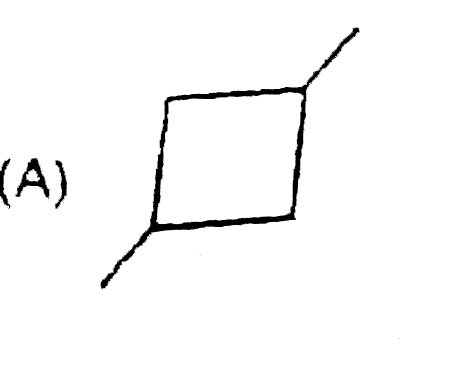
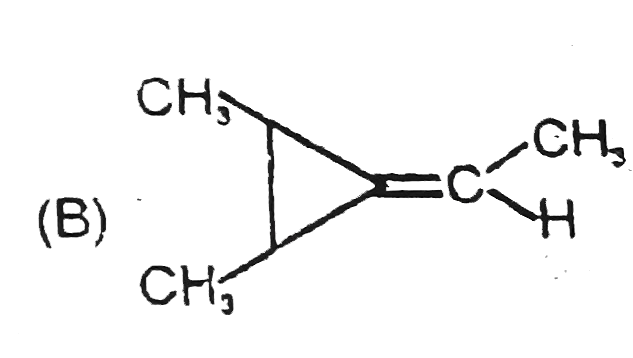
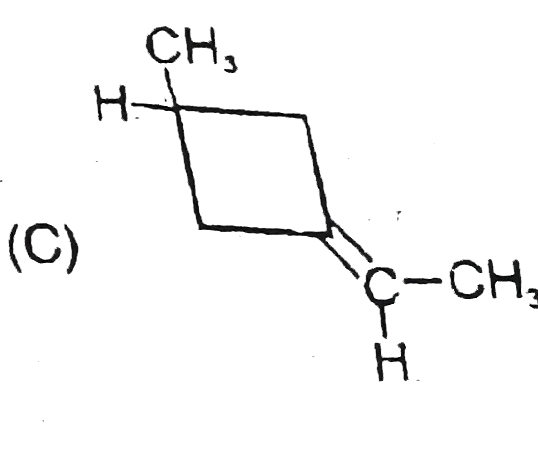
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-RANK BOOSTER-All Questions
- Of the five isomeric hexanes, the isomers which can give five monochlo...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Geometrical isomerism is shown by ?
Text Solution
|
- The inert form of carbon is:
Text Solution
|
- The density (in g ml^(−1) ) of a 3.60M sulphuric acid solution having...
Text Solution
|
- Acetaldehyde and acetylene can be distinguished by :
Text Solution
|
- Catalytic hydrogenation of which of the following gives a product that...
Text Solution
|
- The tautomers of the following compound can be :
Text Solution
|
- Broadly speaking there are four types of stereisomers namely conformat...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the weight of lime (CaO) obtained by heating 150kg of 95% pu...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the weight of lime (CaO) obtained by heating 175kg of 95% pu...
Text Solution
|
- Ortho effect is a special type of effect that is shown by d-substituen...
Text Solution
|
- The concept of resonance explains various properties of compounds.The ...
Text Solution
|
- The density (in g ml^(−1) ) of a 3.60M sulphuric acid solution having...
Text Solution
|
- Match the given compounds in Column-I with their appropriate descripti...
Text Solution
|
- State true or false Diamond is a non conductor of electricity.
Text Solution
|
- Find the concentration of solution in terms of weight percent if 35g o...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the weight of lime (CaO) obtained by heating 270kg of 95% pu...
Text Solution
|
- The density (in g ml^(−1) ) of a 3.60M sulphuric acid solution having...
Text Solution
|
- Find the concentration of solution in terms of weight percent if 33g o...
Text Solution
|