A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3|80 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advance level Problems|35 VideosGEOMATRICAL OPTICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1|141 VideosEXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART -II|10 VideosGRAVITATION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS|16 Videos
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-2
- A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces...
Text Solution
|
- By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is po...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror M is arranged parallel to a wall W at a distance l from...
Text Solution
|
- A man washign to get a picture of a Zebra photographed a white donkey ...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens of refractive index n(2) is placed such that the re...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown , a point object O is placed in air on the princip...
Text Solution
|
- An object is kept on the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal le...
Text Solution
|
- A real object is placed infront of a convex mirror (focal length f). I...
Text Solution
|
- A small air bubble is trapped inside a transparent cube of size 12 cm....
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light is incident normally on the flat surface of a...
Text Solution
|
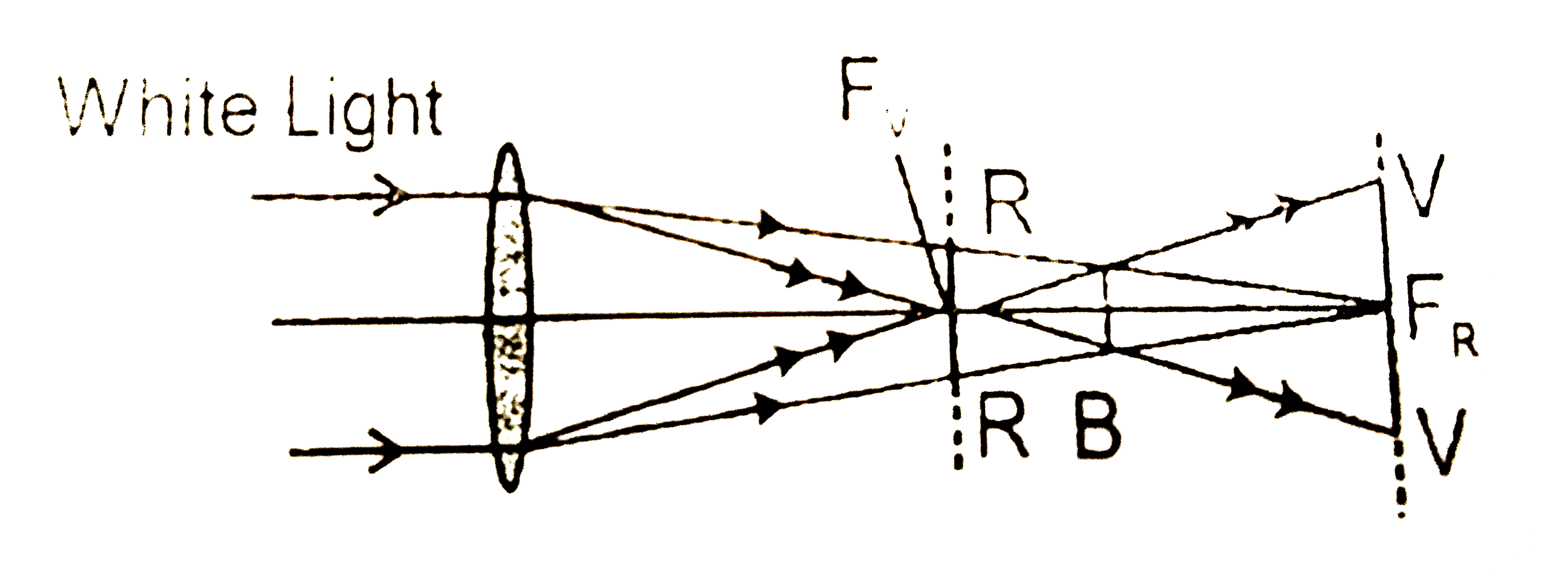
- The image of a white object in with light formed by a lens is usually ...
Text Solution
|
- The image of a white object in with light formed by a lens is usually ...
Text Solution
|
- The image of a white object in with light formed by a lens is usually ...
Text Solution
|
- The image of a white object in with light formed by a lens is usually ...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a solid transport semi cylinder of radius 10 cm. A screen...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a solid transport semi cylinder of radius 10 cm. A screen...
Text Solution
|