Addition of mercuric acetate in the presence of water is called as oxymercuration.The adduct obtained gives alcohol on reduction with `NaBH_4` in alkaline medium.This is known as demercuration.Oxymercuration demercuration allows Markownikoff's addition of H, OH without rearrangement.The net result is the addition of `H_2O` Answer the following question :
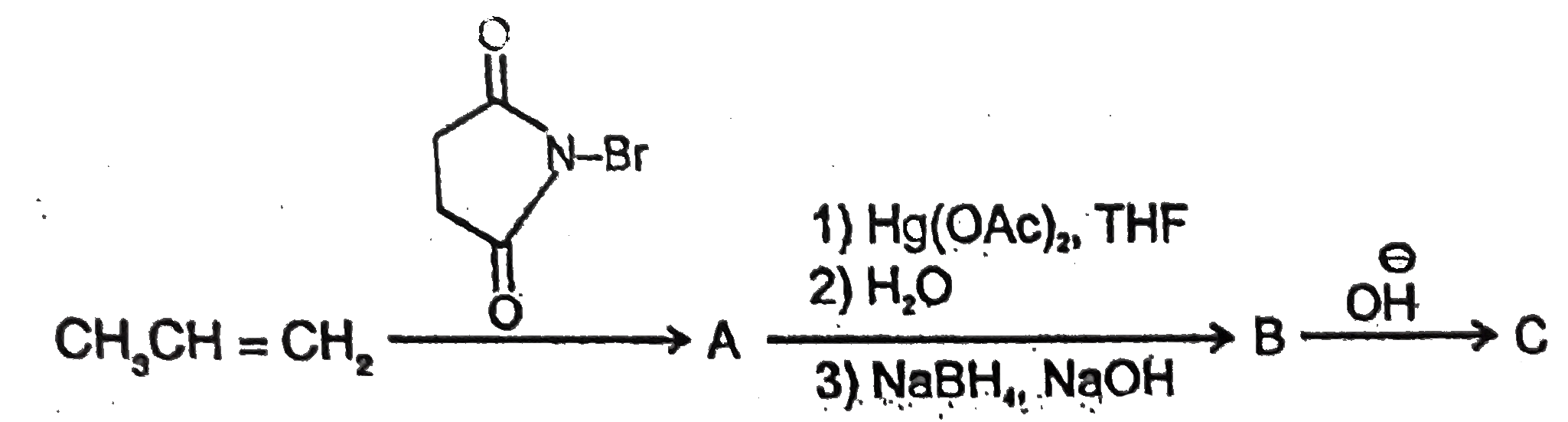
Addition of mercuric acetate in the presence of water is called as oxymercuration.The adduct obtained gives alcohol on reduction with `NaBH_4` in alkaline medium.This is known as demercuration.Oxymercuration demercuration allows Markownikoff's addition of H, OH without rearrangement.The net result is the addition of `H_2O` Answer the following question :
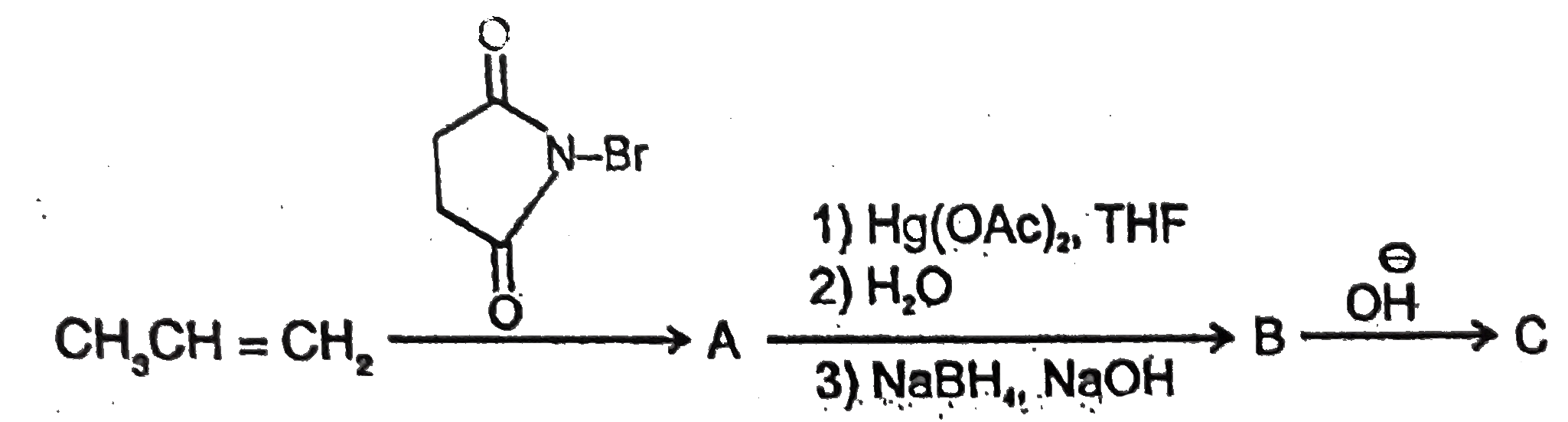
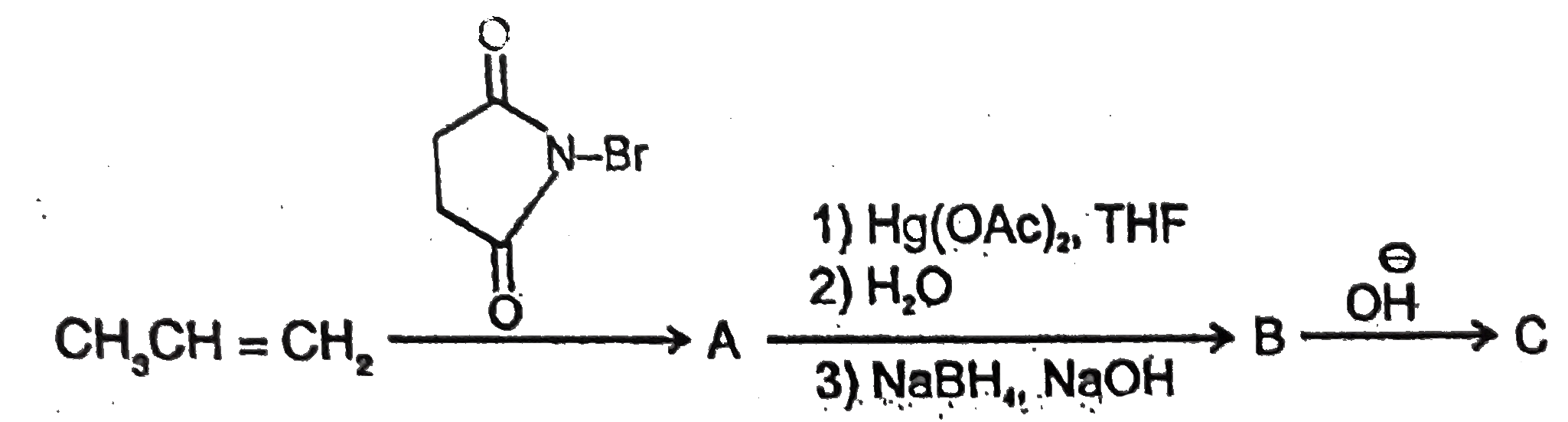
A
enol formation
B
`S_N 1` mechanism
C
Neighbouring group particitation
D
SNAr mechanism
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
C

Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Addition of water to ethyne in the presence of H_2SO_4 and HgSO_4 gives
Addition of water to alkenes in presence of conc. H_(2)SO_(4) produces alcohol Which rule is followed in this reaction?
Name the product obtained on addition of a water molecule of propene in the presence of dil. H_2SO_4
Addition of excess aqueous ammonia to a pink coloured aqueous solution of MCl_(2). 6H_(2)O(X) and NH_(4)Cl gives an octahedral complex Y in the presence of air. In aqueous solution, complex Y behaves as 1:3 electrolyte. The reaction of X with excess HCl at room temperature results in the formation of a blue coloured complex Z. The calculated spin only magnetic moment of X and Z is 3.87 B.M., whereas it is zero for complex Y. Among the following options, which statement is incorrect ?
