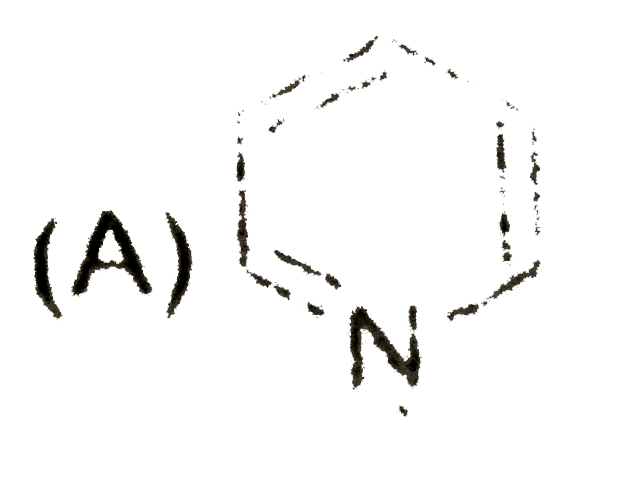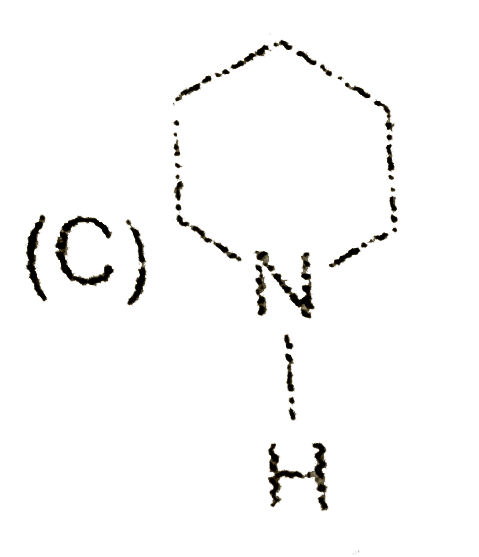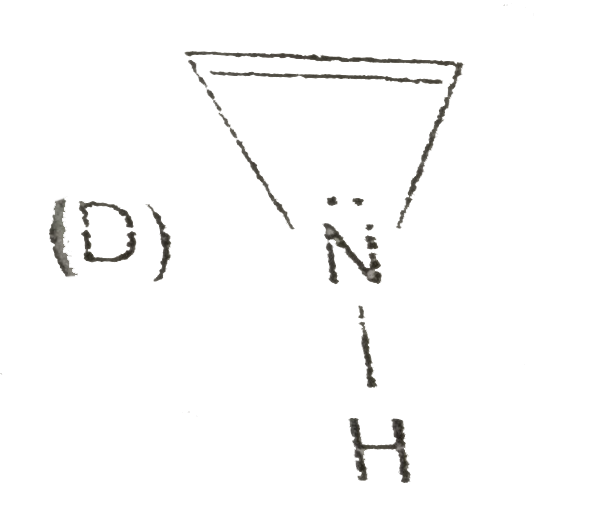A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
IUPAC NOMENCLATURE & STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1 Part-2 Section(B)|5 VideosIUPAC NOMENCLATURE & STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1 Part-2 Section(C)|4 VideosIUPAC NOMENCLATURE & STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1 Part-1 Section(H)|5 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise partIII one or more than one options correct type|10 VideosMETALLURGY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Alkyl Halide, Alcohol,Phenol,Ether)|17 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-IUPAC NOMENCLATURE & STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM -Exercise-1 Part-2 Section(A)
- Number of bonds in given compound is: CH(2)=C=CH-C=CH
Text Solution
|
- Molecular formula of naphthaquinone is
Text Solution
|
- (a) Incorrect statement for the above structure:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not an alicyclic compound?
Text Solution
|
- The saturated heterocyclic compound is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compound is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Text Solution
|