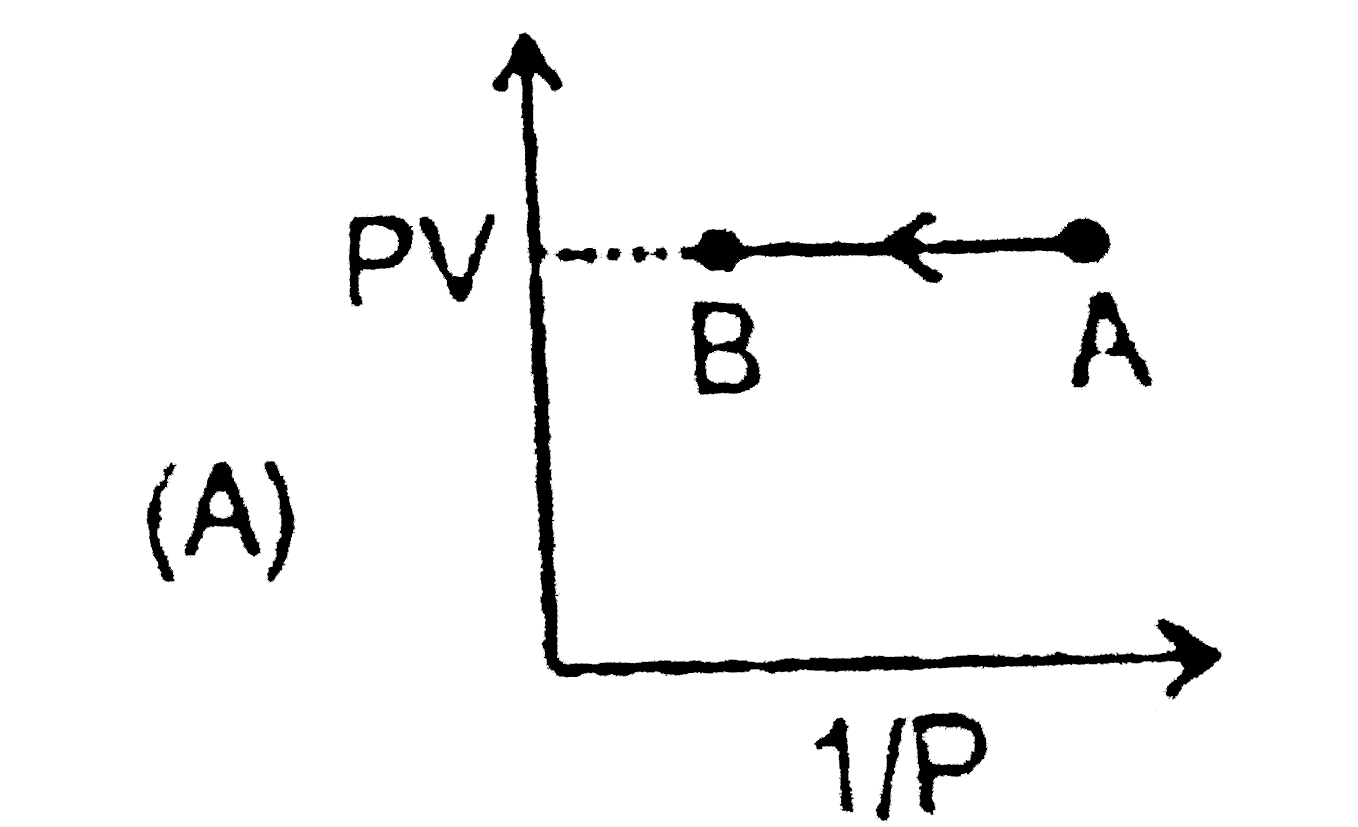
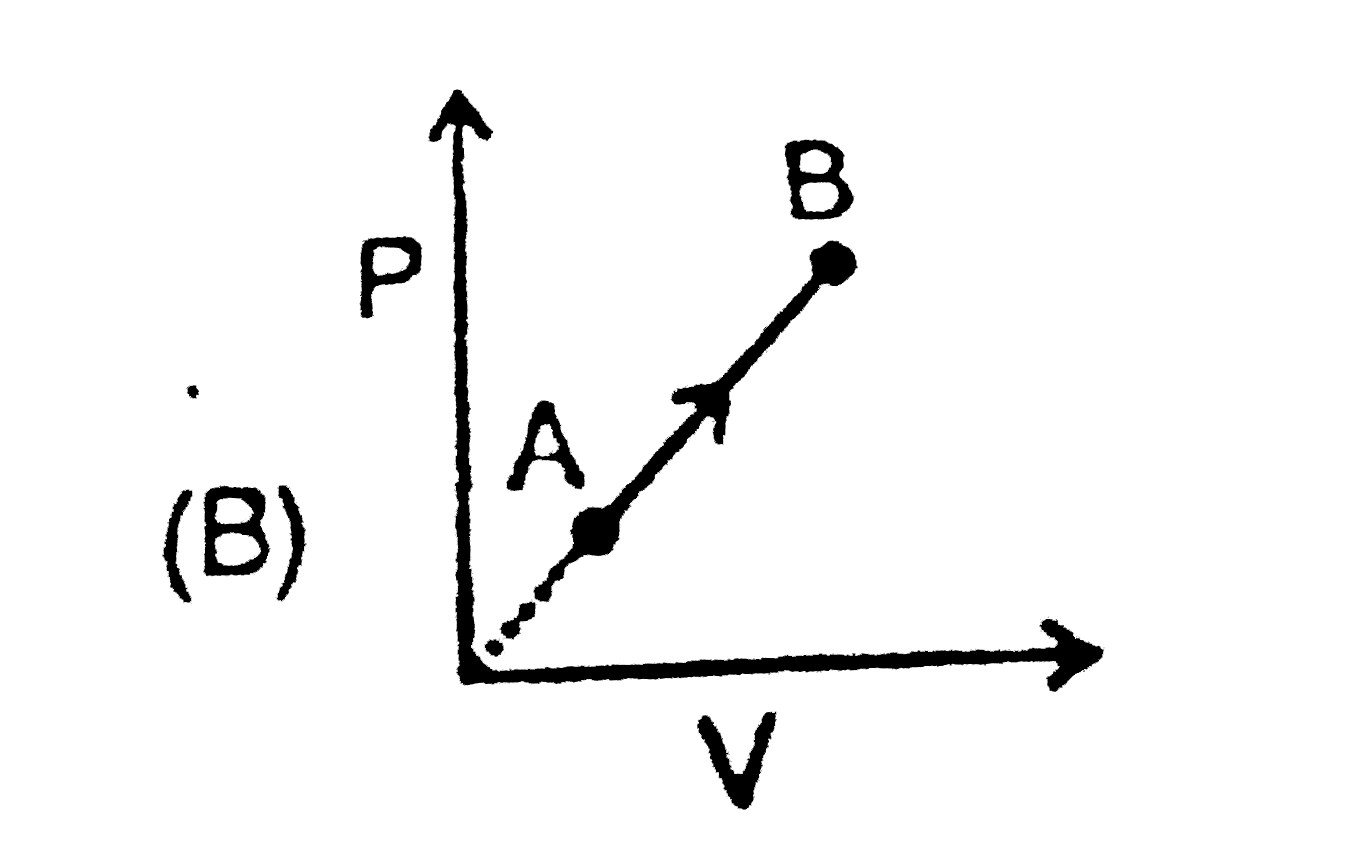
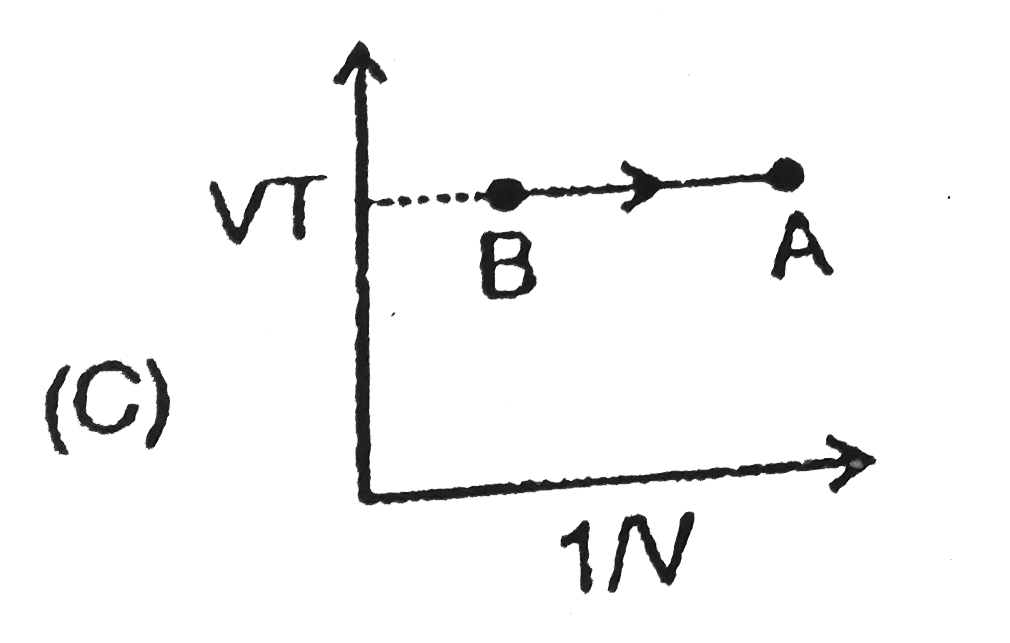
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-RANK BOOSTER-All Questions
- How many moles are represented by 110 g of glucose, C6H12O6.
Text Solution
|
- When a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final...
Text Solution
|
- When a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the effect of pressure on the compressibility factor,...
Text Solution
|
- Two van der waal's gases have same value of a but different value of b...
Text Solution
|
- When a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final...
Text Solution
|
- When a sample of ideal gas is changed from an initial state to a final...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z v/s P for a hypothetical gas for one mole a...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z v/s P for a hypothetical gas for one mole a...
Text Solution
|
- At 200 K and 500 atm value of compressibility factor is 2.Then volume ...
Text Solution
|
- At high pressure suppose all the constant temperature curve varies lin...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z v/s P for a hypothetical gas for one mole a...
Text Solution
|
- Match List : {:("Column-I","Column-II"),((A)PV^(gamma)="Constant",(p...
Text Solution
|
- The number of moles present in 54.5 g of HSO is
Text Solution
|
- The number of moles present in 84 g of HSO is
Text Solution
|
- How many moles are represented by 130 g of glucose,
Text Solution
|
- How many moles are represented by 150 g of glucose
Text Solution
|
- How many moles are represented by 120 g of glucose
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following figure at 500 K.Assuming ideal gas behaviour, c...
Text Solution
|
- If above tube is placed vertically with the open and upward then find ...
Text Solution
|