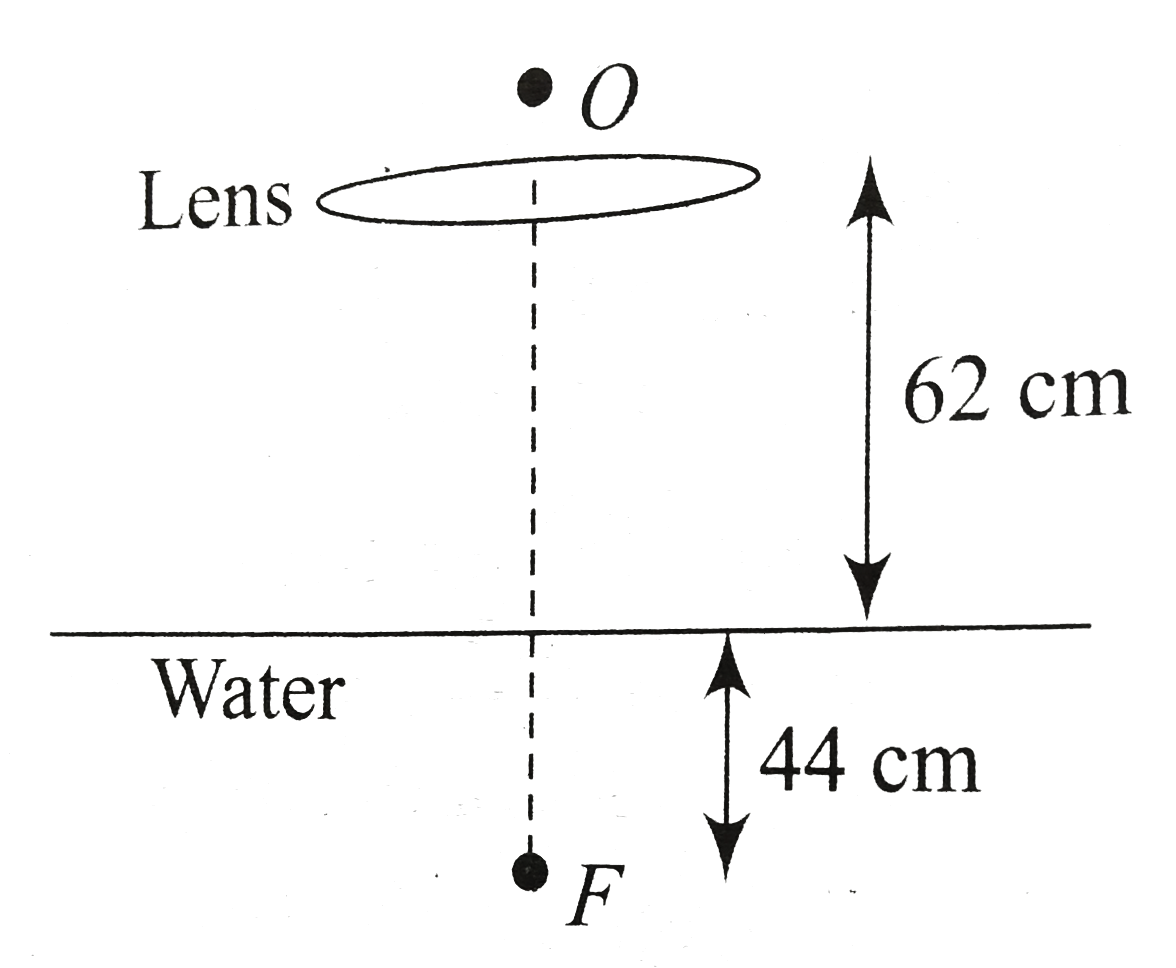
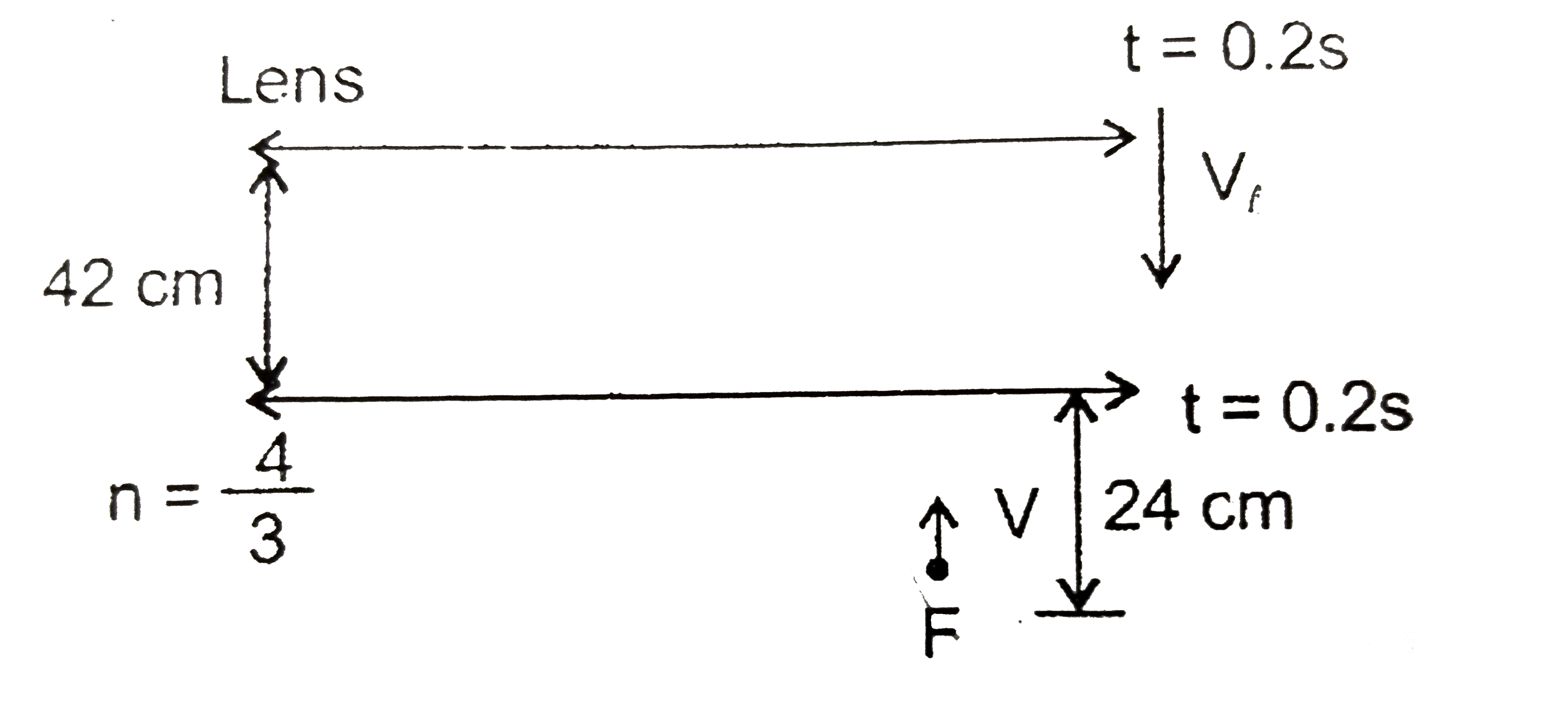
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3|80 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advance level Problems|35 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1|141 VideosEXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART -II|10 VideosGRAVITATION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-2
- A symmetrical converging convex lens of focal length 10 cm & diverging...
Text Solution
|
- An object O is kept in air and a lens of focal length 10 cm (in air) i...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary observer O looking at a fish (in water of mu=4//3 ) throu...
Text Solution
|
- The dispersive power of the material of a lens is 0.04 and the focal l...
Text Solution
|
- The image formed by a concave mirror is twice the size of the object. ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are incorrect for spherical mirror.
Text Solution
|
- A ray of monochromatic light is incident on the plane surface of separ...
Text Solution
|
- For refractin of light through a prism
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral prism deviates a ray through 45^(@) for the two angles ...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interfaces as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- The values of d(1) & d(2) for final rays to be parallel to the princip...
Text Solution
|
- An object O is kept infront of a converging lens of focal length 30 cm...
Text Solution
|
- If a symmetrical bi-concave thin lens is cut into two identical halves...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces...
Text Solution
|
- By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is po...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror M is arranged parallel to a wall W at a distance l from...
Text Solution
|
- A man washign to get a picture of a Zebra photographed a white donkey ...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens of refractive index n(2) is placed such that the re...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown , a point object O is placed in air on the princip...
Text Solution
|
- An object is kept on the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal le...
Text Solution
|