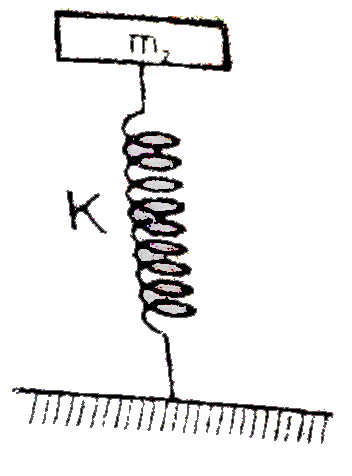Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Board Level Exercise|24 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 1, PART - I|25 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|13 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|88 VideosTEST PAPERS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PHYSICS|784 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -Solved Miscellaneous Problems
- Write the equation of SHM for the situtions shown below:
Text Solution
|
- Block A of mass m is performing SHM of amplitude a. Another block B of...
Text Solution
|
- At particle is executing SHM with amplitude A and has maximum velocity...
Text Solution
|
- The block is allowed to fall, slowly from the position where spring i...
Text Solution
|
- In the above problem if block is released from there, what would be ma...
Text Solution
|
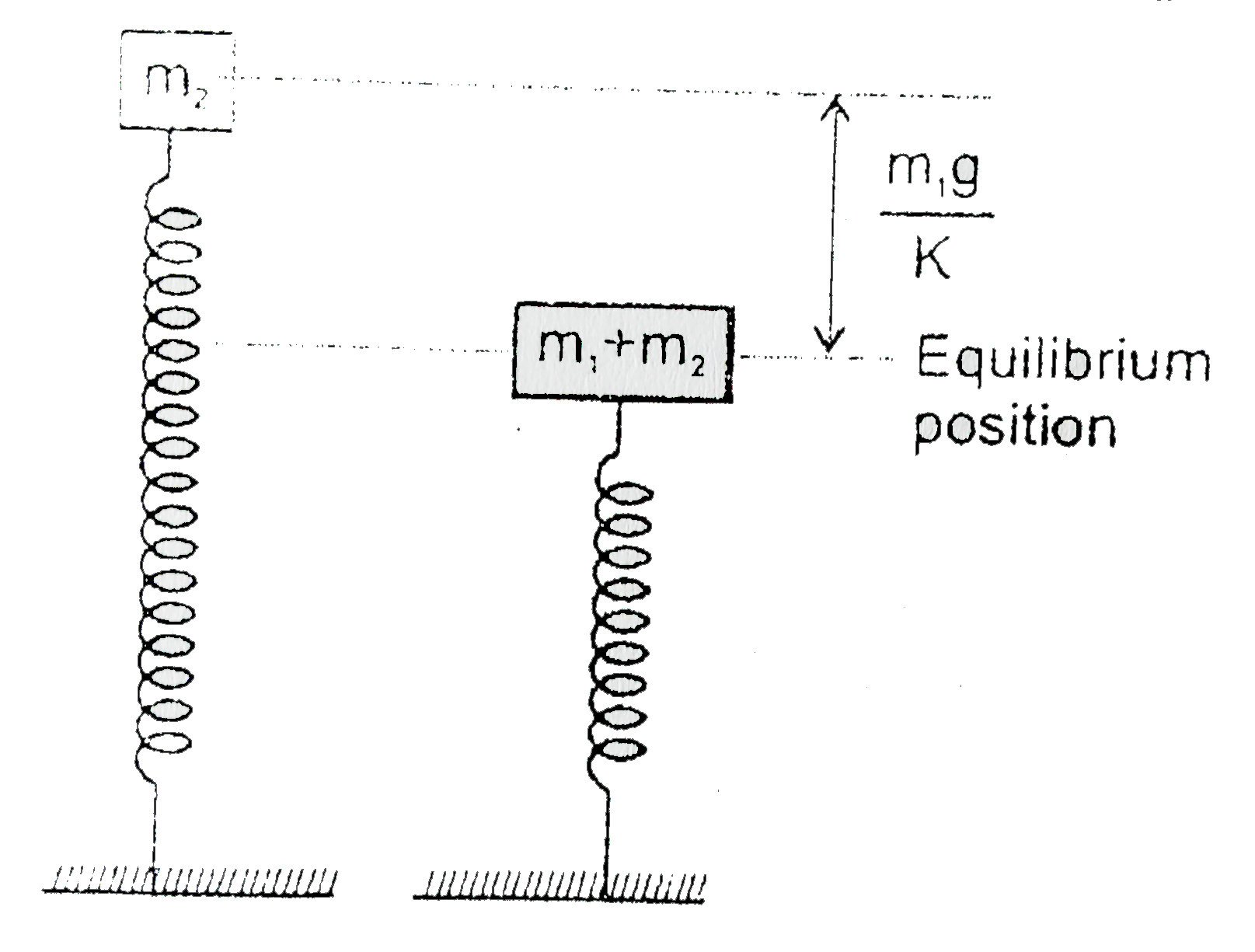
- Block of mass m(2) is in equilibrium as shown in figure. Anotherblock ...
Text Solution
|
- Block of mass m(2) is in equilibrium and at rest. The mass m(1) moving...
Text Solution
|
- A box is placed on a smototh plane end it is free to move. A single pe...
Text Solution
|
- x(1) = 5 sin omega t x(2) = 5 sin (omega t + 53^(@)) x(3) = -...
Text Solution
|