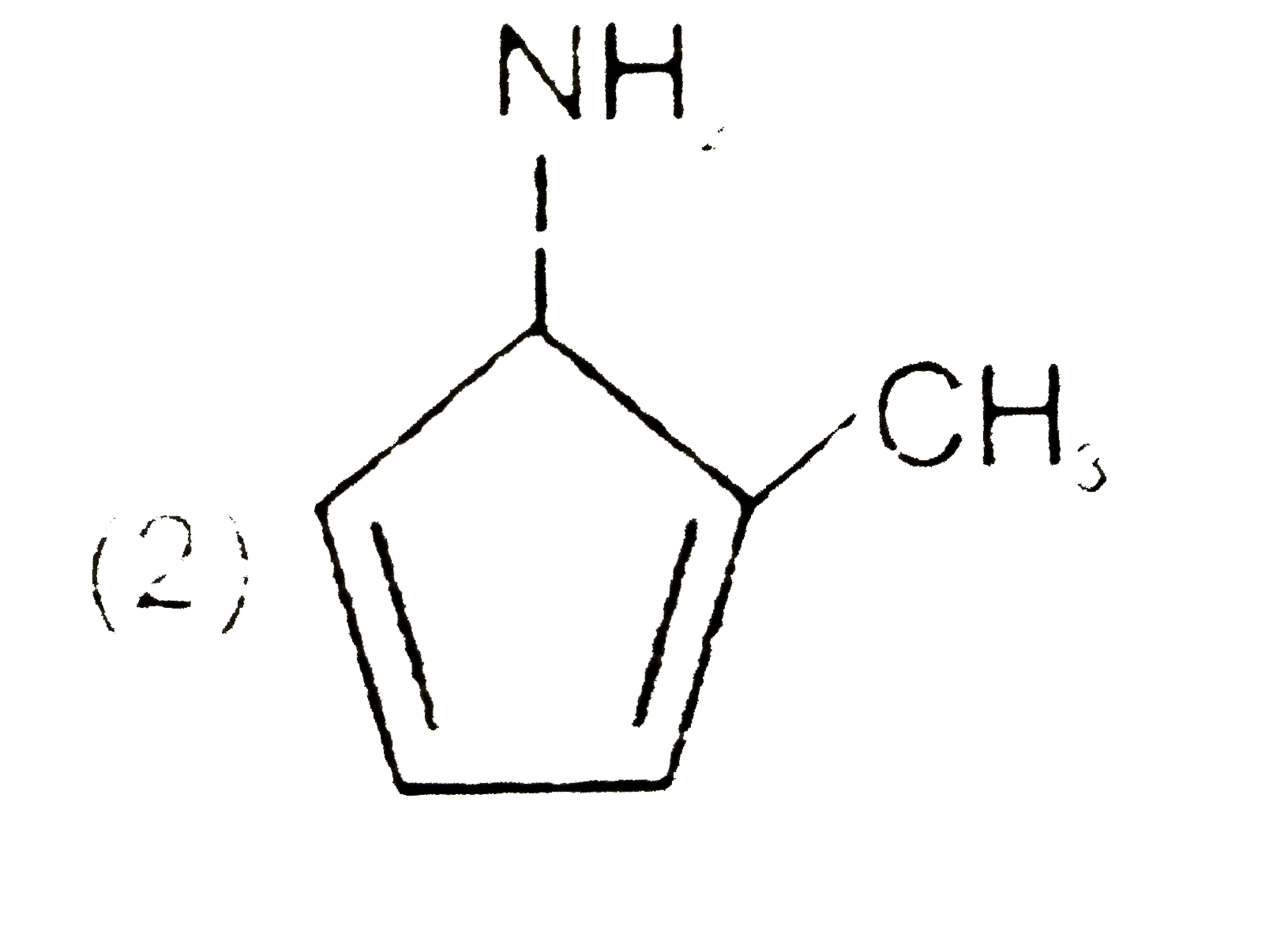
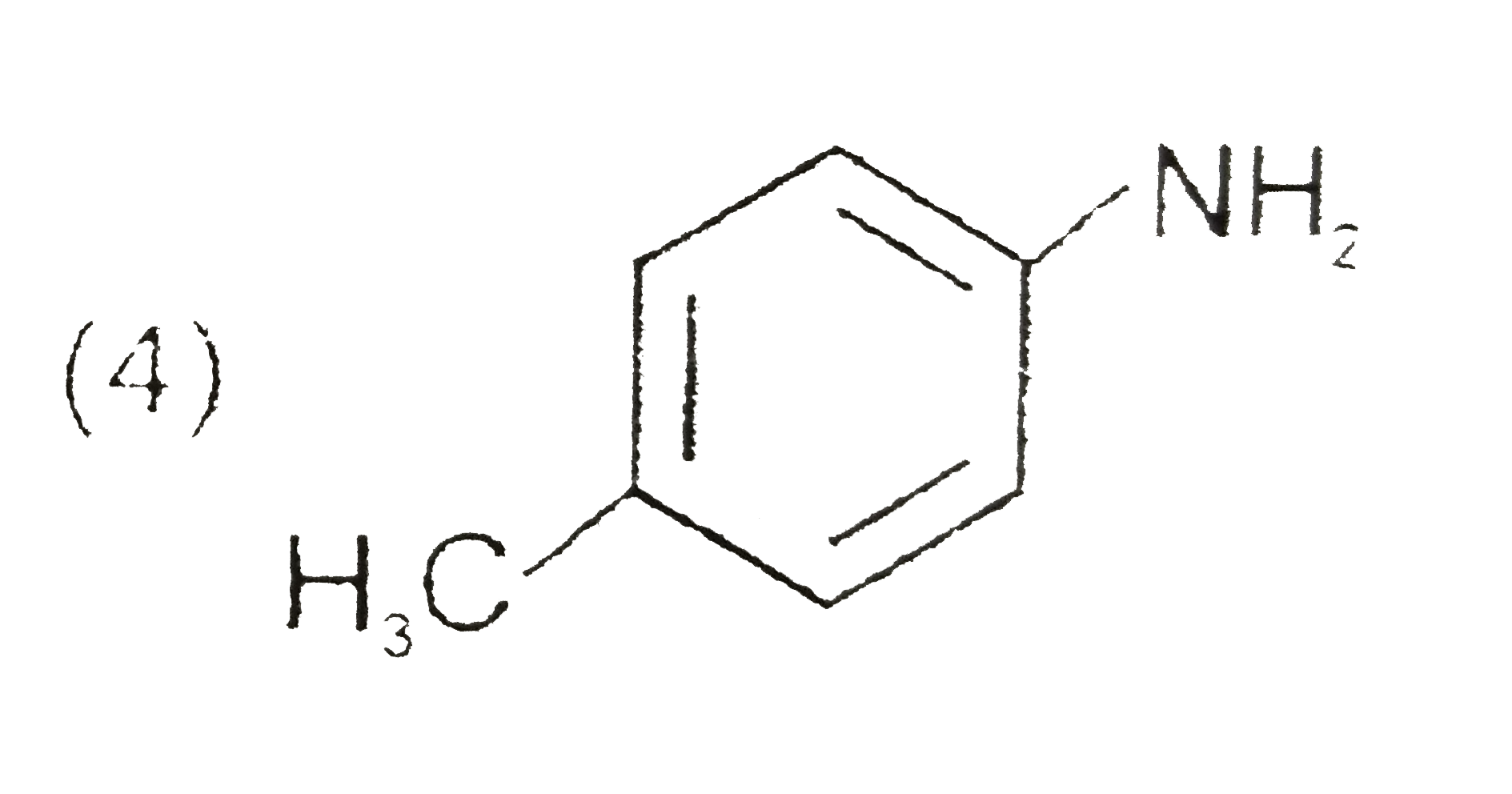
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The compound X(C(7)H(9)N) reacts with benzensulfonyl chloride to give ...
Text Solution
|
- The aqueous solution of a nitrogen and chlorine containing organic com...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (X) having the molecular formula C(3)H(9)N is insoluble in ...
Text Solution
|
- Compound A (C(3)H(9)N) reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to form ...
Text Solution
|
- A compound Z with molecular formula C(3)H(9)N reacts with C(6)H(5)SO(2...
Text Solution
|
- एक ऐमीन (C(3)H(9)N),C(6)H(5)SO(2)Cl से क्रिया करके एक यौगिक बनाती है ज...
Text Solution
|
- C(5)H(13)N reacts with HNO(2) to give an optically active alcohol The ...
Text Solution
|
- A compound Z with molecular formula C(3)H(9)N reacts with C(6)H(5)SO(2...
Text Solution
|
- A(C(3)H(9)N) reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride to give a solid ins...
Text Solution
|