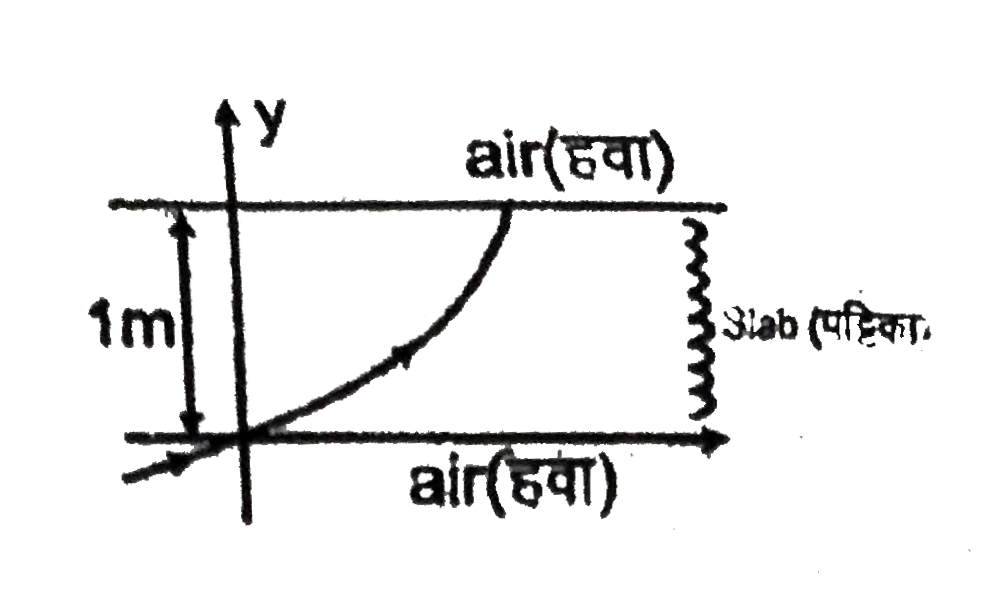
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2|62 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3|80 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Problem|33 VideosEXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART -II|10 VideosGRAVITATION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-1
- A ray of light passes from vaccum into a medium of refractive index n....
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a parallel slab of thickness t and refra...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing incidence on a...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light is converging towards a point. A plane parallel plate ...
Text Solution
|
- Given that, velocity of light in quartz =1.5xx10^(8)m//s and velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- The critical angle of light from medium A to medium B is theta. The sp...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of monochromatic light is incident on one refracting face of a p...
Text Solution
|
- A prism having refractive index sqrt2 and refractive angle 30^@ has on...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at angle I on a surface of a prism of small...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of refractive index sqrt2 has refractive angle 60^@. In the or...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of refractive index sqrt2 has refractive angle 60^@. In the or...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of refractive index sqrt2 has refractive angle 60^@. In the or...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum refractive index of a material, of a prism of apex 90^(@) ...
Text Solution
|
- A prism having an apex angle 4^(@) and refraction index 1.5 is located...
Text Solution
|
- There is a small black dot at the centre C of a solid glass sphere of ...
Text Solution
|
- The image for the converging beam after refraction through the curved ...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-concave lens is placed on a paper on which a flower is drawn. ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If ...
Text Solution
|
- A convexo-concave convergent lens is made of glass of refractive index...
Text Solution
|
- Two symmetric double convex lenses A and B have same focal length but ...
Text Solution
|