The colloidal particles are electrically charged as a indicated by their migration towards cathode or anode under the applied electric field. In a particular colloidal system, all particles carry either positive charge or negative charge. The electric charge on colloidal particles orginate in several ways. According to preferential adsorption theory, the freshly obtained precipitate particles adsorb ions from the dispersion medium, which are common to their lattice and acquire the charge of adsorbed ions. For example, For example, freshly obtained Fe(OH)_(3) precipitated is dispersed, by a little FeCl_(3) , into colloidal solution owing to the adsorption of Fe^(3+) ions in preference. Thus sol particles will be positively charged. In some cases the colloidal particles are aggregates of cations or anions having ampiphilic character. When the ions posses hydrophobic part (hydrocarbon end) as well as hydrophilic part (polar end group), they undergo association in aqueous solution to form particles having colloidal size. The formation of such particles, called micelles plays a very important role in the solubilization of water insoluble substances, (hydrocarbon, oils, fats, grease etc.). In micelles, the polar end groups are directed towards water and the hydrocarbon ends into the centre. The charge on sol particles of proteins depends on the pH. At low pH, the basic group of protein molecule is ionized (protonated) and at higher pH (alkaline medium), the acidic group is ionized. At isoelectric pH, characteristic to the protein, both basix and acidic groups are equally ionized. The stability of colloidal solution is attributed largely to the electric charge of the dispersed particles. This charge causes them to be coagulated or precipitated. On addition of small amount of electrolytes, the ions carrying oppiste charge are adsorbed by sol particles resulting in the neutralization of their charge. When the sol particles either with no charge or reduced charge, come closer due to Brownian movement, they coalesce to form bigger particles resulting in their separation from the dispersion medium. This is what is called coagulating or precipitation of the colloidal solution. The coagulating power of the effective ion, which depend on its charge, is expressed in terms of its coagulating value, defined as its minimum concentration (m mol/L) needed to precipitate a given sol. Which of the following ions would have the minimum coagulating value for sol obtained on peptizing Sn(OH)_(4) by little NaOH solution?
The colloidal particles are electrically charged as a indicated by their migration towards cathode or anode under the applied electric field. In a particular colloidal system, all particles carry either positive charge or negative charge. The electric charge on colloidal particles orginate in several ways. According to preferential adsorption theory, the freshly obtained precipitate particles adsorb ions from the dispersion medium, which are common to their lattice and acquire the charge of adsorbed ions. For example, For example, freshly obtained Fe(OH)_(3) precipitated is dispersed, by a little FeCl_(3) , into colloidal solution owing to the adsorption of Fe^(3+) ions in preference. Thus sol particles will be positively charged. In some cases the colloidal particles are aggregates of cations or anions having ampiphilic character. When the ions posses hydrophobic part (hydrocarbon end) as well as hydrophilic part (polar end group), they undergo association in aqueous solution to form particles having colloidal size. The formation of such particles, called micelles plays a very important role in the solubilization of water insoluble substances, (hydrocarbon, oils, fats, grease etc.). In micelles, the polar end groups are directed towards water and the hydrocarbon ends into the centre. The charge on sol particles of proteins depends on the pH. At low pH, the basic group of protein molecule is ionized (protonated) and at higher pH (alkaline medium), the acidic group is ionized. At isoelectric pH, characteristic to the protein, both basix and acidic groups are equally ionized. The stability of colloidal solution is attributed largely to the electric charge of the dispersed particles. This charge causes them to be coagulated or precipitated. On addition of small amount of electrolytes, the ions carrying oppiste charge are adsorbed by sol particles resulting in the neutralization of their charge. When the sol particles either with no charge or reduced charge, come closer due to Brownian movement, they coalesce to form bigger particles resulting in their separation from the dispersion medium. This is what is called coagulating or precipitation of the colloidal solution. The coagulating power of the effective ion, which depend on its charge, is expressed in terms of its coagulating value, defined as its minimum concentration (m mol/L) needed to precipitate a given sol. 100 ml each of two sols of AgI, one obtained by adding AgNO_(3) to slight excess of KI and another obtained by adding KI to slight excess of AgNO_(3) , are mixed together. Then :
