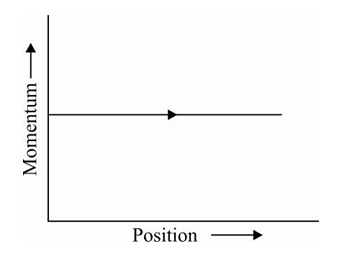
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 3, PART - II|17 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|13 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 2, PART - IV|8 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|88 VideosTEST PAPERS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PHYSICS|784 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -Exercise- 3, PART - I
- A simple pendulum has time period T1. The point of suspension is now m...
Text Solution
|
- A block is performin SHM of amplitude 'A' in vertical direction. When ...
Text Solution
|
- Function x=Asin^(2)omegat+Bcos^(2)omegat+Csinomegatcosomegat represent...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin cylindrical disc of mass M and radius R is attached to ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin cylindrical disc of mass M and radius R is attached to ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin cylindrical disc of mass M and radius R is attached to ...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration a of a particle undergoing SHM is shown in the figure...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length l and mass M is pivoted at the centre. Its two...
Text Solution
|
- The mass M shown in figure ocillates in simple harmonic motion with am...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle of mass m moves on the x-axis in a potential of the fo...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle is mass m moves on the x- axis in a potential of the f...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle is mass m moves on the x- axis in a potential of the f...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod of length 'L' and mass 'm' is pivoted at one end. A thin d...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analyzing all kinds of dynami...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analyzing all kinds of dynami...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analyzing all kinds of dynami...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass is subjected to two simultaneous sinusoidal displacement ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un-stret...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is attached to one end of a mass-less spring of f...
Text Solution
|
- Two independent harmonic oscillators of equal mass are oscillating abo...
Text Solution
|