Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Advance level Problems
- Two concave mirrors each of focal length 'f' are placed infront of eac...
Text Solution
|
- An observer observer a fish moving upwards in a cylindrical container ...
Text Solution
|
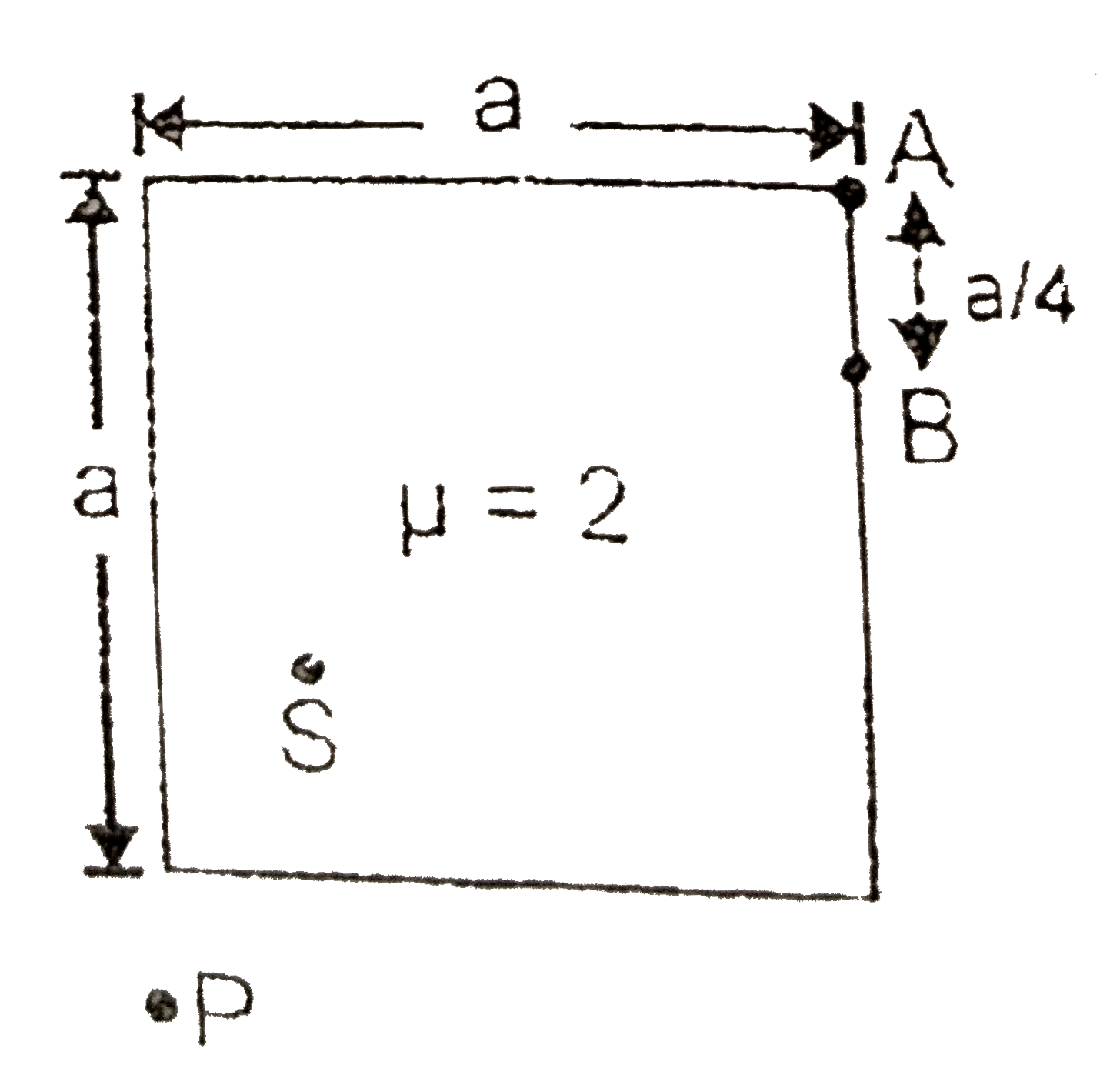
- The figure shows the square face (of side 'a') of a transparent cuboid...
Text Solution
|
- An insect at point 'P' sees its two images in the water mirror system ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a surface in a direction given by vector...
Text Solution
|
- If an observer sees the bottom of the vessel shown in Figure., at 8cm,...
Text Solution
|
- A man starting from point P cross a 4km wide lagoon and reaches point ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, the faces of prism ABCD made of glass with a refr...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light is placed at a distance h below the surface of...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prism with a refracting angle of 60^(@) has a refractive index...
Text Solution
|
- O is a point object kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror M o...
Text Solution
|
- Light travelling in air falls at an incidence angle of 2^(@) on one ra...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure ., L is a converging lens of focal length 10cm and M Iis a c...
Text Solution
|
- An object is kept at rest on the principal axis of a lens. Initially t...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens produces an image of a condle flame upon a screen whose ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin equiconvex lens made of glass of refractive index 3//2 and of ...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of refractive index n(1) & another prism of reactive index n(2...
Text Solution
|
- A pole of length 2.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with lev...
Text Solution
|
- A fly F is sitting an a glass S 45 cm thick & of refractive index 3//...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prothole is made at the botton of a ahip for observing sea lif...
Text Solution
|