The colloidal particles are electrically charged as a indicated by their migration towards cathode or anode under the applied electric field. In a particular colloidal system, all particles carry either positive charge or negative charge. The electric charge on colloidal particles orginate in several ways. According to preferential adsorption theory, the freshly obtained precipitate particles adsorb ions from the dispersion medium, which are common to their lattice and acquire the charge of adsorbed ions. For example, For example, freshly obtained Fe(OH)_(3) precipitated is dispersed, by a little FeCl_(3) , into colloidal solution owing to the adsorption of Fe^(3+) ions in preference. Thus sol particles will be positively charged. In some cases the colloidal particles are aggregates of cations or anions having ampiphilic character. When the ions posses hydrophobic part (hydrocarbon end) as well as hydrophilic part (polar end group), they undergo association in aqueous solution to form particles having colloidal size. The formation of such particles, called micelles plays a very important role in the solubilization of water insoluble substances, (hydrocarbon, oils, fats, grease etc.). In micelles, the polar end groups are directed towards water and the hydrocarbon ends into the centre. The charge on sol particles of proteins depends on the pH. At low pH, the basic group of protein molecule is ionized (protonated) and at higher pH (alkaline medium), the acidic group is ionized. At isoelectric pH, characteristic to the protein, both basix and acidic groups are equally ionized. The stability of colloidal solution is attributed largely to the electric charge of the dispersed particles. This charge causes them to be coagulated or precipitated. On addition of small amount of electrolytes, the ions carrying oppiste charge are adsorbed by sol particles resulting in the neutralization of their charge. When the sol particles either with no charge or reduced charge, come closer due to Brownian movement, they coalesce to form bigger particles resulting in their separation from the dispersion medium. This is what is called coagulating or precipitation of the colloidal solution. The coagulating power of the effective ion, which depend on its charge, is expressed in terms of its coagulating value, defined as its minimum concentration (m mol/L) needed to precipitate a given sol. Under the influence of an electric field, the particles in a sol migrate towards cathode. The coagulation of the same sol is studied using NaCl, Na_(2)SO_(4) and Na_(3)PO_(4) solutions. Their coagulating values will be in the order :
The colloidal particles are electrically charged as a indicated by their migration towards cathode or anode under the applied electric field. In a particular colloidal system, all particles carry either positive charge or negative charge. The electric charge on colloidal particles orginate in several ways. According to preferential adsorption theory, the freshly obtained precipitate particles adsorb ions from the dispersion medium, which are common to their lattice and acquire the charge of adsorbed ions. For example, For example, freshly obtained Fe(OH)_(3) precipitated is dispersed, by a little FeCl_(3) , into colloidal solution owing to the adsorption of Fe^(3+) ions in preference. Thus sol particles will be positively charged. In some cases the colloidal particles are aggregates of cations or anions having ampiphilic character. When the ions posses hydrophobic part (hydrocarbon end) as well as hydrophilic part (polar end group), they undergo association in aqueous solution to form particles having colloidal size. The formation of such particles, called micelles plays a very important role in the solubilization of water insoluble substances, (hydrocarbon, oils, fats, grease etc.). In micelles, the polar end groups are directed towards water and the hydrocarbon ends into the centre. The charge on sol particles of proteins depends on the pH. At low pH, the basic group of protein molecule is ionized (protonated) and at higher pH (alkaline medium), the acidic group is ionized. At isoelectric pH, characteristic to the protein, both basix and acidic groups are equally ionized. The stability of colloidal solution is attributed largely to the electric charge of the dispersed particles. This charge causes them to be coagulated or precipitated. On addition of small amount of electrolytes, the ions carrying oppiste charge are adsorbed by sol particles resulting in the neutralization of their charge. When the sol particles either with no charge or reduced charge, come closer due to Brownian movement, they coalesce to form bigger particles resulting in their separation from the dispersion medium. This is what is called coagulating or precipitation of the colloidal solution. The coagulating power of the effective ion, which depend on its charge, is expressed in terms of its coagulating value, defined as its minimum concentration (m mol/L) needed to precipitate a given sol. How would you obtain a sol of AgI, the particles of which migrate towards cathode under the electric field?
