A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-3
- A monochromatic beam of light is incided at 60^(@) in one face of an e...
Text Solution
|
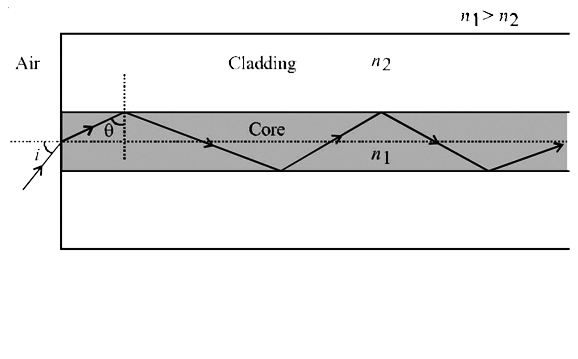
- Light guidance in an optical fibre can be understood by considering a ...
Text Solution
|
- Light guidance in an optical fibre can be understood by considering a ...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of a glass is 1.520 for red light and 1.525 for b...
Text Solution
|
- A student measuring the focal length of convex lens by putting an obje...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent solid cylindrical rod has a refractive index of (2)/(sqr...
Text Solution
|
- In a optics experiment, with the positive of the object fixed, a stude...
Text Solution
|
- A car is fitted with a convex side-view mirror of focal length 20 cm. ...
Text Solution
|
- The XY plane is the boundary between two tranparednt media. Medium 1 w...
Text Solution
|
- A beaker contains water up to a height h1 and K oil above water up to...
Text Solution
|
- When monochromatic red light is used instead of blue light in a convex...
Text Solution
|
- An object 2.4 m in front of a lens forms a sharp image on a film 12cm ...
Text Solution
|
- Diameter of plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3...
Text Solution
|
- The graph between angle of deviation (delta) and angle of incidence (i...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens made from crown glass (mu = 3/2), has focal length...
Text Solution
|
- A green light is incident from the water to the air – water interface ...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light is incident on a glass prism of angle A. If the re...
Text Solution
|
- A right-angle crown glass prism with critical angle 41^(@) is placed b...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a mirror normally. What are the values of angl...
Text Solution
|
- What is far-sightedness or hypermatropia? What cause hypermetropia How...
Text Solution
|