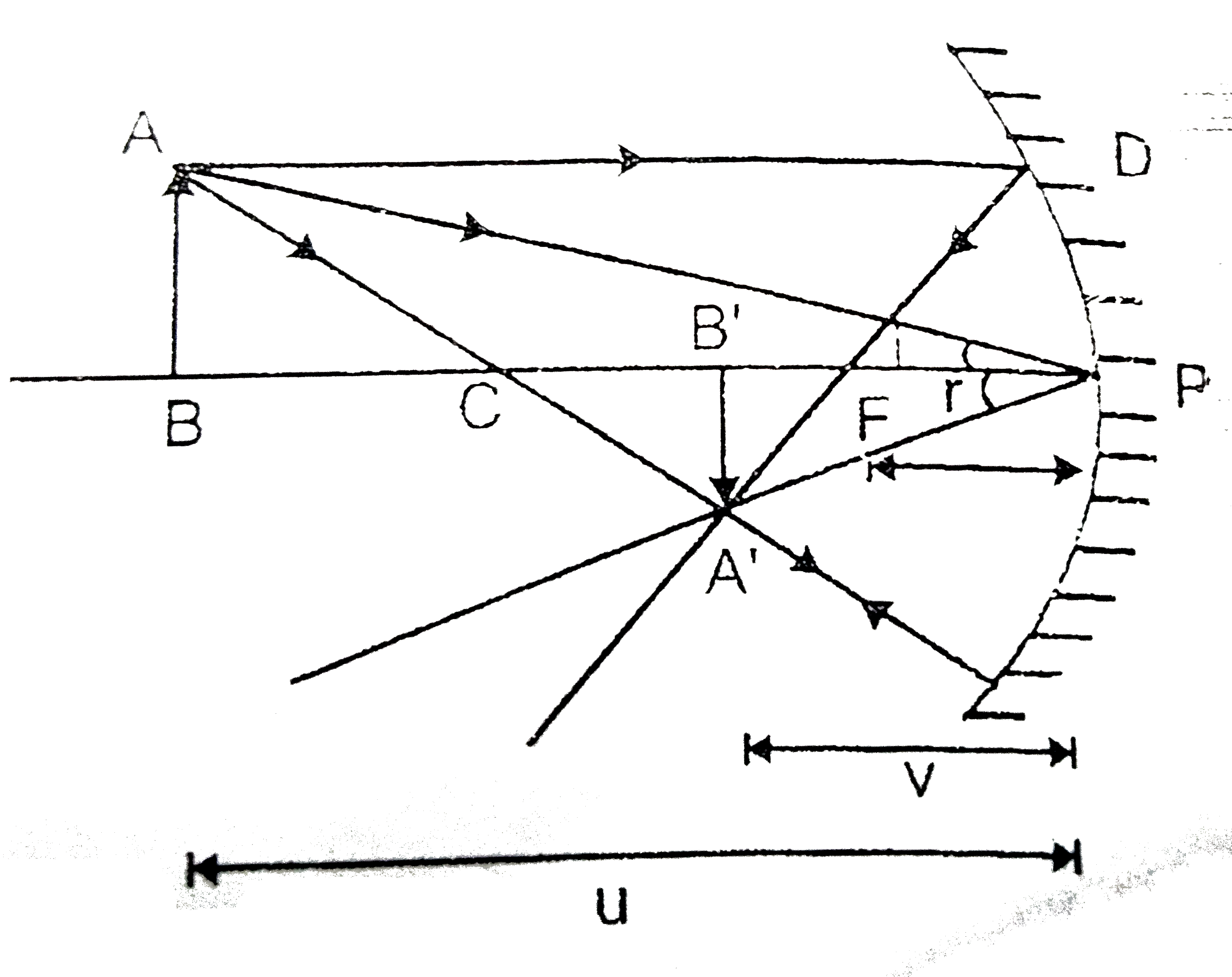
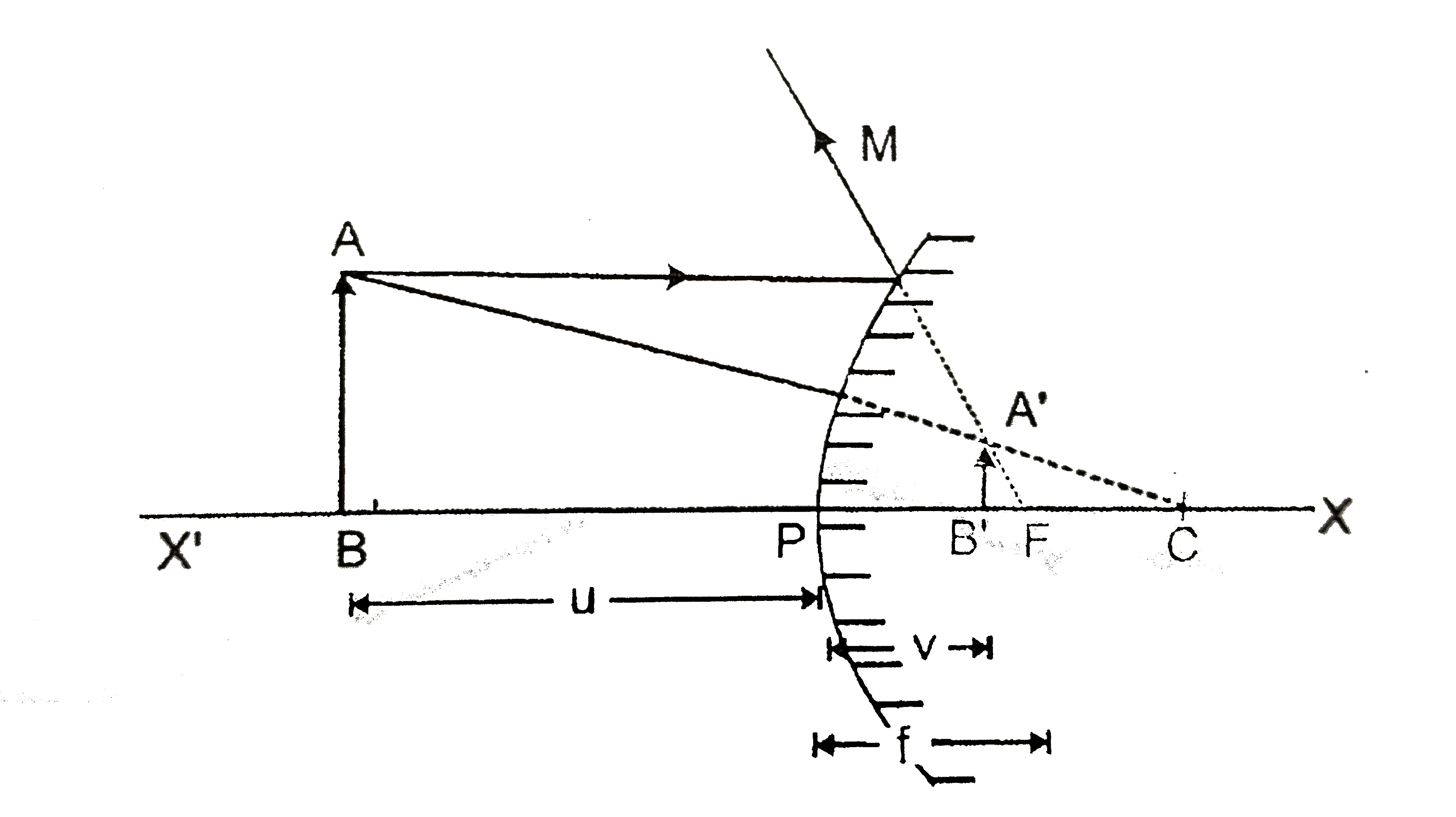
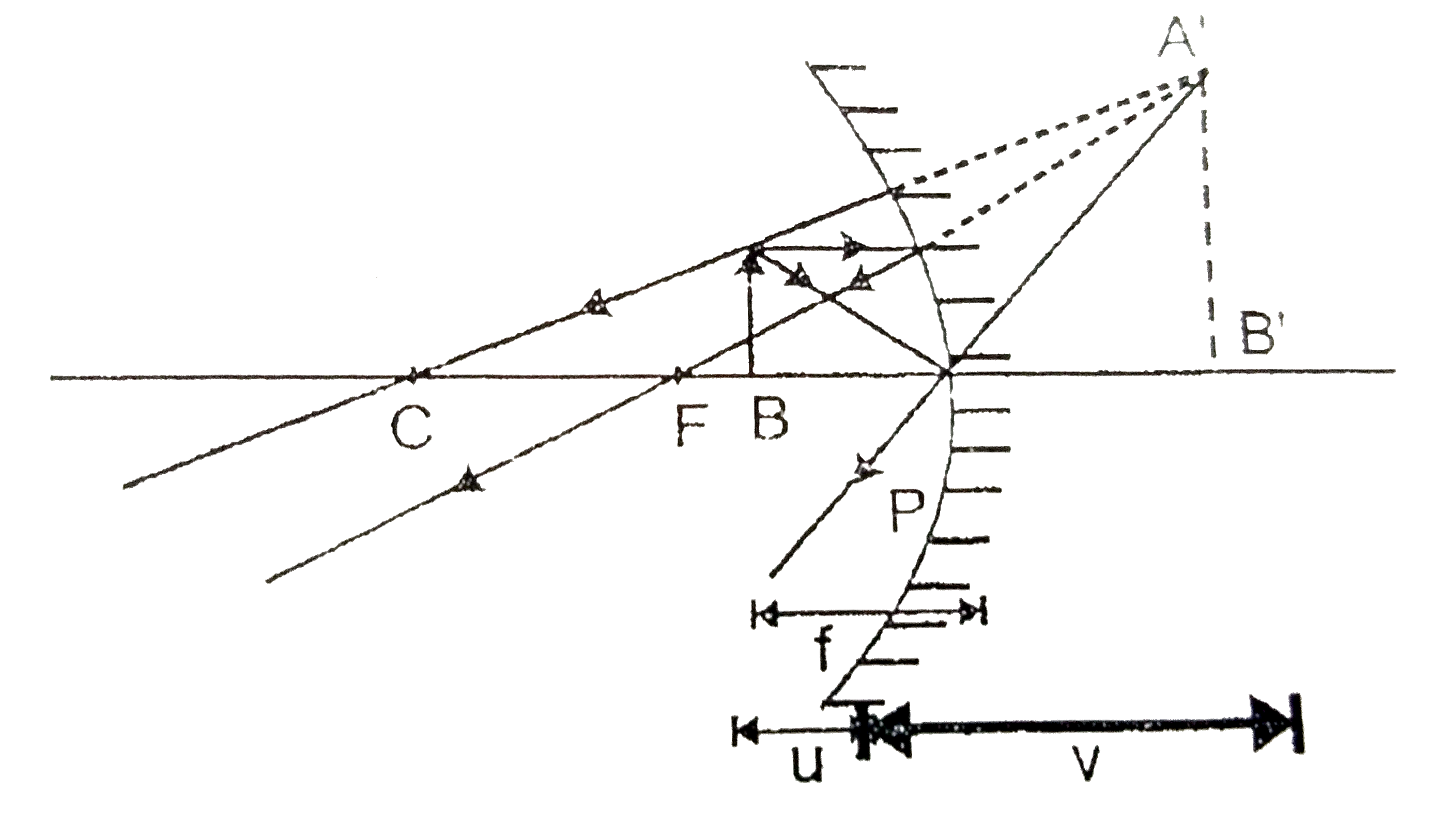
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-3
- The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is...
Text Solution
|
- (a) (i) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw the ray diagram showing the geometry of formation of the imag...
Text Solution
|
- The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is 4 tim...
Text Solution
|
- A converging lens is kept coaxially in contact with a diverging lens -...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to show the working of a compound microscope. Deduc...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical telescope has an objective of focal length 20 cm and a...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens made up of glass of refractive index 1.5 is dipped, in t...
Text Solution
|
- Use the mirror equation to deduct that : (a) an object between f and...
Text Solution
|
- A gaint refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens o...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the pa...
Text Solution
|
- For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in ...
Text Solution
|
- Define magnifying power of a telescope. Write its expression. A smal...
Text Solution
|
- An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figu...
Text Solution
|
- You are given three lenses L(1),L(2) and L(3) each of focal length 20 ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe a reflecting type telescope. What are its advantage over the ...
Text Solution
|
- Which type of lens is used to correct astigmatisum ?
Text Solution
|
- A biconcave lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1...
Text Solution
|
- Two monochromatic ray of light are incident normally on the face AB of...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 20cm is placed coaxilly with a convex mi...
Text Solution
|