A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-RANK BOOSTER-All Questions
- NH4COONH2 (s) hArr 2NH3(g)+CO(2)(g) If equilibrium pressure is 4 atm...
Text Solution
|
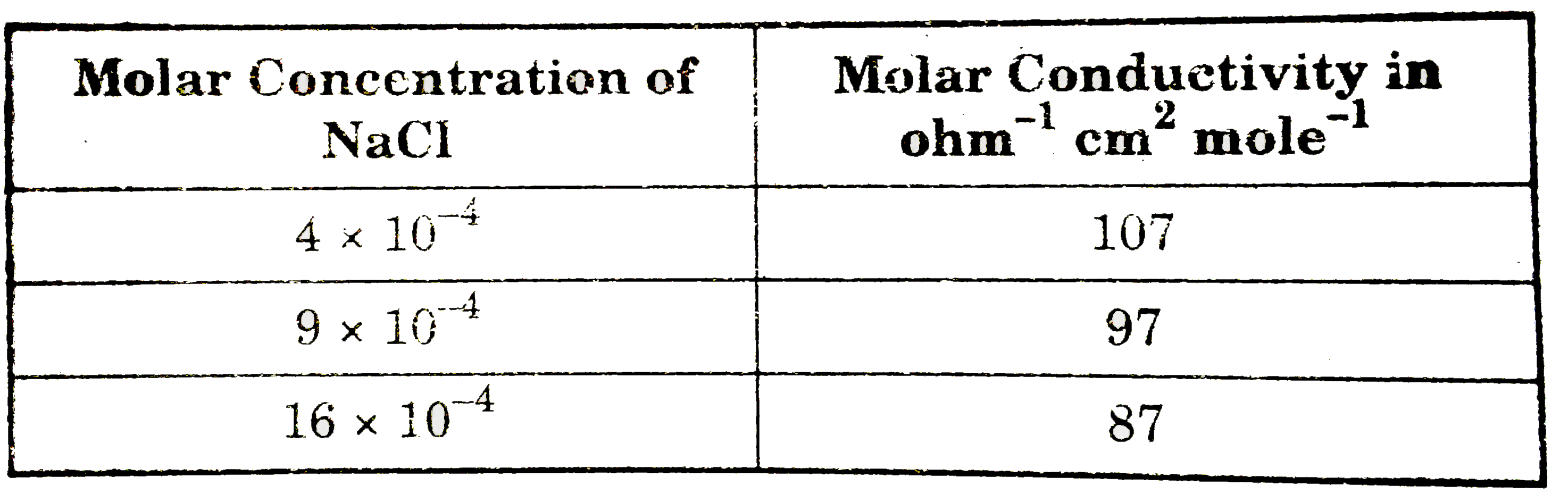
- The molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- The molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- The conductance (G) is
Text Solution
|
- Vitamin C is known to contain 5.16×10^24 Oxygen atoms. Calculate the n...
Text Solution
|
- Vitamin C is known to contain 6.45×10^24 Oxygen atoms. Calculate the n...
Text Solution
|
- Vitamin C is known to contain 3.87×10^24 Oxygen atoms. Calculate the n...
Text Solution
|
- Given : E(cu^(+2)//cu)^0=0.34 V E(Cl2//Cl^(-))^0=1.36 V E(Br2//Br^...
Text Solution
|
- Vitamin C is known to contain 5.16×10^24 hydrogen atoms. Calculate the...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column : {:("Column-I","Column-II"),((A)"Molten" PbCl2 "us...
Text Solution
|
- The standard reduction potential of Ag^(+)//Ag electrode at 298 K is 0...
Text Solution
|
- Vitamin C is known to contain 1.29×10^24 Oxygen atoms. Calculate the n...
Text Solution
|
- 100 ml, 0.05 M CuSO4 solution is electrolysed by using current of 0.96...
Text Solution
|
- Find the no. of moles of O2 present in 1.20x10^23 molecules of oxygen ...
Text Solution
|
- The E(Cell)^(@)=1.18V for Zn(s)||Zn^(+2)(1M)||Cu^(+2)(1M)|Cu(s). The v...
Text Solution
|
- In the acid base titration [H3PO4(0.1 M)+NaOH(0.1 M)] e.m.f of the sol...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of a cell corresponding to the reaction : Zn((s)) + 2H((aq))^(...
Text Solution
|
- A fuell cell uses CH(4)(g) and forms CO(3)^(2-) at the anode. It is us...
Text Solution
|
- For the cells in opposition, Zn(s) | ZnCl(2)(sol).|AgCl(s)|Ag|AgCl(s...
Text Solution
|
- The conductivity ofa solution may be taken to be directly proportional...
Text Solution
|