The colloidal particles are electrically charged as a indicated by their migration towards cathode or anode under the applied electric field. In a particular colloidal system, all particles carry either positive charge or negative charge. The electric charge on colloidal particles orginate in several ways. According to preferential adsorption theory, the freshly obtained precipitate particles adsorb ions from the dispersion medium, which are common to their lattice and acquire the charge of adsorbed ions. For example, For example, freshly obtained Fe(OH)_(3) precipitated is dispersed, by a little FeCl_(3) , into colloidal solution owing to the adsorption of Fe^(3+) ions in preference. Thus sol particles will be positively charged. In some cases the colloidal particles are aggregates of cations or anions having ampiphilic character. When the ions posses hydrophobic part (hydrocarbon end) as well as hydrophilic part (polar end group), they undergo association in aqueous solution to form particles having colloidal size. The formation of such particles, called micelles plays a very important role in the solubilization of water insoluble substances, (hydrocarbon, oils, fats, grease etc.). In micelles, the polar end groups are directed towards water and the hydrocarbon ends into the centre. The charge on sol particles of proteins depends on the pH. At low pH, the basic group of protein molecule is ionized (protonated) and at higher pH (alkaline medium), the acidic group is ionized. At isoelectric pH, characteristic to the protein, both basix and acidic groups are equally ionized. The stability of colloidal solution is attributed largely to the electric charge of the dispersed particles. This charge causes them to be coagulated or precipitated. On addition of small amount of electrolytes, the ions carrying oppiste charge are adsorbed by sol particles resulting in the neutralization of their charge. When the sol particles either with no charge or reduced charge, come closer due to Brownian movement, they coalesce to form bigger particles resulting in their separation from the dispersion medium. This is what is called coagulating or precipitation of the colloidal solution. The coagulating power of the effective ion, which depend on its charge, is expressed in terms of its coagulating value, defined as its minimum concentration (m mol/L) needed to precipitate a given sol. A gelatin sol at pH less than the isoelectric value is subjected to an electric field. The sol particles migrate toward :
Acetic acid on reaction with hydrazoic acid (N_3 H) in the presence of H_2 SO_4 followed by heating and hydrolysis in basic medium gives acetamide. Methyl isocyanate (Me-N=C=O) is formed is an intermediate compound.
RESONANCE ENGLISH-RANK BOOSTER-All Questions
- When HBr adds to 1-butene in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the pro...
Text Solution
|
- Addition of mercuric acetate in the presence of water is called as oxy...
Text Solution
|
- Addition of mercuric acetate in the presence of water is called as oxy...
Text Solution
|
- Addition of mercuric acetate in the presence of water is called as oxy...
Text Solution
|
- (A)underset(250^@C)overset(Al2O3)to(B)underset((ii)AgOH)overset(HI)to(...
Text Solution
|
- (A)underset(250^@C)overset(Al2O3)to(B)underset((ii)AgOH)overset(HI)to(...
Text Solution
|
- The number of atoms in 5.4mole of Na are?
Text Solution
|
- Mole fraction of ethyl alcohol in aqueous ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) solut...
Text Solution
|
- Mole fraction of ethyl alcohol in aqueous ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) solut...
Text Solution
|
- Mole fraction of ethyl alcohol in aqueous ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) solut...
Text Solution
|
- CH3-CH=CH2 reacts with Cl2 at 500^@C Find out total no . Of possible...
Text Solution
|
- The number of atoms in 7.4mole of Na are?
Text Solution
|
- Mole fraction of ethyl alcohol in aqueous ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) solut...
Text Solution
|
- The number of atoms in 0.4mole of Na are?
Text Solution
|
- The number of atoms in 0.6mole of Na are?
Text Solution
|
- When nucleophile encounters a ketone site of attack is
Text Solution
|
- The only correct combination that reaction nature is stereospecific an...
Text Solution
|
- When primary amine reacts with chloroform in ethanolic KOH then produc...
Text Solution
|
- Study the following reactions and identify the reactant 'R'. It can be
Text Solution
|
- Which can be the product of the following reaction
Text Solution
|